Overview[1]
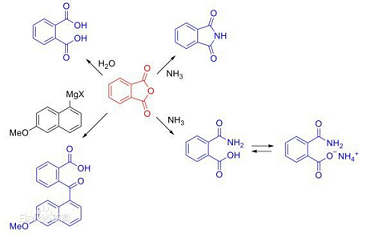
Phthalic anhydride, referred to as phthalic anhydride, phthalic anhydride, 1,3-isobenzofurandione, English name: o-Phthalic anhydride, English alias: 2,5-Isobenzofurandione; Phthalic anhydride 99+%; 2 -benzofuran-1,3-dione; 2,2′-(oxydicarbonyl)dibenzoic acid, molecular formula: C8H4O3, Abbreviation: PA. It is a cyclic anhydride formed by intramolecular dehydration of phthalic acid. It is a white powder or scaly crystalline solid with a specific gravity of 1.527 (4℃). The flash point of pure phthalic anhydride is 152℃, the melting point is 130.8℃, and the boiling point is 284.5℃; easy Sublime, slightly soluble in cold water, hydrolyzed into phthalic acid in hot water, easily soluble in ethanol, benzene and pyridine, slightly soluble in ether; this product has moderate toxicity and can cause asthma: there are reports that long-term inhalation can cause It can cause damage to the reproductive, nervous, liver and kidney systems, and is also irritating to the skin, mucous membranes, especially the cornea. Pay attention to protection when coming into contact with this product to ensure personal safety.
Phthalic anhydride is a white solid and an important raw material in the chemical industry, especially used in the manufacture of plasticizers. Dibutyl phthalate and dioctyl phthalate are important plasticizers. Phthalic anhydride is condensed with polyols (such as glycerin and pentaerythritol) to produce polyarylate resin, which is used in the paint industry; if it is condensed with ethylene glycol and unsaturated acids, it is condensed to produce unsaturated polyester resin, which can be used to manufacture insulating paint and glass. Fiber reinforced plastic. Phthalic anhydride is also a raw material for the synthesis of benzoic acid and terephthalic acid, and is also used in drug synthesis. Phthalic anhydride can undergo hydrolysis, alcoholysis and aminolysis reactions, and can react with aromatic hydrocarbons to synthesize anthraquinone derivatives. Phthalic anhydride is industrially produced by gas phase oxidation of naphthalene and air at 350-360°C under the catalysis of vanadium pentoxide. It can also be produced by oxidizing o-xylene with air.
Chemical properties
Phthalic anhydride can undergo hydrolysis, alcoholysis and aminolysis reactions, and can synthesize anthraquinone derivatives by reacting with aromatic hydrocarbons. Phthalic anhydride is industrially produced by gas phase oxidation of naphthalene and air at 350-360°C under the catalysis of vanadium pentoxide. It can also be produced by oxidizing o-xylene with air. Phthalic anhydride can be used instead of phthalic acid and mainly reacts with monohydric alcohols to form esters, such as dibutyl phthalate and dioctyl phthalate.
Preparation method[2]
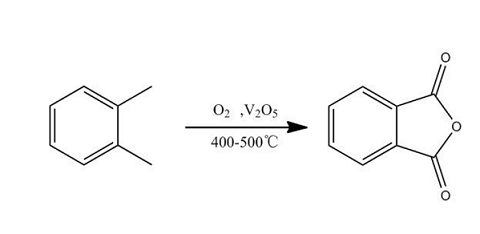
There are two process routes for the production of phthalic anhydride: o-benzene oxidation method and naphthalene oxidation method.
O-xylene oxidation method: The main reaction is as shown in the figure. In addition, benzoic acid, maleic anhydride, etc. are also generated from side reactions. This reaction is a strongly exothermic reaction, so selecting an appropriate catalyst (high activity and selectivity) and removing the reaction heat to inhibit the deep oxidation reaction are the keys to the industrial process. From this a number of different production methods were developed. The industrial production method generally uses vanadium-based catalysts (see metal oxide catalysts) based on vanadium pentoxide for gas-phase oxidation of o-xylene. In 1974, a vanadium-based catalyst with a high load surface coating was developed. The catalyst carrier was inert non-porous porcelain balls, corundum balls, silicon carbide balls, etc. A cyclic carrier is used to prepare the catalyst. This new catalyst can reduce the deep oxidation reaction caused by internal diffusion, thereby improving the yield, selectivity and catalyst load of phthalic anhydride. The reactor mostly uses a tubular fixed bed.
The typical process is to compress and preheat the filtered dust-free air, mix it with the gasified o-xylene vapor, and then enter the reactor to perform an oxidation reaction at 400~460°C. The feed space velocity is 2000~ 3000h-1, the o-xylene concentration in the air is 40~60g/m3 (standard), and the reaction heat is taken out by the molten salt circulating outside the tube. The reaction product enters the steam generator, and the cooled reaction gas is further cooled to recover crude phthalic anhydride. The tail gas is washed with water to recover maleic anhydride and then vented, or purified by catalytic combustion and then vented. The crude phthalic anhydride is distilled under reduced pressure to separate low-boiling maleic anhydride, methylmaleic anhydride and benzoic acid from the top of the tower; the material at the bottom of the tower is vacuum distilled to obtain the phthalic anhydride product.
