[Overview]
Calcium dobesilate (calcium dobesilate, trade names include Dobesilate, Dobesilate, Endoamine, Haochang, etc.), chemical name 2,5-dihydroxybenzenesulfonate calcium monohydrate. It is a vasodilator that selectively acts on capillary walls. It can not only adjust and improve the permeability and fragility of capillary walls, but also inhibit active substances such as bradykinin. It is mainly used to treat capillary diseases caused by various causes, such as diabetic retinopathy, varicose veins, phlebitis, Leg cramps, phlegm itching dermatitis and other symptoms. This product has high bioavailability, low toxicity and high therapeutic index, making it an ideal drug for the treatment of capillary diseases.
[Pharmacological effects]
1. Calcium dobesilate can inhibit the high permeability effect of vasoactive substances (histamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, bradykinin, hyaluronidase, prostaglandins) on microvessels, and reduce the damage to the intima of blood vessels. Improving the biosynthesis of basement membrane collagen also improves the permeability of capillary walls, increases the flexibility of red blood cells, reduces blood viscosity, and improves lymphatic return, thereby reducing the pathological hyperpermeability of capillary walls.
2. Calcium dobesilate can reduce the levels of fibrinogen and globulin, reduce the polymerization of red blood cells, activate fibrinoprotein activity, increase the dissolving ability of blood fibrin, thereby reducing blood viscosity. Reduces the synthesis and release of platelet aggregation factors, inhibits a variety of aggregation factors, causes aggregation reactions and spontaneous aggregation of platelets, reduces platelet activity, and prevents thrombosis. Its effect is dose-related.
3. For microvascular disease, calcium dobesilate can increase the diameter of arterioles and veins, increase the number of open capillaries, significantly accelerate blood flow, and significantly improve microcirculation. Eliminate or relieve edema, capillary bleeding, heaviness and pressure in the lower limbs.
4. Calcium dobesilate can significantly reduce the content of sorbitol, block the channel of sugar to sorbitol, and inhibit dysfunction caused by the increase of sorbitol in blood cells.
[Pharmacokinetics]
After oral administration of 500 mg of calcium dobesilate, the blood concentration level was above 6 μg/ml between the 3rd and 10th hours, and the blood concentration (Cmax) reached the maximum value after 6 hours (Tmax). Average 8μg/ml. The plasma concentration 24 hours after administration is approximately 3 μg/ml. The protein binding rate is 20% to 25%. Found in trace amounts in breast milk. Calcium dobesilate does not enter the enterohepatic circulation and is mainly excreted unchanged, with only 10% excreted as metabolites. Within 24 hours after administration, approximately 50% of the oral dose is excreted in the urine and approximately 50% is excreted in the feces. The plasma half-life is about 5 hours.
[Preparation method]
Add hydroquinone (22g, 0.2mol) and 150ml of 1,2-dichloroethane into the three-necked flask and stir for about 20 minutes. Add dropwise 70 ml of 1,2-dichloroethane containing 0.5 mol of sulfuric acid. Continue stirring at room temperature for 2 hours, then raise the temperature to about 80°C and stir for 2 hours. After cooling, remove the solvent by pouring, and then wash the sticky substance with a small amount of 1,2-dichloroethane. Dissolve this sticky substance with ethanol and water (4:1), and add slightly more than the calculated amount of powdered CaCO3 in batches with stirring at about 50°C to make the pH of the solution 2.6-4.0. After adding CaCO3, if the pH is less than 2.5, add more to bring the pH to above 2.5, and continue stirring for 0.5-lh. Filter, and the filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure below 50°C to about 1/5 of the original volume, then cooled to below 5°C, and the filtered solid is washed with toluene-ethanol (2:1) to obtain 35g of crude product. Dissolve the crude product in as little hot water as possible (about 15 ml), filter out if there is any solid, and place the filtrate below 6°C for 3 hours. Filter, wash with toluene-ethanol (2:1), and dry below 60°C for 3 hours. A white (turns into reddish after standing) solid (1) was obtained, weighing 32.5g, and the yield was 56%.
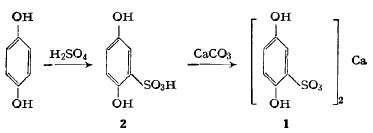
Figure 1 shows the synthesis route of calcium dobesilate
【Clinical Application】
1. Application of calcium dobesilate in the treatment of diabetic complications
(1) Calcium dobesilate treats diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy and long-term abnormalities in sugar, protein, and fat metabolism lead to high capillary permeability, high blood viscosity, and high platelet activity, causing retinal blood vessels to It is related to increased permeability, causing complications such as increased retinal exudation, retinal tissue ischemia and hypoxia, and retinal neovascularization. Calcium dobesilate can improve microcirculation, reduce capillary permeability, reduce blood viscosity, and reduce platelet activity. Therefore, the application of calcium dobesilate in the treatment of diabetic retinopathy has achieved good therapeutic effects. Studies have shown that it can significantly improve and stabilize diabetic retinopathy fundus lesions, with a total effective rate of 95.24%, especially for simple stage I and II lesions.
