Background and overview[1]
The chemical formula of dimethyl oxalate is CH3OOCCOOCH3. Molecular weight 118.09. The melting point is 50~54℃, the boiling point is 163.5℃, the relative density is 1.148, and the refractive index is 1.379. Soluble in ether, benzene, chloroform, slightly soluble in water. Can perform condensation reactions with certain ketones. Dimethyl oxalate is mainly used in organic synthesis and can also be used in plasticizer, pharmaceutical, pesticide and other industries. The gas-phase catalytic coupling of carbon monoxide to synthesize dimethyl oxalate, as part of the synthesis gas to ethylene glycol technology, has become an important research topic in the domestic fields of carbon-chemistry and organic chemical industry. Research units such as Chengdu Institute of Organic Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Fujian Institute of Structure of Matter, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Southwest Research Institute of Chemical Industry, Zhejiang University, Tianjin University, and East China University of Science and Technology have been dedicated to catalyst development, process condition selection, and engineering development in this field.
Apply[2]
As an important chemical and pharmaceutical raw material, dimethyl oxalate is often used to prepare various organic solvents, extractants, adhesives, plasticizers and various pharmaceutical intermediates. For example, it is used to synthesize vitamin B13, add Hydrogen can be used to prepare methyl glycolate, ethylene glycol, and replace diethyl oxalate to synthesize sulfamethoxazole, etc. For example, dimethyl oxalate can be used instead of diethyl oxalate as the starting material, and 5-methyl-3 can be produced through multi-step reactions such as Kirschner’s reaction, acidification, cyclization and aminolysis without changing the other production processes and raw materials. -Formylisoxazole, and the obtained products were inspected and analyzed, and it was found that there was no difference in product quality; at the same time, because the price of dimethyl oxalate is lower than that of diethyl oxalate, the production cost of the product is reduced and its popularity in the market is improved. competitiveness. Dimethyl oxalate can also react with ammonia to generate oxamide. Oxamide can be used as a stabilizer for nitrocellulose products, and can be used as a gas-generating agent and a cooling agent in gas generators. At the same time, oxamide can also be used as a retarding agent. Nitrogen-releasing fertilizers, etc.
Preparation[2-3]
Method 1: The traditional oxalate ester synthesis method uses oxalic acid and monohydric alcohol as raw materials, inorganic acid (such as concentrated sulfuric acid, etc.) or strongly acidic ion exchange resin as the catalyst, and performs esterification reaction in a reactor. The reaction equation is as follows:
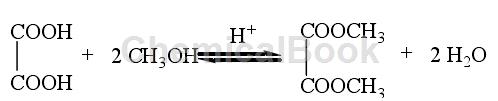
Since a large amount of water is produced during the reaction, and the water produced is not conducive to the forward progress of the esterification reaction, the water produced by the reaction needs to be removed from the system in time. In industrial production, a certain amount of water-carrying agent is usually added to the reaction system to remove a large amount of water produced during the reaction process. Taking the traditional production process of diethyl oxalate as an example, the oxalate production method is introduced: first, the mixture of oxalic acid, ethanol and aqueous agent is esterified for the first time, and the product is distilled after heating and refluxing for a period of time; Secondly, it is subjected to secondary esterification and distillation with a mixture of water-carrying agent and ethanol to obtain the crude product diethyl oxalate. After distillation under reduced pressure, the finished product diethyl oxalate can be obtained. The entire reaction process takes 20 to 24 hours, and the yield of oxalate ester can reach more than 80%.
Method 2: Preparation of nitric oxide and carbonylation to synthesize dimethyl oxalate. Carbon monoxide, the raw material for the carbonylation reaction, is used as a gas for stirring. Sodium nitrite and dilute nitric acid are fully reacted in the NO preparation reactor to produce nitric oxide. Together with the carbon monoxide used for stirring, they are added to the dimethyl oxalate circulation system for esterification, carbonyl chemical, and finally synthesize dimethyl oxalate; specifically including the following process steps:
① During the NO production process, the concentration of dilute nitric acid is controlled at 50-65%, the concentration of sodium nitrite solution is controlled at 30-45%, the purity of CO is not less than 98.5%, and the ratio of CO to generated NO is CO:NO=1-8;
② Set up an independent gas mixer before the esterification reaction, so that oxygen with a purity greater than 99% is fully mixed with the circulating gas and the oxidation reaction of NO initially occurs, and then the mixed gas enters the esterification reactor to generate methyl nitrite; where , the esterification reactor adopts a packed tower, with 10-40 theoretical plates, a cooler is set at the top, the condensate is completely refluxed, the methanol content in the reflux liquid is greater than 99%, a reboiler is set at the bottom, and the tower still temperature is 70-120 ℃; fresh methanol is added to the reflux tank, and the purity is not less than 99.8%;
③ The gas coming out of the top of the esterification reactor is processed by the gas purifier, and after removing the impurity components, it is mixed with the raw material CO and enters the carbonylation reactor. The pressure is 0.1-0.5MPa, and the reaction temperature is 120-150°C. Finally, Generate dimethyl oxalate;
④The material from the carbonylation reactor enters the methanol washing tower, and liquid methanol is used to wash the dimethyl oxalate in the mixed gas; the tower is equipped with a top cooler and a still reboiler, and the top temperature is 10 -20℃, the temperature of the tower kettle is 70-110℃, fresh methanol is added to the reflux tank, and the molar ratio of the amount of methanol used for alcohol washing to the amount of mixed gas is 1:4-8;
⑤The mixed gas coming out of the top of the methanol scrubber is separated by a vapor-liquid separator with a separation accuracy of 5-30 μm, and then pressurized by a circulating gas compressor and sent to the esterification reactor;
⑥The material from the bottom of the methanol washing tower enters the dimethyl oxalate refining tower. The temperature at the top of the tower is 60-75°C, and the temperature of the tower still is 150-170°C. The dimethyl oxalate product is obtained at the bottom of the tower, and the top of the tower is Methanol, dimethyl carbonate and water.
Main reference materials
[1] Compound Dictionary
[2] Study on the autocatalytic esterification reaction for the synthesis of dimethyl oxalate and diethyl oxalate
[3] CN201210542727.3 A method for preparing nitric oxide and carbonylation to synthesize dimethyl oxalate

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

