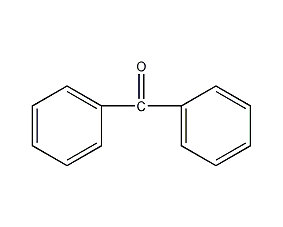
Structural formula
| Business number | 03B4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C13H10O |
| Molecular weight | 182.22 |
| label |
benzophenone, benzophenone, Diphenyl-methanone, absorbent, inhibitors, spice fixative |
Numbering system
CAS number:119-61-9
MDL number:MFCD00003076
EINECS number:204-337-6
RTECS number:DI9950000
BRN number:1238185
PubChem number:24866768
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: The stable form (and two unstable forms) are white and shiny prismatic crystals. Like rose fragrance. There is a sweet taste.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.111
3. Relative density (20℃, 4℃): 1.079950
4. Melting point (ºC): 52~54
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 303~305
6. Refractive index at room temperature ( n25): 1.581480
7. Refractive index(n19D): 1.6077
8. Flash point (ºC): 143
9. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1 ): -6599.7
10. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 54.9
11. Crystal Phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -6510.3
12. Crystal phase standard claim heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol– 1): -34.5
13. Critical temperature (ºC): 556.85
14. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.35
15. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.32
16. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1 ): 568
17. Critical compression factor: 0.276
18. Eccentricity factor: 0.545
19. Solubility: 1g product is dissolved in 7.5ml ethanol, 6ml ether, soluble in chloroform, insoluble in water.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: >10g/kg
Mouse oral LC50: 2895mg/kg
Mouse intraperitoneal LC50: 727mg/kg
Rabbit transdermal LD50: 3535mg/kg
2. Other multiple dose toxicity: Rat oral TDLO: 14g/kg/28D-C
Large Rat pass: 91g/kg/13W-C
Guinea pig inhaled TDLO: 75mg/kg/15d-i
3. Acute toxicity:
Oral cavity LD50 >10000mg/kg(rat)
Skin LD50 3535mg/kg(rbt)
Main irritating effects:
On the skin: irritating skin and Mucous membrane
Above the eyes: irritatingEffects
Sensitization: No known sensitizing effects
Ecological data
General Notes
Do not allow this product to come into contact with groundwater, waterways or sewage systems.
Water hazard class 2 (German Regulation) (self-assessment via list) The substance is hazardous to water.
Even extremely small amounts of the product seeping into the ground can be dangerous to drinking water
It is also toxic to fish and plankton in the water.
Do not discharge materials into the surrounding environment without government permission.
Highly toxic to organic matter in water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 56.04
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 167.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 426.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 42.1
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 22.21
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 17.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 14
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 165
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with strong oxidants and reducing agents.
2. Exist in mainstream smoke.
Storage method
1. This product should be sealed and stored in a cool place.
2. During the production process, equipment should be sealed, the workshop should be well ventilated, and operators should wear labor protection supplies.
Synthesis method
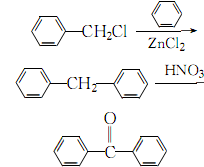
1. Obtained from the condensation of benzyl chloride with benzene and then oxidation with nitric acid.
2. Obtained from the condensation of benzene with carbon tetrachloride and then hydrolysis. In the laboratory, aluminum trichloride is used as a catalyst to react benzene with benzoyl chloride.
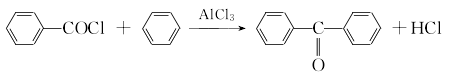
After mixing dry benzene and freshly steamed benzoyl chloride, add powdered anhydrous aluminum trichloride. Heat and reflux for 3 hours until no hydrogen chloride is released. Pour into a mixture of ice water and concentrated hydrochloric acid while it is hot, and separate the layers; wash the upper layer with 5% sodium hydroxide solution and then with water. After recovering benzene, it is dried with anhydrous magnesium sulfate and distilled under reduced pressure to obtain benzophenone.
