Basic information 【1】
Benzoyl peroxide is also known as diphenyl peroxide, and its molecular formula is C14H10O4. , the relative molecular mass is 242.23. The structural formula is shown in the figure below.
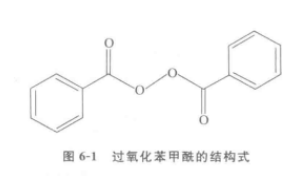
Benzoyl peroxide is a white or light yellow powdery solid or white crystal with a slight odor of benzaldehyde and almond. Insoluble in water, hardly soluble in ethanol, soluble in benzene, ether, acetone and chloroform, etc. It decomposes slowly in alkaline solution and is stable at room temperature. It may explode due to impact, friction or heating in a dry state. It is a highly reactive oxidant that is irritating to skin and mucous membranes and can be reduced to benzoic acid. The melting point is 103~106% (it decomposes and can cause explosions), and can explode due to heating and impact.
Category: Therapeutics. Antibacterial agents. Pregnancy classification.
Indications and dosage: Used for acne vulgaris, boils, prickly heat, various ulcers and bedsores, etc. Apply 2.5%, 5% or 10% lotion, cream or gel to the affected area.
Mechanism of action
It is a benzoic acid derivative and has broad-spectrum antibacterial effects, especially against anaerobic bacterial infections. For external use in the treatment of acne vulgaris, it can penetrate acne and release ecological oxygen. Destroys acnes bacteria and inhibits free fatty acid formation. It has a synergistic effect when combined with vitamin A acid. It also has the effect of inhibiting Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, and Candida. It also promotes cell repair and wound healing on traumatic skin and ulcer wounds.
Used as flour whitening agent
Benzoyl peroxide was once used as a flour whitener in the food industry. It releases active oxygen under the action of moisture and enzymes in the flour. The conjugated double bond structure of the pigment in the flour is oxidized and destroyed, causing it to fade and turn the flour white. Benzoyl peroxide can bleach flour as quickly as 24 hours. The highest bleaching value is reached in 2 weeks, and the benzoic acid produced at the same time has anti-mildew and other effects on flour. The oxidation of benzoyl peroxide can oxidize the SH group of protein in flour to S-S group, which is beneficial to the formation of protein network structure, thus improving the taste of new wheat flour products and significantly improving the after-ripening of wheat. The flour maturation period is shortened from 2 months to 2 to 3 days. Benzoyl peroxide can also inhibit the action of proteolytic enzymes in wheat flour, enhance dough elasticity, extensibility, and air-holding properties, improve dough texture, thereby improving the quality of baking; it can make wheat process the same grade of flour. The powder extraction rate is increased. Adding benzoyl peroxide to flour at 0.06 g/kg can generally increase the whiteness of flour by 3 to 4 U and increase the flour extraction rate by 3% to 5%. However, benzoyl peroxide can also damage vitamin A, vitamin E, and vitamin B1.
Dispute【2】
Benzoyl peroxide is a permitted wheat flour bleaching agent and treatment agent. It can slowly oxidize the lutein and carotene in the flour, oxidizing the double bonds of the carotenoid and other pigments and turning it colorless. The flour changes from the original slightly yellow to snow white, while the original content of the flour The wheat flavor will disappear. It has a strong destructive effect on B-carotene and vitamins A, E, B, etc. contained in flour. Therefore, although flour whiteners have been commonly used in China for more than two decades, the debate continues. Both those who insist on prohibiting the ban and those who insist on using it argue vigorously. The banned party believes that benzoyl peroxide, benzoic acid, phenol, etc. are decomposed in flour. Detoxification occurs in the liver, and long-term consumption of flour containing self-enhancing agents can cause chronic poisoning. Cause neurasthenia, dizziness and fatigue. It also destroys micronutrients such as folic acid in flour, causing harm to the human body. Opponents of the ban believe that my country’s food hygiene standards stipulate that the maximum dosage of benzoyl peroxide in flour is 60 mg/kg, and use according to the standards will not cause harm to human health.
