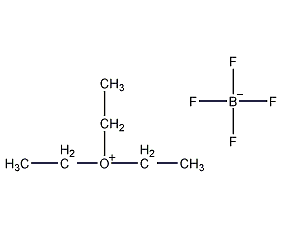
Structural formula
| Business number | 04H2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H15BF4O |
| Molecular weight | 189.99 |
| label |
Meerwein salt |
Numbering system
CAS number:368-39-8
MDL number:MFCD00044423
EINECS number:206-705-1
RTECS number:RR4584700
BRN number:3598090
PubChem number:24889377
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and transparent to yellow or light brown liquid
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.33
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Not available
4. Melting point (ºC): 96-97
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Not available
p>
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Not available
7. Refractive index: Not available
8. Flash point (ºC): Not available
p>
9. Specific rotation (º): Not available
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Not available
11. Vapor pressure (kPa , 25ºC): Not available
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Not available
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Not available
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Not available
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Not available
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient : Unavailable
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Unavailable
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Unavailable
19. Solubility: Soluble in CH2Cl2.
Toxicological data
Ecological data
This substance may be harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
None yet
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 5
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 12
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 44.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 2
Properties and stability
It has strong hygroscopicity and should be stored in a solution of ether and methylene chloride at a low temperature of 0~5 oC. Trimethoxyboron tetrafluoride can be stored directly in a drying oven at low temperature. Because it is not hygroscopic, it can be operated and used in the air for a short time.
Storage method
Should be stored at 2-8℃.
Synthesis method
1. Prepared by the reaction of 3-chloro-1,2-epoxypropane and BF3-OEt2 complex.
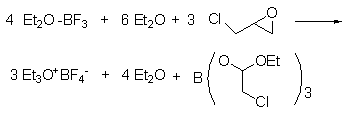
2. Three-neck the 2 liters Flask, stirrer, liquid funnel and condenser with drying tube��Put it into an oven at 110℃ to dry, install it while hot, and cool it in a dry nitrogen flow. Add 500 ml of sodium-dried ether and 284 g (252 ml, 2.00 mol) of freshly distilled boron trifluoride ether solution into the flask. Add 140 grams (119 ml, 1.51 mol) of 3-chloropropylene oxide dropwise into the stirring liquid at a rate that maintains vigorous boiling (it takes about 1 hour). After the addition is complete, reflux for 1 hour and leave at room temperature overnight. Replace the stirrer with a suction filter. Aspirate the clear ether above the triethyloxytetrafluoroborate crystals. These operations need to be carried out under nitrogen protection to avoid humid air entering the flask. The crystals were washed with three 500 ml portions of sodium-dried ether. Place the flask into a drying oven. The product is collected in a glass core funnel under nitrogen protection and bottled. Triethyloxytetrafluoroborate is a colorless crystal.
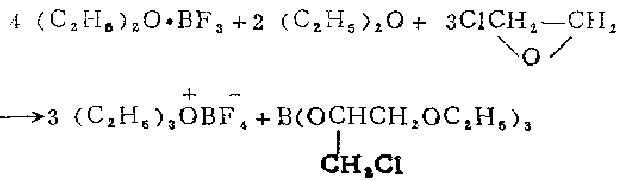
Purpose
1. Powerful ethylating agent, acid esterification, protein carboxyl modification.
2. Ethylation reagents of oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur in ethers, thioethers, nitriles, ketones, esters, and amides react with alcohol to form ether. O-ethylation of enol hydroxypyridine. With nitrile generates ethyl secondary amine. Esterify and split thioacetals. Remove N-benzoyl and N-acetyl groups. Reduction of secondary and tertiary amides to equivalent secondary and tertiary amines. Preparation of thiolactone from lactone. Preparation of beta-keto acid ester from ketone azoacetate. Preparation of L-proline.
3.Meerwein salt is a very effective alkyl reagent, which can act on the alkylation reaction of many relatively inert weak nucleophilic functional groups.
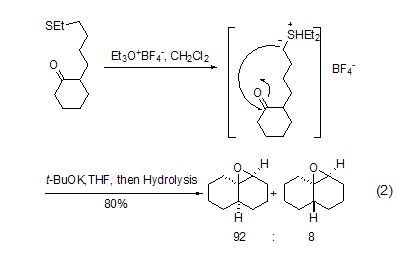
Thioethers can be converted into the corresponding sulfonium salts under the action of trimethoxyboron tetrafluoride, thus showing better functional group leaving ability and triggering a series of reactions (Formula 2)[1].
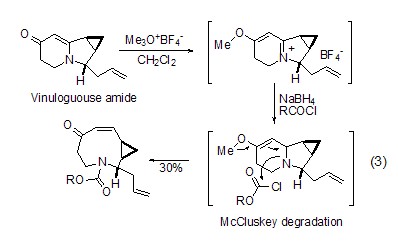
Amide substrate Both O-alkylation and S-alkylation of sulfamide substrates can react well under the action of Meerwein salt, and the generated imine ester has higher reaction Activity, such as in the total synthesis of indolizomycin, the generated imide ester is reduced by sodium borohydride to obtain a nine-membered ring natural product (formula 3)[2].
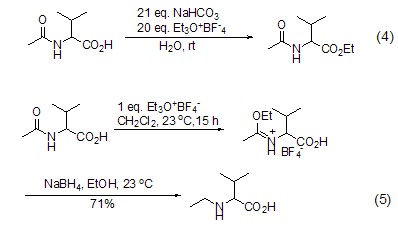
Meerwein salt energy in aqueous phase Acts on carboxylic acid to achieve esterification reaction (Formula 4)[3]. Under these reaction conditions, the amide group does not undergoO-alkylation. In the absence of aprotic solvents and bases, carboxylic acid amide compounds will only undergo an O-alkylation reaction (Formula 5)[4].
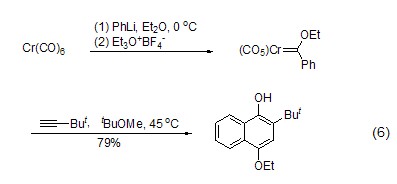
An important preparation of Fisher carbene The method of complexing is to utilize the alkylation ability of triethoxyboron tetrafluoride. With the action of appropriate nucleophiles such as alkyllithium or aryllithium, Fisher’s reagent can be synthesized in one step, and then other reactions can be realized (Formula 6)[5].

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