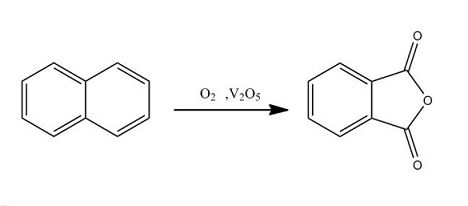
Naphthalene oxidation method: The naphthalene oxidation reaction occurs at the α position. Under moderate conditions, naphthalene is oxidized to form quinone. Under severe conditions, naphthalene is oxidized to form phthalic anhydride. Side reactions generate naphthoquinone, maleic anhydride, etc. The catalyst used is also a vanadium-based catalyst. The process is similar to o-xylene oxidation. There are two types of reactors for naphthalene oxidation: tubular fixed bed and fluidized bed. The heat of reaction in the fluidized bed reactor is removed by cooling tubes in the reactor. The particle size of the fluidized bed catalyst requires a suitable range, usually 40 to 300 μm. The advantages of using a fluidized bed are that the reactor can operate at a relatively uniform temperature and a high raw material-to-air ratio, and the product is easier to capture.
Fluidized bed process: First, use steam to melt naphthalene into a liquid, then use a pump to pump it into the bottom of the oxidation furnace containing 0402 catalyst (V-K-Si series), and raise the temperature to 320~340°C, and the naphthalene will be vaporized and distribute it to the entire bed. The filtered and purified air is sent to the bottom of the reactor by a blower at a rate of 6000m3/h to ensure that the catalyst is in a fluidized state, and the naphthalene is at 360~ It is oxidized by air to generate phthalic anhydride gas within the temperature range of 385°C. The air mixture containing phthalic anhydride gas is cooled by the condenser/hot melt condenser, and the liquid enters the crude phthalic anhydride storage tank. The obtained crude phthalic anhydride is heated in the distillation tower, treated with sulfuric acid, and treated with sodium carbonate. ChineseFinally, the pure phthalic anhydride product is obtained through vacuum distillation, condensation, phase separation, crystallization and tableting, with a content of ≥99.7%.
Purpose
1. Phthalic anhydride is one of the most important organic chemical raw materials. Its main derivatives include dibutyl phthalate; dioctyl ester and diisobutyl ester, etc., which are used as plasticizers for PVC; they can also be used It is used in the production of unsaturated polyester resins; alkyd resins; dyes and pigments; a variety of paints; food additives; phenolphthalein, a laxative in medicine; phosmetin in pesticides; bentazone and saccharin sodium, etc.
2. This product is used as epoxy resin curing agent. This product is an important organic chemical raw material, mainly used in the production of phthalate plasticizers, coatings, saccharin, dyes and important intermediates of organic compounds, pesticides, fungicides, rubber processing aids, and photosensitive materials wait.
3. Used as analytical reagent. Organic synthesis intermediates. In the dye industry, it is used to prepare important intermediates such as anthraquinone, 2-chloroanthraquinone, and 1,4-dihydroxyanthraquinone, and dyes such as phthalocyanine blue BS, phthalocyanine blue BX, and phthalocyanine blue B.
4. Used as a curing agent for epoxy resin, the reference dosage is 30 to 50 parts by mass, and the pot life of 100g of resin complex is rt/6h, 120℃/1.5h. Curing conditions: 100/2h+150℃/5h or 100℃/12h, 140℃/8h, 200℃/6h. It generates little heat during curing, and the cured product has good electrical properties and mechanical strength, with a heat distortion temperature of 110 to 152°C.
5. It is an important organic chemical raw material. In the synthetic resin industry, it is used to produce polyester resin, amino resin, unsaturated polyester resin, alkyd resin, etc. In the dye industry, it is used to prepare dye intermediates such as anthraquinone and chloroanthracene dihydroxyanthraquinone and dyes such as phthalocyanine blue BS, phthalocyanine blue BX, and phthalocyanine blue B. It is used in the plastics industry to prepare plasticizers such as dibutyl phthalate, dioctyl phthalate and their mixed esters. It is also an important intermediate in the manufacture of various drugs, paints and organic compounds.
6. Used in the manufacture of plasticizers, dibutyl phthalate, resins and dyes, etc.
References
[1] Wang Yanguang, Lu Ping, Zhang Shujia, Wu Jun. Organic Chemistry. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008
[2] Zhang Quanying, Ding Min, Wu Fanning, et al. Production and industrial status of phthalic anhydride [J]. Contemporary Chemical Engineering Research, 2005(10):8-11+7.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

