[Background and Overview][1][2]
N-Methylaniline is the main product in the N-alkyl aromatic amine series and an important intermediate in fine chemicals. Very versatile. my country’s first set of production equipment was built with assistance from the former Soviet Union in the 1950s. The products are mainly used to make explosives and are often used to blend straight-run gasoline. Since straight-run gasoline has more n-alkanes, its octane number is generally low. , so some technicians use straight-run gasoline as the base oil for blended gasoline, and increase the octane number by adding N-methylaniline to achieve the goals of low investment and high efficiency. N-methylaniline has a good anti-knock effect. The use of organic amine compounds can widen the ignition limit range of the mixture, improve the ignition success rate, and effectively increase the octane number of gasoline. Adding this type of antiknock agent to gasoline can increase the research octane number by one unit based on the original properties and composition of the gasoline and the properties of the solvent such as polarity or nonpolarity. The antiknock agent was sold under the trade name Kellomore MMA in Germany. N-methylaniline compounds have electron transfer properties and can react with peroxide through the electron transfer mechanism. This reaction will eliminate the peroxide, change the reaction path, and extend the induction period of spontaneous combustion of the unburned mixture. Limit the rate of fuel combustion to within the normal combustion range. It can be inferred that the anti-knock mechanism of methylaniline is that oxidation occurs in the cylinder, which eliminates peroxides produced when gasoline is burned, thereby reducing the peroxide concentration, hindering automatic ignition, and slowing down the rate of energy release. Reduce detonation and improve the anti-knock performance of fuel.
[Features][3]
N-Methylaniline is a colorless oily liquid at room temperature. Molecular weight 107.16. Melting point -57℃. Boiling point 196.1℃. Relative density 0.9891 (20/4℃). Refractive index 1.5684. Flash point 78℃. Soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, insoluble in water. Place gradient yellow. The vapor pressure is 0.13kPa at 36°C and the flash point is 78°C. It is not prone to evaporation loss, but it is also not conducive to distribution in the cylinders of multi-cylinder engines. Stable in nature and not easily decomposed in air and dark environments. The main characteristics of blended gasoline with N-methylaniline antiknock agent are odor, high density, unstable unwashed gum, low olefin value, and the need for auxiliary antiknock agents such as MTBE and MMT.
[Production process][1][2][3][4]
1. The traditional N-methylation method of aniline uses aniline as the raw material, methanol as the alkylation reagent, and sulfuric acid as the catalyst under a pressure of 3.0 MPa for liquid phase synthesis. The resulting crude product is distilled to remove methanol, water, aniline and N, N-dimethylaniline to obtain N-methylaniline finished product. The reaction formula is:
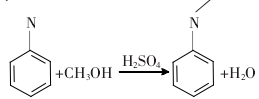
The disadvantages of this method are that it cannot selectively produce N-methylaniline, has low yield, large waste pollution, and serious equipment corrosion, and has been eliminated by most manufacturers.
2. The crude product is generated from aniline and methanol under the action of copper-zinc-chromium catalyst, and then distilled to obtain this product. The content of N-methylaniline is usually 96%, unreacted aniline and N, N-di The content of methylaniline is low, and qualified N-methylaniline is obtained through distillation. At present, most industrial production adopts this method.
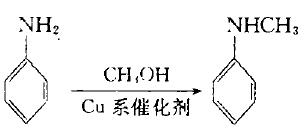
3. Phosphorus trichloride catalytic method. Aniline and methanol react in the presence of phosphorus trichloride at 300°C and 70 atmospheres to obtain N-methylaniline. The content is usually 60-65%, and the unreacted aniline content is about 15-20%. N, N- The content of dimethylaniline is about 20%, and N-methylaniline is obtained by distillation.
4. In the laboratory, aniline can be used as raw material and dimethyl sulfate as methylating agent:
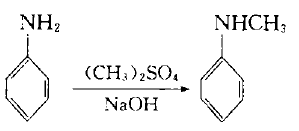
Add dimethyl sulfate dropwise into the mixture of aniline and water below 10`C. After stirring for 1 hour, add 30% sodium hydroxide solution dropwise, let it stand, separate the upper organic phase, and use benzene to separate the lower layer. After extraction, the oil obtained after recovering benzene from the extract liquid is combined with the organic phase, which is a mixture of aniline, N-methylaniline and N,N-dimethylaniline. Treat the mixture with sulfuric acid to make aniline form sulfate crystals and filter them out. N, N-dimethylaniline can be converted into N-methylaniline with acetate through the following reaction:
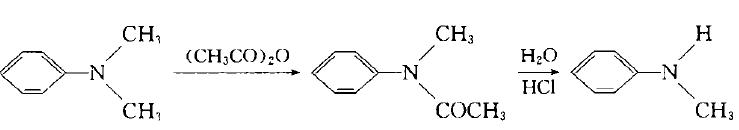
[Products and Applications][3][5]
N-methylaniline is a fine chemical product with a wide range of uses. It is mainly used to make pesticides, dyes, dye intermediates, rubber additives and explosive stabilizers. It can also be used as a solvent and acid acceptor. Organic synthesis intermediates, acid absorbers and solvents. In the dye industry, it is used in the production of cationic brilliant red FG, cationic pink B, reactive yellow-brown KGR, etc. It can also be used to increase the octane number of gasoline and organic synthesis, and can also be used as a solvent.
