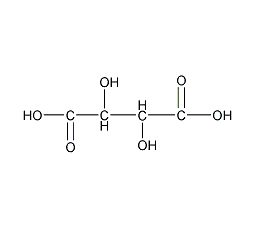
Structural formula
| Business number | 01YF |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C4H6O6 |
| Molecular weight | 150.09 |
| label |
D-2,3-dihydroxysuccinic acid, Dextral grape acid, natural tartaric acid, L-Tartaric acid, [R-(R*,R*)]-2,3-Dihydroxybutanedioic acid, Japanese Pharmacopoeia, acidic solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:87-69-4
MDL number:MFCD00064207
EINECS number:201-766-0
RTECS number:WW7875000
BRN number:1725147
PubChem number:24855129
Physical property data
1. Properties: White monoclinic prismatic crystals with a sour smell.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.76
3. Relative steam Density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 168-170
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Undetermined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): 210
7. p>
9. Specific optical rotation (º): 12° (c=20, H2O)
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC) : Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13 . Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Logarithmic value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion Lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Easily soluble in water, ethanol and glycerol, slightly soluble in ether, insoluble in chloroform
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity
Mouse intravenous LC50: 485mg/kg;
Dog caliber: 5mg/kg;
Rabbit caliber: 5mg/kg; irritating sex
Ecological data
None yet
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 26.69
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 79.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K): 263.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 119.4
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 10.58
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -1.9
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 4
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 6
p>
4.Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 115
7. Number of heavy atoms :10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 134
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11 .Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 2
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Found in tobacco leaves.
Storage method
This product should be sealed and stored in a cool, dry place.
Synthesis method
1. It is obtained by using tartar generated during the production of wine as raw material, converting it into calcium salt, and then decomposing it with a slight excess of dilute acid. Or use maleic acid and hydrogen peroxide as raw materials, convert it into epoxy succinic acid at a certain temperature, and then hydrolyze it to obtain DL-tartaric acid. L(+) tartaric acid can also be obtained from epoxysuccinic acid obtained by chemical synthesis through the action of the ring-opening enzyme contained in Nocardia succinic acid.
2.Add distilled water to industrial tartaric acid, heat it with steam and stir to dissolve it. Add an appropriate amount of activated carbon, stir thoroughly, let it stand, and filter. When the filtrate is heated and concentrated until a film forms on the surface, filter it with suction while it is hot. The filtrate will crystallize after cooling. After it is complete, use a small amount of distilled water for crystallization. After rinsing, lay it flat and dry at 30-40°C until it does not stick to a spoon. If the activated carbon decolorization temperature is controlled to 80°C, filter and concentrate under reduced pressure at 80°C, cool and crystallize,
recrystallize the obtained crystals in a non-ferrous container, refine and dry at low temperature to obtain dextrotartaric acid [L (+) Tartaric acid] Finished product.
Purpose
1.L(+)-Tartaric acid is widely used in beverages As a sour agent for other foods, it is used in wine, soft drinks, candies, bread, and some gelatinous sweets. Utilizing its optical activity, it can be used as a chemical resolving agent to produce the anti-tuberculosis drug intermediate DL- for the resolution of aminobutanol; it can also be used as a chiral raw material. Synthesis of tartaric acid derivatives; using its acidity as a catalyst for resin finishing of polyester fabrics and PH regulator produced by oryzanol; using its complexing properties for electroplating and desulfurization It is used as a complexing agent, masking agent, chelating agent, and anti-dye agent in printing and dyeing, pickling, chemical analysis, and medical testing; using its reducing properties, it is used as a reducing agent in chemical lens making. Photographic developer. It can also complex with a variety of metal ions and can be used as a cleaning agent and polishing agent for metal surfaces.
2.Biochemical research, Masking agent, tanning industry, beer foaming agent. Test or determine potassium salts. It can react with several elemental salts to form soluble complexes (such as niobium oxide, tantalum oxide and potassium pyrosulfate). Photography industry.
3.Used as a sour agent, The acidity is 1.2 to 1.3 times stronger than citric acid. It has high solubility and strong chelating ability for metal ions. It has a flavoring effect on wine, but is weaker than citric acid. Often combined with other organic acids such as citric acid or malic acid. It can be used in various types of food and can be used in appropriate amounts according to production needs.
4.Used as analytical reagents, If combined with masking agent. Used as biochemical reagents and beer foaming agent. Also used in the photography industry and tanning industry.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

