Synthesis method【1】
Diphenylmethane diisocyanate, MDI, generally has three isomers:
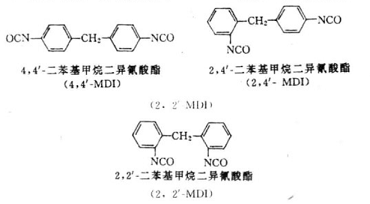
Diphenylmethane diisocyanate is mainly used in polyurethane resins as 4,41-MDI. The synthesis process is divided into two steps: condensation of diamine (i.e., diphenylmethanediamine) and phosgenation reaction of diamine.
1. Condensation of diphenylmethanediamine
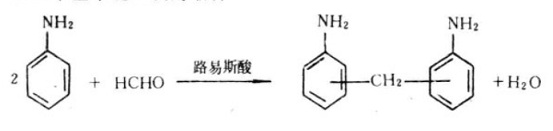
There are two phenomena in the condensation reaction of aniline and formaldehyde. The first phenomenon is that the primary amine on aniline directly condenses and dehydrates with formaldehyde to form methine:
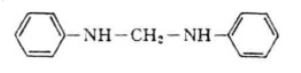
The second phenomenon is that the hydrogen atoms on the benzene nucleus of aniline condense with formaldehyde to form methine. With different reaction conditions, that is, catalyst type, properties, reaction temperature, stirring conditions, etc., the proportions of the above two reaction intermediates are also inconsistent. Generally, the hydrogen atoms on the amine group are more active and can easily condense with formaldehyde at low temperatures. Therefore, after the condensation reaction, the temperature still needs to be raised to carry out molecular translocation and rearrangement. At the same time, the diamine compound prepared with the change of raw material ratio contains a certain amount of low polymer. That is, three-polymerization, four-polymerization and other condensates.
It is a compound with a high amount of synthesized diamine. In industry, Lewis acids are mostly used as catalysts, usually hydrochloric acid. The condensation temperature is controlled at 50-80°C, the translocation rearrangement temperature is controlled at 90-150°C, and the molar ratio of aniline to formaldehyde is controlled within the range of 2-3. The weight ratio of aniline and water is adjusted to 1 to 6.
The intermittent preparation process of diamine: Aniline reacts with 25-35% hydrochloric acid to first generate an aniline hydrochloride solution, then dropwise add about 37% formaldehyde aqueous solution, conduct a condensation reaction at 80°C for 1-2 hours, and then at 100°C The left and right transposition rearrangement is carried out for 1 hour, and then neutralized with caustic soda aqueous solution to make the neutralized product alkaline. Separate the layers and wash with water until neutral. The oil layer is then steam distilled or vacuum distilled to remove trace amounts of water and residual aniline to obtain a polyfunctional diamine mixture containing a certain amount.
The reaction between aniline and hydrochloric acid to produce aniline hydrochloride is an exothermic reaction, and the heat of reaction is -49.4Kj/mol HCL. The condensation reaction is also an exothermic reaction, and its heat of reaction is 155.7kj/mol formaldehyde.
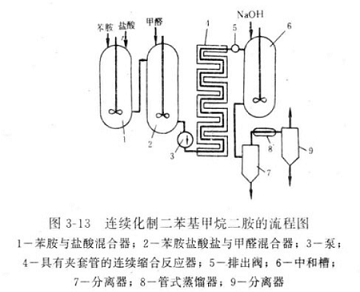
Diamine continuous production process, the flow chart is as follows. It can be seen from the figure that the raw material aniline and the catalyst hydrochloric acid enter the mixer l in proportion. Aniline hydrochloride is generated, and then formaldehyde aqueous solution is added to the mixer 2 at 60-80°C, and pumped into the continuous condensation reactor 4 through the pump 3. The temperature is maintained at 110-150°C, the reaction time is 15s-5min, and the pressure is 70KPa· S. The reaction material is input into the neutralization tank 6 from the discharge valve 5, and then neutralized with caustic soda aqueous solution, and the salt aqueous solution is separated through the separator 7. Then, the reaction crude product passes through the tubular distiller 8 and the separator 9 to separate trace amounts of water and aniline, and the remaining part is the crude diphenylmethanediamine (MDA).
2. Phosgenation of diphenylmethanediamine
In the process of synthesizing 4,4/-diphenylmethanediamine from diphenylmethane diisocyanate, there is still a by-product of 2,4/-diamine. Phenylmethanediamine and some oligomers.
The amount of these by-products depends on the synthesis conditions and raw material ratio. Generally, when preparing 4,4 /-MDI, diamine compounds can be directly used in the phosgenation reaction without prior purification and separation. Refined 4,4/-MDI is produced by vacuum distillation under reduced pressure after phosgenation. If part of the MDI fine product and part of the isocyanate containing multifunctionality are separated by vacuum distillation; that is, the method in which two products can be obtained by one distillation is called the co-production method.
The principle and process of phosgenation of amine compounds have been described in the previous section. Here are just examples. The phosgenation of diphenylmethanediamine is divided into two steps: low-temperature reaction and high-temperature reaction. The main reactions in the low-temperature reaction section are as follows.
