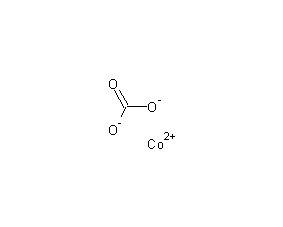
Structural formula
| Business number | 05AY |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CoCO3 |
| Molecular weight | 118.94 |
| label |
cobalt chloride, Cobalt carbonatetechgr, Colorant, beneficiation agent, catalyst, indicator |
Numbering system
CAS number:513-79-1
MDL number:MFCD00149654
EINECS number:208-169-4
RTECS number:None
BRN number:None
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: light pink powder, trigonal crystal.
2. Density (g/ cm3, 25/4℃): 4.13
3. Solubility: Almost insoluble in water, alcohol, and ether Methyl ester and ammonia.
Toxicological data
Inhalation of cobalt compounds sometimes causes bronchial asthma; grinding cobalt compounds can cause acute dermatitis, and sometimes ulcers form on the skin surface.
Ecological data
This substance may be harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 63.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 5
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 18.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 2
Properties and stability
Use and store according to specifications. It will not decompose and avoid contact with oxides. Almost insoluble in water, alcohol, methyl acetate and ammonia. Soluble in acid. Does not interact with cold concentrated nitric acid and concentrated hydrochloric acid. It begins to decompose when heated to 400°C and releases carbon dioxide. In the air or in the presence of weak oxidants, it is gradually oxidized to cobalt carbonate. Soluble in dilute acid and ammonia, insoluble in water, it easily decomposes into trivalent cobalt carbonate when heated in the air.
Toxicity and protection: Bronchial asthma sometimes occurs when inhaling cobalt compounds; grinding cobalt compounds can cause acute dermatitis, and sometimes ulcers form on the skin surface. The maximum allowable concentration of metallic cobalt and cobalt oxide is 0.5mg/m3. Pay attention to dust prevention and removal when working, and wear a gas mask to prevent aerosols from damaging respiratory organs. You should also wear dust-proof overalls and protective gloves to protect your skin when working.
Storage method
Stored in a cool, dry and well-ventilated warehouse. �Keep away from fire and heat sources. Protect from direct sunlight. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from acids and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Packed in woven bags lined with polyethylene plastic bags, with a net weight of 50kg per bag. Store in a ventilated, dry warehouse, insulated from heat and moisture, and must not be stored or transported together with acids or liquid ammonia.
Synthesis method
Hydrochloric acid After the cobalt metal or cobalt-containing waste reacts with hydrochloric acid to generate a cobalt chloride solution, sodium carbonate is added to react to generate cobalt carbonate precipitate. After rinsing, centrifugal separation, and drying, the finished cobalt carbonate product is obtained. Its reaction equation
![]()
![]()
2. Weigh 122g (0.42mol ) Cobalt nitrate hexahydrate, dissolve it with as little water as possible, then weigh 60g (0.57mol) anhydrous sodium carbonate and dissolve it in 600mL water, and add the hot solution to the cobalt nitrate aqueous solution several times. Heat the solution to boiling, stir for 15 minutes, and a precipitate will form. After suction filtration, wash with water and absorb the water with filter paper.
Purpose
1. In chemical production, it is a raw material for the production of other cobalt salts and cobalt oxide. Used as colorant in ceramic industry. Used as mineral processing agent in the mining industry. Used in the organic industry to make catalysts, camouflage coatings and chemical temperature indicators. Used as trace element fertilizer in agriculture. Used as analytical reagents in analytical chemistry.
It is used to make cobalt oxide and is a raw material for making lithium battery cathode materials. Used as mineral processing agents, catalysts, pigments for camouflage coatings, feeds, micro-fertilizers, ceramics and raw materials for the production of cobalt oxide
2. Used as mineral processing agents, catalysts, pigments for camouflage coatings, feeds, trace fertilizers, Ceramics and raw materials for the production of cobalt oxide

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

