[Background and Overview][1][2][3]
N, N-dimethylacetamide, also known as acetyldimethylamine (DMAc or DMA), has a relative molecular mass of 87.12 and a molecular formula of CH3CON(CH3 )2, boiling point 164-166℃ (1×103Pa), melting point -20℃, flash point (open) 66℃, fire point 490℃, relative density 0.9429 (20/4℃), refractive index 1.4373. It is a colorless and transparent liquid that can be mixed with water, alcohol, ether and other organic solvents. It is a highly polar aprotonated solvent with good thermal stability and is stable without decomposition even at the boiling point. It can be refined by distillation. Not easy to hydrolyze, low corrosion signal, low toxicity and other advantages.
N, N-dimethylacetamide is widely used in petroleum processing and organic synthesis industries. It has good solubility in a variety of resins, especially polyurethane resins and polyimide resins. It is often used as an additive for heat-resistant fibers, plastic films, coatings, medicines, catalysts and acrylonitrile spinning. It is also used for spinning from C8 Extractive distillation solvent for fraction separation of styrene. In the petrochemical process, N, N-dimethylacetamide is a good catalyst. It can accelerate reactions such as cyclization, halogenation, cyanation, alkylation and dehydrogenation, and can increase the yield of the main product. . Currently, N,N-dimethylacetamide is widely used in medicine and pesticides to synthesize antibiotics and pesticides. As an aprotic polar solvent, N,N-dimethylacetamide is an excellent solvent for many organic synthesis reactions. At present, dimethylacetamide is mostly used in the country to produce polyimide films, soluble polyimides, polyimide-polyperfluoroethylene-propylene composite films, polyimide films, etc.
【Synthesis】[3][4]
1. Acetic anhydride method
The acetic anhydride method uses acetic anhydride and dimethylamine to react to produce dimethylacetamide. The process is to first heat the dimethylamine aqueous solution until it vaporizes. After the gaseous dimethylamine is dehydrated and purified, it is passed into acetic anhydride at room temperature to perform the acylation reaction. The reaction is an exothermic reaction. When the reaction temperature no longer rises, it is The end point of acylation is about 170℃. Then, control the acylation solution at 0-20°C, add alkali solution for neutralization, and react to generate sodium acetate. When the pH=8-9, sodium acetate is separated; then, after washing the neutralization solution with alkali, add ethyl acetate, Azeotropic dehydration; rough evaporation and then rectification, take the 164-166.5°C fraction to obtain the finished product dimethylacetamide. The production process of lt dimethylacetamide consumes 1.15-1.20t of acetic anhydride (about 95%) and 1.89-1.90t of dimethylamine (40%).
2. Acetyl chloride method
The acetyl chloride method uses the reaction of dimethylamine and acetyl chloride to prepare dimethylacetamide. It adopts advanced catalytic reaction and distillation technology to intensify the reaction, reduce energy consumption, and greatly improve the separation effect and product yield. The process is simplified, and compared with the current acetic anhydride method, the production cost is lower and the economic benefits are better. The process of this method is to first pass dimethylamine into diethyl ether in a cooling state, and then slowly add the mixture of acetyl chloride and diethyl ether, stirring while adding, and the white solid of dimethylamine hydrochloride will immediately precipitate. Strain it out. The filtrate is recovered in a water bath, dried and distilled, and the 164-166.5°C fraction is collected to obtain the finished product dimethylacetamide.
3. Acetic acid method
The acetic acid method uses acetic acid and dimethylamine to react to produce dimethylacetamide, including the catalytic condensation method and the high compression method. These two methods are also the main methods for the production of dimethylacetamide internationally. In the acetic acid production process, the yield of dimethylacetamide is not very high, and there is a large amount of acetic acid in the product. Since acetic acid can form a high boiling point azeotrope with dimethylacetamide (containing 84.9% dimethylacetamide and 15.1% acetic acid), the product after the reaction cannot be distilled and purified according to conventional methods and must be neutralized and purified. Refining can be completed only through a series of processes of filtration and distillation.