On March 1, 2011, six departments including the Ministry of Health and the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued an announcement requiring that starting from May 1, 2011, it is prohibited to add food additives benzoyl peroxide and calcium peroxide in flour production; food additives Manufacturing enterprises are not allowed to produce and sell benzoyl peroxide and calcium peroxide; the food standards that allow the addition of benzoyl peroxide and calcium peroxide to flour (wheat flour) will be abolished on their own. At this point, the debate over whether whitening agents should be added to flour has come to an end.
Toxicity【3】
The oral LD50 of benzoyl peroxide in mice is 3590 mg/kg body weight, the oral LD50 in rats is 7710 mg/kg body weight, and the ADI is 0~40 mg/kg body weight. After benzoyl peroxide is hydrolyzed in flour and enters the human body with food, 90% of it can be combined with glycine to form hippuric acid and excreted in the urine; part of it can be combined with glucuronic acid to form l-benzoylglucuronic acid. The toxicity is greatly reduced. Since benzoyl peroxide needs to be metabolized in the liver after entering the human body, if a large amount enters with flour, it will increase the burden on the liver. There is no “three causes” effect.
At present, the FAO/WHO United Nations Food Regulation Committee allows the use of benzoyl peroxide in flour, and the United States, Canada, Australia, New Zealand and other countries also allow it. Since May 1, 2011, my country has banned the production and addition of benzoyl peroxide and calcium peroxide to flour.
Purification of benzoyl peroxide【4】
Benzoyl peroxide is purified using�Crystalization method usually uses chloroform as the solvent and methanol as the precipitant for refining. Benzoyl peroxide can only be dissolved in chloroform at room temperature.
Caution: Explosive when heated.
The solubility of benzoyl peroxide in different solvents is shown in the table below (under 20°C conditions).

Add 59 mL benzoyl peroxide and 20 mL chloroform into a 100 mL beaker, stir continuously to dissolve, filter, and drop the filtrate directly into 50 mL methanol cooled with ice salt, then filter the needle crystals and use cold methanol Wash and drain. After repeated recrystallization twice, the crystallized product was dried in a vacuum desiccator and weighed. Product is placed in brown bottles and stored in a desiccator.
Methanol is toxic and can be replaced by ethanol. Acetone and ether can induce the decomposition of benzoyl peroxide, so they are not suitable as solvents for recrystallization. During recrystallization, benzoyl peroxide is generally dissolved at room temperature. Dissolution at high temperatures may cause an explosion, so special attention is required.
Security
The daily allowable intake of human body is 0-40 mg/kg (40-75 mg/kg under special conditions).
Notes【5】
1. Pregnant women, lactating women, and children should use with caution.
2. If adverse reactions occur, the drug should be stopped first and treatment should be resumed after symptoms subside.
3. This product is for external use only and should not be used around the eyes or on mucous membranes. 4. This drug is a strong oxidant, and its simultaneous use with topical retinoic acid drugs will reduce the potency of retinoic acid drugs.
5. Some patients may experience local redness and itching after applying the medicine. Disappears after discontinuation of medication.
6. Avoid contact with mucous membranes.
7. People who are allergic to this product are prohibited from taking this product.
References
[1] Huang Jun, edited by Huang Zuhu, Clinical handbook of drugs 5th edition, Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2015.01, page 1731
[2] Editor-in-Chief Zhu Hongfa, Living Chemicals and Health, Golden Shield Publishing House, 2013.04, page 131
[3] Ding Xiaowen, editor-in-chief Liu Chunhong, Food Safety 2nd Edition, China Agricultural University Press, 2016.09, page 137
[4] Liu Changsheng, editor-in-chief Yu Xianghua, Comprehensive Experimental Tutorial on Polymer Chemistry and Polymer Physics, China University of Geosciences Press, 2008.11, page 91
[5] Zhao Xuyuan, Li Bo, Zeng Linggui, editors-in-chief, Pharmacist Tips in Drug Treatment, Hunan Science and Technology Press, 2006.12, page 944

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