Diamine reacts with phosgene to form carbamoyl chloride
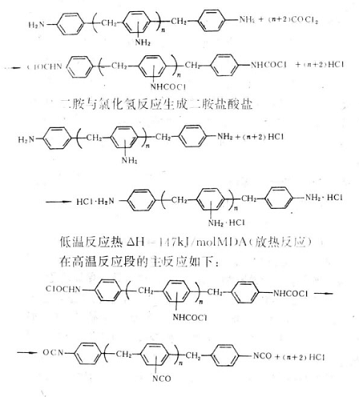
High temperature reaction heat AH=147kJ/molMDA (endothermic reaction)
Dissolve 200 parts of diamine compounds in 1200 parts of chlorobenzene to form an amine chlorobenzene solution. Then slowly add it dropwise into the phosgene-chlorobenzene solution composed of 350 parts of phosgene and 1900 parts of chlorobenzene in the temperature range of 20 to 50°C. The slurry reaction material formed under stirring was gradually heated up. The temperature rose to 110 C within 2 hours. While the temperature is rising, phosgene is supplied until the solid in the reaction mass disappears. A total of about 650 parts of phosgene is required. Then the actinic liquid is heated and bubbled with inert gas, N2 or methane, etc. to analyze the remaining HCl and phosgene in the material. After phosgene and HCl are driven out, the semi-finished product is distilled under vacuum and reduced pressure, and the solvent and a small amount of low boiling matter (such as benzene isocyanate, etc.) are removed to obtain crude MDI.
To refine MDI products, the above crude products also need to be separated and purified by high vacuum distillation. The relationship between the boiling point of MDI and the degree of vacuum is as follows:
160℃/0.1kPa·s; 180℃/O. 36kPa·S
190℃/8kPa·S; 200℃/1.07kPa·S
During the process of distilling MDI, the temperature in the kettle must be strictly controlled not to exceed 250°C, otherwise it will cause isocyanate formation.The substance decomposes at high temperature, leading to the risk of explosion.
As a fiber-grade Jingyi MDI product, its acidity and hydrolyzed chlorine content are required to be very low. At the same time, in order to ensure safety and increase product yield, before high vacuum distillation, it is necessary to add acidity, hydrolytic chlorine treatment agent (copper acetylacetonate, iron dioxide, etc.) and heat stabilizer (2.6-di-tert-butyl 4 Monomethylphenol). The dosage is about 0.1% respectively.
During the storage process, high-quality MDI will also form insoluble substances such as dimers, and the product color will become darker and its performance will decrease, etc., which will seriously affect the physical properties of polyurethane products. For this reason, storage stabilizers such as triphenyl phosphate, tosyl isocyanate or carbonyl isocyanate compounds need to be added before the finished product is packaged.
Production
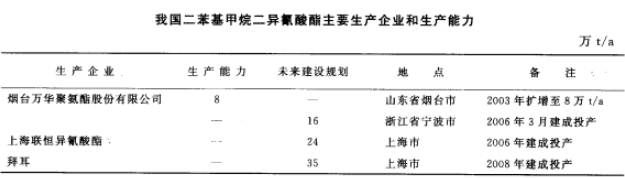
my country’s diphenylmethane diisocyanate (MDI) industry has made great progress in recent years. Yantai Wanhua Polyurethane Co., Ltd. and Qingdao Institute of Chemical Technology jointly researched MDI manufacturing technology and successfully developed a production capacity of 15,000 t/a, 20,000 t/a and 40,000 t/a MDI manufacturing technology, and has mastered MDI core manufacturing technology with a production capacity of more than 80,000 t/a, making my country the fourth country after Germany, the United States and Japan. A country with independent intellectual property rights for MDI manufacturing technology. The production scale will first reach 40,000 t/a, producing five series of 19 brands of MDI products. In 2002, Yantai Wanhua Polyurethane Co., Ltd. expanded its MDI plant production capacity to 60,000 t/a, and in 2003 to 80,000 t/a.
The development goal of Yantai Wanhua Polyurethane Co., Ltd. is to become an enterprise with comprehensive international competitiveness. It has built a world-scale 160,000 t/a MDI device in Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province. It is the first in the world to expand its total production capacity to 24 An enterprise with 10,000 t/a. Yantai Wanhua Polyurethane Co., Ltd. mainly produces a series of isocyanate products based on MDI. Currently, its annual sales revenue and profits are increasing at a rate of more than 50%. In 2005, the company’s MDI output reached 103,000 tons, and its main product sales accounted for 103,000 tons. Domestic market share exceeds 30%. The 160,000 t/a MDI device built by Yantai Wanhua Polyurethane Co., Ltd. in Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province started construction in August 2003 and was successfully put into operation in Daxie Island, Ningbo City in early March 2006. This move marks the end of my country’s long-term reliance on imports of MDI. The scale of this device has become the largest of its kind in Asia, and Yantai Wanhua Polyurethane Co., Ltd. has subsequently become the largest MDI manufacturer in Asia and the fifth largest in the world.
Consumption【2】
In recent years, the average annual growth rate of my country’s MDI demand has been more than 18%. In 2003, my country surpassed Germany and became the world’s second largest MDI demand country. The United States, which ranks first, has an annual demand of 950,000 to 1 million tons. . At present, there is only one enterprise that produces large-scale MDI in my country, Yantai Wanhua Polyurethane Co., Ltd. From 2003 to 2005, the actual output of MDI products exceeded 80,000 tons, but the actual import volumes were respectively 105,000 tons and 12.1 tons. 10,000 tons and 134,000 tons. In 2003, 2004 and 2005, my country’s MDI consumption was approximately 250,000 tons, 290,000 tons and 360,000 tons. my country’s annual imported MDI accounts for about 80% of the total demand. The products produced by BASF from its MDI production facility in Yeosu, South Korea are mainly supplied to the Chinese market.
References
[1] Edited by Fang Yusheng and Zhu Lumin, Polyurethane Foam 2nd Edition, Chemical Industry Press, 1994.08, page 139
[2] “China Chemical Industry Yearbook” Editorial Department Editor, China Chemical Industry Yearbook Volume 23 Volume 1 2007, China Chemical Industry Information Center, page 153

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