1. Application in pesticides
In terms of pesticides, domestic N-methylaniline is mainly used to produce the insecticides buprofen (promethazin, chloride), which is a new type of highly selective insecticide with high nymphicidal activity. Pests exposed to the agent die during the molting period. The recommended dose cannot kill adult insects, but it can reduce egg laying and prevent eggs from hatching, greatly reducing the number of offspring. Safe against natural enemies of pests and flower-visiting insects. Instead ofThere is no cross-resistance problem with other types of insecticides. Due to the above characteristics, the production of buprofezinone has developed rapidly. N-methylaniline is used to synthesize herbicides and fungicides abroad. The pesticide variety methylbenzofuron developed by Japan’s Showa Electronics Co., Ltd. is used to control sedges and water borers in lawns and dry fields, and has very low toxicity to useful plants. West Germany’s Schering Company has developed a new pesticide variety, anilinephthalofuron, which is used as a herbicide in dry fields and gardens, and is especially suitable for pre-emergence use on various types of plants. The West German Schering Company also developed the herbicide broadleafin, which is mainly used for weed control and can also be used as a pre-emergent herbicide for peanuts, cotton and soybeans. In addition, Monsanto Company, Side Bayer Company, etc. have also developed other types of herbicides using N-methylaniline.
2. Application in dyes
In the dye industry, N-methylaniline is mainly used in the manufacture of intermediates and cationic dyes.
1) Used in the production of dye intermediates: The dye intermediates produced from N-methylaniline as raw materials mainly include N-methyl-N-benzylaniline and N-methyl-N-hydroxyethylaniline. N-Methyl-N-benzylaniline is used to produce cationic red X-GRL (dye index number, refer to C.1., basic red 46), which is a dark red powder with a compatibility value of 3.5. It is used for the printing and dyeing of cylindrical fiber and its blended fabrics, and can also be used for the dyeing of modified cylindrical fiber and polyester. N-Methyl-N-hydroxyethylaniline is used to produce cationic blue X-GRRL (dye index number, refer to C.1., basic blue 41), which is a blue-green powder with a compatibility value of 3.5. Used for dyeing of eye fiber and its blends.
2) Used to produce cationic dyes: dyes directly produced from N-methylaniline include cationic brilliant red SGN (dye index number, refer to C.1., basic red 14), dark red powder, compatibility value 3.5 : Cationic pink FG (dye index number C.1., basic red 13), dark red powder, compatibility value 4, cationic pink B (dye index number, refer to C.1., basic red 27) and reactive yellow brown KGR. These dyes are mainly used for printing and dyeing of nylon fiber and its blended fabrics. It can also be used for dyeing modified polyester fiber, polyester fiber and polyvinyl chloride fiber and printing acetate fiber.
3. Application in rubber additives
N-methylaniline can be used to produce the rubber additive ZMPC (zinc methylphenyldithiocarbamate), which is an accelerator for natural rubber and synthetic rubber. It is especially suitable for difficult-to-vulcanize rubber materials, such as ethyl alcohol. Propylene rubber is characterized by fast vulcanization speed, scorch resistance, no blooming of products, and good thermal aging stability. Domestically, this product was developed by the Northwest Rubber Industry Research Institute and Zhejiang Huangyan Rubber Additives Group Company. In addition, it can also be used to manufacture dithiodimethyldiphenylthiuram as a vulcanization accelerator for natural rubber, styrene-butadiene and nitrile rubber. This product is produced by Shandong Luye Auxiliary Co., Ltd. In recent years, the annual domestic consumption of N-methylaniline for synthetic rubber additives has been approximately 100 tons. With the development of the rubber industry, its consumption is expected to increase year by year.
4. Gasoline antiknock agent
Gasoline antiknock agents are a type of oil additive that can increase the octane number of gasoline and prevent or reduce knocking. It is widely used in gasoline. At present, antiknock agents can be generally divided into two categories. One is metal antiknock agents, such as alkyl lead antiknock agents, manganese-based antiknock agents such as methylcyclopentadienyl manganese, and iron-based antiknock agents. Such as ferrocene, rare earth metal compounds, etc. The other type is non-metallic antiknock agents, such as alcohols, phenols, ethers, aromatic amines, carboxylic acid esters and various polymers. The addition amount of this type of antiknock agent is relatively large. So it’s often thought of as a high-octane blend for gasoline. N-methylaniline has a good anti-knock effect. The use of organic amine compounds can widen the ignition limit range of the mixture, improve the ignition success rate, and effectively increase the octane number of gasoline.
5. Applications in other areas
N-methylaniline and phosgene are reacted in acetyl acetate, and then the ethyl acetate is evaporated and recrystallized with ethanol to obtain N-methyl-N-phenylcarbamophthalein chloride, which can be used to manufacture emission products. The centralizing agent of gunpowder and nitroglycerine. In addition, N-methylaniline can also be used as a solvent and acid acceptor.
[References]
[1] Xu Hua. Production and application of N-methylaniline[J]. Guizhou Chemical Industry, 1997 (1): 53-55.
[2] Liu Ling. Review of N-methylaniline gasoline antiknock agents[J]. Petroleum Depots and Gas Stations, 2011, 20(3): 32-34.
[3] Wu Shimin, Yin Delin, editor-in-chief. Concise Dictionary of Fine Chemical Engineering. Shenyang: Liaoning Science and Technology Press. 1999.
[4] Xu Long, Zhu Yifeng, Li Xiaonian. Research progress on the synthesis of N-methylaniline and N, N-dimethylaniline[J]. Chemical Production and Technology, 2009, 16(3): 30-33+ 41.
[5] Ma Shichang, editor-in-chief. Dictionary of Organic Compounds. Xi’an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press. 1988. Page 143.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