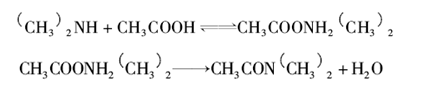
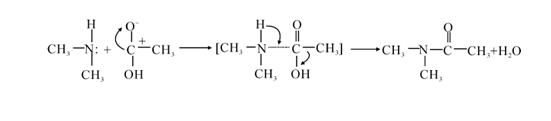
This reaction is an N-acylation reaction using acetic acid as the acylating agent. Acylation is an electrophilic substitution reaction that occurs on the N atom of the amine group. The acyl C atom in acetic acid has a partial positive charge, and the N atom in dimethylamine has an unshared electron pair. The two interact to form dimethylamine acetate, which is decomposed and dehydrated into an amide. . The reaction process is as follows:
1) Catalytic cultivation method: This method uses molybdenum oxide as a catalyst, which can increase the yield and appropriately shorten the reaction time, and accelerate the synthesis of dimethylacetamide. In addition to molybdenum oxide, commonly used catalysts include molybdenum silicate, tungsten trioxide, phosphotungstic acid, and sodium metavanadate. Compared with the high compression method, the reaction time of this method is not shortened sufficiently.
2) High compression method: This method prepares dimethylacetamide by reacting acetic acid and dimethylamine under pressure while removing the reaction water. The advantage of the high compression method is that the reaction time is greatly shortened, but the material of the pressure device used in this method must be acid-resistant, and the dehydration device must be connected to the pressure device. Therefore, compared with the catalytic condensation method, the equipment investment cost of this method is higher.
4. Other methods
1) Carbonylation method of trimethylamine and carbon monoxide: Foreign countries have developed a method of using pure trimethylamine and carbon monoxide to undergo a carbonylation reaction to synthesize dimethylacetamide through pressurized catalysis. The process of this method is simple, the raw materials are cheap and easily available, and its cost is much lower than that of existing production methods.Craftsmanship.
2) Ethyl acetate method: This method uses ethyl acetate and dimethylamine to react to produce dimethylacetamide. The yield of this method is 98%, and the reaction temperature is 30°C.
3) Reactive distillation method: Based on the catalytic condensation method in the acetic acid method, the process is improved and dimethylacetamide is directly synthesized using reactive distillation technology, so that the reaction heat can be utilized and the energy consumption during the reaction process can be reduced. Low. At the same time, because the reaction and distillation are in the same system, the process flow is greatly shortened. This process regulates reaction conditions and catalyst ratio. The average yield of dimethylacetamide can reach more than 95%, the product purity is greater than 98%, and the acetic acid conversion rate is close to 100%.
[Application][3][4]
Dimethylacetamide is widely used in petroleum processing and organic synthesis industries. It has good solubility in a variety of resins, especially polyurethane resin and polyimide resin. It is often used as an auxiliary for heat-resistant fibers, plastic films, coatings, medicines, catalysts and acrylonitrile spinning. It is also used from The C8 fraction is the extractive distillation solvent used to separate styrene. In the petrochemical process, dimethylacetamide is a good catalyst, which can accelerate reactions such as cyclization, halogenation, cyanation, alkylation and dehydrogenation, and can increase the yield of the main product. Currently, dimethylacetamide is widely used in medicine and pesticides to synthesize antibiotics and pesticides. As an aprotic polar solvent, dimethylacetamide is an excellent solvent for many organic synthesis reactions. At present, in China, dimethylacetamide is mostly used to produce polyimide films, soluble polyimides, polyimide-polyperfluoroethylene-propylene composite films, polyimide (aluminum) films, soluble polyimide films, etc. Amine molding powder YS-20, etc.
[Main reference materials]
[1] Zhang Yue; Liu Naiqing; Yan Shenghu; Han Tieliang; Shen Jiefa; Qu Shihong; Ma Jinguo; Liu Changqing; Sheng Guang; Liu Jianwu; Xiao Jianye; Lu Rihong; Wu Yongxiang. A method for synthesizing high-purity N, N-dimethylethane Method of amide. CN200610090011.9, application date 2006-06-23
[2] Sun Qiang; Wu Jianguo; Wan Haibing. A process for synthesizing N, N? dimethylacetamide. CN201710200756.4, application date 2017-03-30
[3] Xiao Jinping. Synthetic route and market prospects of N, N-dimethylacetamide [J]. Chinese and Foreign Medicine, 2006 (2): 28-29.
[4] Li Baichun, Fan Xiaoyan, Yang Ruiling, et al. Synthesis reaction kinetics of N, N-dimethylacetamide [J]. Chemical Engineering, 2015, 43(6): 51-54.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

