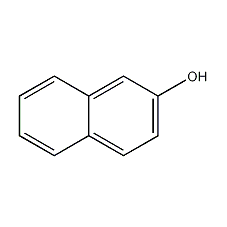
Structural formula
| Business number | 03Q2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H8O |
| Molecular weight | 144 |
| label |
2-Hydroxynaphthalene; β-naphthol; ethanol, 2-Naphthol, β-Naphthol, β-Hydroxyonaphthalene, Phenol, aromatic alcohols and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:135-19-3
MDL number:MFCD00004067
EINECS number:205-182-7
RTECS number:QL2975000
BRN number:742134
PubChem number:24851145
Physical property data
1. Properties: White to red flaky crystals, the color becomes darker when stored in the air for a long time.
2. Density (g/mL, 20/4℃): 1.181
3. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.25
4 . Melting point (ºC): 122~123
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 285~286
6. Flash point (ºC): 153
7. Solubility: Insoluble in cold water, easily soluble in hot water, ethanol, ether, chloroform, benzene, glycerol and alkali.
8. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -5048.4
9. Gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) ( kJ·mol-1): -30.0
10. Crystal phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): – 4954.2
11. Crystal phase standard claim heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -124.2
12. Crystal phase standard entropy (J ·mol-1·K-1): 179.0
13. Crystal phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1 sup>·K-1): 172.8
Toxicological data
Toxicology is similar to phenol
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 45.97
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 121.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 326.1
4. Surface tension (3.0 dyne/cm): 51.0
5. Polarizability (0.5 10-24cm3): 18.22
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: 3
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 20.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 133
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine chemistryNumber of bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. The toxicology is similar to that of phenol, and it is a stronger corrosive agent. Strongly irritating to skin. Easily absorbed through skin. Toxic to blood circulation and kidneys. In addition, it can also cause corneal damage. Although the lethal dose is not clear, there are cases of death after external use of 3 to 4 g. Production equipment must be sealed and leak-proof, and any spills on the skin must be washed immediately. The workshop should be ventilated and the equipment should be sealed. Operators should wear protective equipment.
2. Combustible, the color gradually becomes darker when stored for a long time. Medium stable, but gradually darkens when exposed to sunlight. It sublimates when heated and has a pungent phenol smell
3. Exists in smoke.
4. The aqueous solution reacts with ferric chloride to turn green.
Storage method
1. Packed in lined plastic bags, coated sacks or woven bags, with a net weight of 50kg or 60kg per bag.
2. Protect against fire, moisture and exposure during storage and transportation. Store in a dry, ventilated place. Store and transport according to regulations for flammable and toxic substances.
Synthesis method
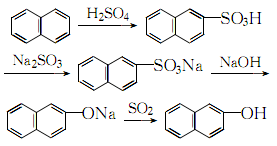
1. Prepared from naphthalene through sulfonation and alkali melting. The sulfonation alkali fusion method is a production method widely used at home and abroad, but it suffers from serious corrosion, high cost and high biological oxygen consumption of wastewater. The 2-cumonaphthalene method developed by American Cyanamid Company uses naphthalene and propylene as raw materials. While producing 2-naphthol, acetone is produced as a by-product. This method is similar to the cumene method to produce phenol. Raw material consumption quota: refined naphthalene 1170kg/t, sulfuric acid 1080kg/t, solid caustic soda 700kg/t.
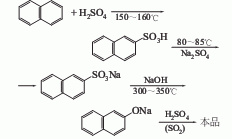
2.Heat the molten refined naphthalene to 140℃, add 98% sulfuric acid evenly within 20 minutes
at the ratio of naphthalene: sulfuric acid = 1: 1.085 (molar ratio), and then raise the temperature The sulfonation reaction is carried out at 160~164°C for 2.5 hours. When the 2-naphthalenesulfonic acid content reaches more than 66% and the total acidity is 25%~27%, the reaction ends. Then the hydrolysis reaction is carried out at 160°C for 1 hour. At 140~ Blow off free naphthalene with water vapor at 150°C, then slowly and evenly add sodium sulfite solution with a relative density of 1.14 that has been preheated to 80-90°C to carry out neutralization reaction until the Congo red test paper does not change to blue
. The sulfur dioxide gas generated during the reaction is promptly removed with steam, and the neutralized product is cooled to 35-40°C for cooling and crystallization. The crystals obtained by suction filtration are washed with 10% salt water, dried, and then added to molten 98 at 300-310°C. % sodium hydroxide, stir and maintain 320~330℃ to melt the sodium 2-naphthalenesulfonate alkali into sodium 2-naphthol, and then dilute the alkali with hot water The melt is then passed through the sulfur dioxide generated by the above-mentioned neutralization reaction, and the acidification reaction is carried out at 70 to 80°C until phenolphthalein becomes colorless. The acidified product is allowed to stand for stratification, and the upper liquid obtained is heated to boiling, left to stand, and the water layer is separated. The crude 2-naphthol obtained is dehydrated by heating and then distilled under reduced pressure to obtain the pure product.
The process reaction formula is:
3. This method uses extraction and crystallization to remove 1-naphthol from 2-naphthol. Mix 2-naphthol and water in a certain proportionheat to 95℃. When 2-naphthol melts, stir the mixture vigorously and quickly cool it to about 85℃ to crystallize The slurry product is cooled to room temperature and filtered. After purity analysis, the 1-naphthol content was trace.
4. It is prepared from 2-naphthalenesulfonic acid through alkali melting.
Purpose
1. Important organic raw materials and dye intermediates, used to produce toric acid, butyric acid, β-naphthol-3-carboxylic acid, and used to produce antioxidants DNP, antioxidant DNP and other antioxidants and organic pigments and fungicides, etc.
2. Used as a reagent for the determination of sulfonamides and aromatic amines by thin layer chromatography. Also used in organic synthesis.
3.In acidic tin plating, it is used to improve cathode polarization, refine crystallization and reduce pores. Since this product is hydrophobic, if the content is too high, it will cause gelatin to condense and precipitate, resulting in streaks on the coating.
4. Mainly used to produce acid orange Z, acid orange II, acid black ATT, acid medium black T, acid medium black A, acid medium black R, acid complex pink B, Acid complex red brown BRRW, acid complex black WAN, naphthol AS, naphthol AS-D, naphthol AS-OL, naphthol AS-SW, active brilliant orange X-GN, active brilliant orange K-GN, active Red K-1613, neutral violet BL, neutral black BGL, direct copper salt blue 2R, direct light fast blue B2PL, direct blue RG, direct blue RW and other dyes.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