(2) The application of calcium dobesilate in the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Calcium dobesilate can change the hemodynamics in the kidneys under diabetes, dilate the contracted glomerular afferent and efferent arterioles, and reduce Calcium dobesilate, an inflammatory transmitter and extracellular matrix produced by diabetic nephropathy, can reduce vascular endothelial damage and apoptosis, reduce the shedding of endothelial cells, inhibit the synthesis of basement membrane collagen, and prevent the proliferation of capillary basement membrane. Thick, reduce glomerulosclerosis and kidney damage caused by early diabetes, and achieve a protective effect on the kidneys. Calcium dobesilate reduces proteinuria, increases serum albumin concentration, and reduces elevated…�The levels of inflammatory markers play an important role in improving the inflammatory status of patients with diabetic nephropathy. Calcium dobesilate can reduce urinary protein in patients with diabetic nephropathy.
(3) Calcium dobesilate treats diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Calcium dobesilate capsules inhibit vasoactive substances, reduce microvascular permeability, reduce vascular intimal damage, improve basement membrane collagen biosynthesis, and improve Lymph returns, reduces edema, inhibits dysfunction caused by the increase in sorbitol in blood cells, inhibits the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle and relaxes microvessels, thereby improving nerve ischemia and hypoxia.
(4) Treatment of diabetic skin ulcers Calcium dobesilate can significantly improve the local microcirculation disorder of skin ulcers, eliminate edema, and accelerate the repair and healing of ulcer epidermis and subcutaneous tissue. Calcium dobesilate is a safe and effective drug for treating diabetic skin ulcers.
(5) Treatment of diabetic erectile dysfunction Calcium dobesilate improves microcirculation disorders in diabetic patients through various ways. Reduces superoxide anions and hydroxyl free radicals produced by the xanthine/xanthine oxidase system. It also inhibits the excessive release of endothelin, promotes the restoration of endothelial function, thereby dilating blood vessels, and increases blood flow to treat diabetic erectile dysfunction.
(6) Calcium dobesilate can inhibit the development of atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes. Calcium dobesilate intervention can slow down the thickening of carotid artery intima-media thickness and significantly reduce plasma fibrinogen. Studies have shown that calcium dobesilate can significantly reduce capillary permeability, blood viscosity and platelet activity, and improve abnormal blood rheology and microcirculation status. It can reduce the synthesis and release of platelet aggregation factors, reduce capillary endothelial damage and the synthesis of platelet activating factors, inhibit vasoactive substances, reduce plasma fibrinogen levels, reduce platelet activity, and inhibit thrombosis.
2. Clinical application of calcium dobesilate in non-diabetic patients
(1) Calcium dobesilate has achieved significant efficacy in treating angina pectoris due to coronary heart disease in the elderly. Calcium dobesilate can reduce platelet activity, significantly reduce capillary permeability, and reduce fibrin. The original level and the high polymerization of red blood cells can increase the dissolving ability of blood fibrinoprotein, reduce blood viscosity, improve abnormal blood rheology and microcirculation status, and can effectively relieve vasospasm; reduce the dosage of nitroglycerin; improve blood Sticky state; improve myocardial blood supply, thereby preventing further aggravation of angina pectoris and improving the quality of life of elderly patients with coronary heart disease.
(2) The use of calcium dobesilate in the treatment of non-diabetic nephropathy in the treatment of chronic renal insufficiency has achieved good results. Serum creatinine and urea nitrogen have significantly decreased, and urinary creatinine has increased significantly. Patients in the uremic stage have the largest decrease in serum creatinine. , reaching 37.88%.
(3) Calcium dobesilate used to treat chilblains can inhibit the synthesis of vasoactive substances such as histamine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, and bradykinin and antagonize their effects, reducing the high permeability of capillaries. ; Reduce the level of macromolecular plasma proteins, thereby reducing blood viscosity and improving microcirculation; improving lymphatic return and eliminating tissue edema; reducing macrophage adhesion and anti-inflammatory effects to treat frozen blisters. Calcium dobesilate can significantly improve the local microcirculation disorder of chilblains, prevent and reduce hypoxic damage to tissues, reduce local tissue edema and inflammation, thereby accelerating its repair and healing.
【Adverse reactions】
The side effects of calcium dobesilate are very rare. The main adverse reactions are fever (26%), gastrointestinal discomfort (12.5%), skin reactions (8.2%), joint pain (4.3%) and agranulocytosis. (4.3%), no deaths were reported.
[Main reference materials]
[1] Yang Wenbo, Wang Hongyan. Pharmacological effects and clinical application of calcium dobesilate [J]. Modern Medicine and Health, 2012, 28(07):1043-1044.
[2]Jiang Fengchao, Zhou Xiao. Synthesis of calcium dobesilate[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Industry, 1994(09):389-390.
[3] Chen Xinghua, Duan Guisheng. Progress in clinical application of calcium dobesilate[J]. Journal of Practical Medicine, 2007(04):593-595.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

