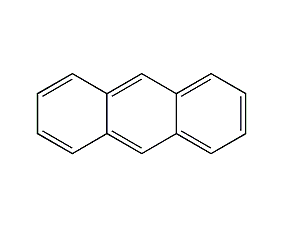
structural formula
| business number | 03bq |
|---|---|
| molecular formula | c14h10 |
| molecular weight | 178.23 |
| label |
green oil brain, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, rough anthracene, anthracene (coarse), p-naphthalene, sterilite hop defoliant, aromatic compounds |
numbering system
cas number:120-12-7
mdl number:mfcd00001240
einecs number:204-371-1
rtecs number:ca9350000
brn number:1905429
pubchem id:none
physical property data
1. characteristics: light yellow needle-shaped crystals with blue fluorescence. [1]
2. melting point (℃): 217[2]
3. boiling point (℃): 345 [3]
4. relative density (water = 1): 1.24[4]
5. relative vapor density (air=1): 6.15[5]
6. saturated vapor pressure (kpa): 0.13 (145℃)[6]
7. heat of combustion (kj/mol): -7156.2[7]
8. critical temperature (℃): 596.1[8]
9. critical pressure (mpa): 3.03[9]
10. octanol/water partition coefficient: 4.45[ 10]
11. flash point (℃): 121 (cc) [11]
12. ignition temperature (℃) :540[12]
13. explosion upper limit (%): 5.2[13]
14. explosion lower limit (%) %): 0.6[14]
15. solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol and ether. [15]
16. refractive index: 1.5948
17. solubility parameter (j·cm-3)0.5: 17.809
18. van der waals area (cm2·mol-1): 1.084×1010
19. van der waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 99.560
20. crystal phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kj·mol-1): -7064.3
21. crystal phase standard claim heat (enthalpy) (kj·mol-1): 126.0
22. crystal phase standard entropy (j·mol-1·k-1): 207.15
23. crystal phase standard formation free energy (kj·mol-1): 282.8
24. crystal phase standard hot melt (j·mol -1·k-1): 210.50
25. gas-phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kj·mol-1): -7166.0
26. gas phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kj·mol-1): 227.7
27. gas phase standard entropy (j·mol-1·k-1): 386.03
28. gas phase standard free energy of formation (kj·mol-1 ): 331.4
29. gas phase standard hot melt (j·mol-1·k-1): 182.84
toxicological data
1. irritation: mouse transdermal standard drez test: 118ug mild irritation
2. acute toxicity: rat oral ld50: >16g/kg; mouse oral ld50 : 4900mg/kg; mouse oral ld: >17g/kg
3. acute toxicity [16] ld50: 430mg/kg (small mouse vein)
4. irritation[17] mouse transdermal: 118μg, mild stimulation.
ecological data
1. ecotoxicity[18] lc50: 0.36mg/l (24h) (fathead minnow); 11.9μg/l (96h) (bluegill) fish, juvenile fish)
2. biodegradability[19]
aerobic biodegradation (h): 1200 ~11040
anaerobic biodegradation (h): 4800~44160
3. non-biodegradability [20]
aqueous phase photolysis half-life (h): 0.58~1.7
photolysis maximum light absorption wavelength range (nm): 251.5~374.5
photooxidation in water half-life (h): 1111~38500
half-life of photooxidation in air (h): 0.501~5.01
4. bioaccumulation [21] bcf: 162 (goldfish); 1029 (mosquito fish); 4400~9200 (rainbow trout); 759~912 (fleas); 7760 (green algae)
molecular structure data
1. molar refractive index: 61.93
2. molar volume (cm3/mol): 157.6
3. isotonic specific volume (90.2k ): 414.9
4. surface tension (dyne/cm): 47.9
5. dielectric constant (f/m): 3.08
6. polar chemical rate (10-24cm3): 24.55
compute chemical data
1. reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (xlogp): none
2. number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. number of tautomers: none
6. topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. number of heavy atoms: 14
8. surface charge: 0
9. complexity: 154
10. number of isotope atoms: 0
11. determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. number of covalent bond units: 1
properties and stability
1. it is relatively active in nature. it is easily oxidized in the air and sunlight, and sublimates when heated.
2. this product is toxic and can irritate the respiratory tract, respiratory organs and skin. direct exposure to sunlight in summer can cause dermatitis. long-term exposure can cause pigmentation on the face and hands, and keratosis of the upper layer of the skin. mice were given industrial anthracene ld504.88g/kg by gavage. the maximum allowable concentration in the air in the workplace is 0.1mg/m3.
3. stability[22] stable
4. incompatible substances[23] strong oxidizing agent
5. polymerization hazard[24] no polymerization
storage method
1. storage precautions [25] store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. keep away from fire and heat sources. the storage temperature does not exceed 30°c and the relative humidity does not exceed 80%. the packaging is sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
2. the production equipment needs to be airtight, the production site needs to be well ventilated, the operators should wear protective equipment, and some protective ointment can be applied to the skin. packed with inner plastic bag and outer sack. 25kg or 50kg per bag. store in a cool, ventilated and dry place.
synthesis method
1. in coal tar, the content of anthracene is 1.4%. the i anthracene oil fraction obtained by continuous distillation of tar accounts for 12-14% of the tar. the initial boiling point is 300°c, and the distillation volume before 350°c is 95%. 1. anthracene oil is cooled and crystallized, vacuum filtered or part of the oil is removed with a centrifuge. the oil content of the crude anthracene after centrifugation is greater than 20-25%. the remaining components are: anthracene 25-30%, carbazole 20-25%, phenanthrene 30 %about. the yield of anthracene accounts for 58-87% of the anthracene source in tar. besides benzene and naphthalene, anthracene is one of the most important components of coal tar. in the industrial production of anthracene, it is much more difficult to manufacture than naphthalene because phenanthrene and carbazole, which have similar boiling points, must be separated. even if distillation, crystallization and solvent extraction are skillfully combined, the yield is only 40-50%. to extract and refine anthracene from crude anthracene, we first use the property of phenanthrene to be easily soluble in oil to separate phenanthrene from anthracene and carbazole. methods for further separation of anthracene and carbazole include distillation separation and potassium fusion.
2. obtained in the final stage of distillation of coal tar.
purpose
1. used to test indene. manufacture of anthraquinone and alizarin dyes, etc. this product is mainly used to manufacture dye intermediates anthraquinone and tannins. it can be used as insecticide, fungicide and gasoline anti-coagulant. high-purity anthracene is used to prepare single crystal anthracene, which is used in scintillation counters.
2. used in the production of anthraquinone, and also used as pesticides, fungicides, gasoline retarder, etc. [26]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