3.Mix the benzene and zinc chloride catalyst evenly, control the pressure to 174~348Pa, and stir under Heat to 70-75°C, react for 10 hours, let stand and separate into layers, take the upper oil and wash it twice with water to remove zinc chloride and hydrochloric acid. Wash once with 1% dilute alkali solution, and distill away benzene and fractions below 150°C. Add fragments or zeolite to the obtained crude diphenylmethane, stir and heat to 100-115°C, slowly add 70% nitric acid dropwise while stirring, and then keep it at 106-116°C for 8 hours. After layering, take the oil layer and wash it three times with hot water and 3% sodium carbonate, and finally distill it under reduced pressure to collect 145~180℃ (667~1200Pa) or 160~210 ℃ (1333~2400 Pa) fraction is the finished product.
Process reaction formula:
4. First cool the mixture of carbon tetrachloride and aluminum trichloride with 3 times the amount of benzene to 10~15℃, add benzene, and continue to cool to 5~10℃ , then add dropwise a two-component mixture of carbon tetrachloride: benzene = 1: 6 (molar ratio) (the amount of benzene is 11 times the amount of benzene added last time), control the dropping speed to maintain the reaction temperature at 5 ~10℃, and reacted at 10℃ for 3h. After that, add an appropriate amount of water, stir evenly, add
heat distillation, first steam out excess carbon tetrachloride, and then raise the temperature for steam distillation to ensure the steam distillation time, complete the hydrolysis reaction, and steam the product together out. Let it stand, extract the water layer with benzene liquid, merge the extract into the oil layer, and then crystallize the oil layer. After filtration, heat the crystallization, melt and distill under reduced pressure. Collect the 157~176℃ (1333~2666Pa) fraction, which is the finished product.
Process reaction formula:
5.Thermal decomposition of calcium benzoate first produces calcium benzoate, and then from benzene It is obtained by dissolving calcium formate powder. A newly developed green synthesis route for benzophenone.
① Synthesis of calcium benzoate by rheological phase method Weigh a certain amount of calcium carbonate and benzoic acid with a molar ratio of 1:2, mix the two evenly, and add water Adjust it to a rheological state, move it into the reactor, and control the temperature at 100°C for 8 hours. Wash the product three times with diethyl ether, and then dry it in a drying oven at 240°C to obtain anhydrous calcium benzoate.
② Calcium benzoate is thermally decomposed in nitrogen, and the decomposition products at 500°C are collected to obtain calcium carbonate, benzophenone, etc. product. Calcium carbonate further decomposes to form calcium oxide.
Purpose
1. Spices and fixatives. Styrene polymerization inhibitor. Organic Synthesis. Manufacture of antihistamines, hypnotics, and pesticides.
2.Used in spice preparation and organic synthesis. Also used as gas chromatography stationary liquid.
3.It is used as a photocuring agent for photosensitive adhesives and photocurable coatings, but it is ineffective when used alone for photocurable coatings and must be combined with Active hydrogen compounds such as fatty amines are used together. Benzophenone is also a UV absorber for polymer materials and an intermediate for organic pigments, medicines, spices, and pesticides. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used to produce dicyclohexane piperidine, benztropine hydrobromide, diphenhydramine hydrochloride, etc. It is also a styrene polymerization inhibitor and flavoring agent. It can give flavors a sweet smell and is used in many perfumes and soap flavors.
�, collect the decomposition products at 500℃ to obtain products such as calcium carbonate and benzophenone. Calcium carbonate further decomposes to form calcium oxide.
Purpose
1. Spices and fixatives. Styrene polymerization inhibitor. Organic Synthesis. Manufacture of antihistamines, hypnotics, and pesticides.
2.Used in spice preparation and organic synthesis. Also used as gas chromatography stationary liquid.
3.It is used as a photocuring agent for photosensitive adhesives and photocurable coatings, but it is ineffective when used alone for photocurable coatings and must be combined with Active hydrogen compounds such as fatty amines are used together. Benzophenone is also a UV absorber for polymer materials and an intermediate for organic pigments, medicines, spices, and pesticides. In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used to produce dicyclohexane piperidine, benztropine hydrobromide, diphenhydramine hydrochloride, etc. It is also a styrene polymerization inhibitor and flavoring agent. It can give flavors a sweet smell and is used in many perfumes and soap flavors.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

