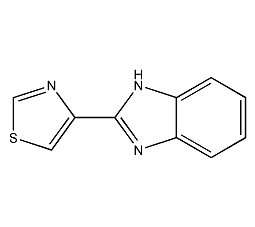
Structural formula
| Business number | 03XJ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C10H7N3S |
| Molecular weight | 201.25 |
| label |
Thiabendazole, 2-(4-thiazolyl)-1H-benzimidazole, 2-(1,3-thiazol-4-yl)benzimidazole, 2-(thiazol-4-yl)benzimidazole, 2-(4-Thiazolyl)benzimidazole, Fungicide |
Numbering system
CAS number:148-79-8
MDL number:MFCD00005587
EINECS number:205-725-8
RTECS number:DE0700000
BRN number:None
PubChem number:24900571
Physical property data
1. Physical property data:
1. Appearance: white to off-white odorless powder
2. Melting point (ºC): 304-305 ºC
3 . Solubility: Insoluble in water, slightly soluble in alcohol and acetone, easily soluble in ether and chloroform. Substitute salicylic acid.
Toxicological data
2. Toxicology data:
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 2080 mg/kg;
Mouse oral LD50: 1300 mg/kg;
Rabbit oral LD50: 3850 mg/kg. Rainbow trout LC50: 5.5mg/L(48h), 3.5 mg/L(96h)、Blue Gill fish
LC50: 18.5mg/L (48h), 4.0mg/L (96h)
Ecological data
3. Ecological data:
Other harmful effects: This substance may be harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
5. Molecular property data:
1. Molar refractive index: 57.68
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 143.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 415.5
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 71.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 22.86
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 69.8
7. Number of heavy atoms: 14
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 212
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and��Qualitative
Stable under normal temperature and pressure.
Incompatible materials: strong oxidizing agents
Storage method
Store at 0-6ºC.
Synthesis method
1. Mix thiazole-4-carboxylic acid bromide and o-phenylenediamine, add polyphosphoric acid, heat to 240°C with stirring, and keep warm for 3 hours. Pour the hot reaction solution into ice, filter, and wash the filtrate with 30% sodium hydroxide solution. When the pH is about 6, 2-(4′-thiazolyl)-benzimidazole precipitates. Filter, wash with water, and dry to obtain a melting point of 296-298 ℃ crystal. Recrystallize with boiling ethanol, melting point 301-302°C. Another process is to stir and heat the mixture of 4-ethoxyformylthiazole, o-phenylenediamine, and polyphosphoric acid to 125°C, then heat it at 175°C for 2 hours, pour the mixture into ice water, and neutralize it with sodium hydroxide solution. pH 6, precipitate crystals, filter, extract with hot acetone, decolorize the extract with activated carbon, concentrate, and dry under vacuum to obtain thiabendazole.
2. Obtained from the reaction of 4-thiazolecarboxamide and o-phenylenediamine in condensed phosphoric acid.
3. Preparation method 1
The preparation of 4-ethoxyformylthiazole uses tartaric acid as raw material, which is cracked to obtain pyruvic acid, and then through esterification and bromination, it is combined with thioformamide Produced by ring closure.
Synthesis of thiabendazole Stir and heat the mixture of 4-ethoxyformylthiazole, o-phenylenediamine and polyphosphoric acid to 125℃, then heat it at 175℃ for 2 hours, pour the mixture into ice water, and use sodium hydroxide The solution is neutralized to pH 6, crystals are precipitated, filtered, and extracted with hot acetone. The extract is decolorized with activated carbon, concentrated, and dried under vacuum to prepare thiabendazole.
Preparation method two
Mix thiazole-4-hydroxyacyl bromide and o-phenylenediamine, add polyphosphoric acid, heat to 240°C with stirring, and keep warm for 3 hours. Pour the hot reaction solution into ice water, filter, and wash the filtrate with 30% sodium hydroxide solution. The pH value is about 6 to precipitate 2-(4′-thiazolyl)-benzimidazole. Filter, wash with water, and dry to obtain thiobacterium. spirit. Recrystallize with boiling ethanol, m.p. 301~302℃.
4. Method 1
React 4-ethoxyformylthiazole and o-phenylenediamine in condensed phosphoric acid at 175°C for 2 hours. The reactant was poured into ice water, neutralized with sodium hydroxide to a Ph value of 6, and crystals were precipitated. After filtration, the mixture was recrystallized with acetone and decolorized with activated carbon. The decolorized liquid is concentrated and vacuum dried to obtain the finished product.
Method 2
React 4-thiazole carboxamide (or acid bromide) and o-phenylenediamine in condensed phosphoric acid at 240°C for 3 hours. Pour the reactant into ice water. After filtration, the filtrate is treated with 30 % sodium hydroxide solution until Ph = 6, the benzimidazole crystallizes out, and is filtered, washed, and dried to obtain the crude product, which is then recrystallized from ethanol to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
1. As a preservative, our country stipulates that it can be used to preserve fruits, and the maximum usage amount is 0.02g/kg.
2. A highly efficient, broad-spectrum, long-acting systemic fungicide that can conduct to the top when applied to roots, but cannot conduct to the base. It can be used as a foliar spray, and the spraying amount is 2.25 to 3.75g. It is effective Component /hm2 can prevent and treat fungal diseases and root rot of various crops, and has both protective and therapeutic effects. At present, it is also widely used for storage period diseases of fruits such as citrus, apples, pears and bananas, and is treated with 500-1000mg/L and 700-1500mg/L liquid respectively.
3. Antifungal agent.
According to GB 2760–2001 (g/kg): fruit preservation 0.02; garlic moss and green pepper preservation 0.01 (residue ≤ 0.02).
Japanese regulations (1997) are mainly used for citrus and bananas. Maximum residue amount (g/kg): citrus 0.01, banana 0.003; banana flesh 0.0004.
Residue amounts (mg/kg) specified by FAO/WHO (1974): citrus ≤ 10, banana ≤ 3 (whole) or 0.4 (pulp).
4. Systemic fungicides. It can prevent and cure fungal diseases of a variety of plants. It is used to treat post-harvest fruits and vegetables. It can prevent and cure some diseases that occur during storage. It has been widely used at home and abroad. For example, citrus should be soaked with 500-1000ppm liquid to prevent penicillium and green mold during storage; bananas should be soaked with 750-1500ppm liquid to prevent crown rot and anthracnose during storage; 500-1000ppm liquid can also be used Prevent and control diseases during storage of apples, pears, pineapples, grapes, strawberries, cabbage, cabbage, tomatoes, mushrooms, beets, sweet potatoes, etc.
5. It is a systemic fungicide, widely used in the antiseptic and preservation of fruits and vegetables, the antiseptic and mildew proofing of paper, leather, paint, etc., and the repellent in the intestines of humans and animals.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

