Background and overview[1][2]
Diphenylmethane, commonly known as artificial geranium oil. The reaction process of industrial catalytic synthesis of diphenylmethane mainly uses liquid acid or Lewis acid as catalyst, such as sulfuric acid, hydrofluoric acid, aluminum trichloride or zinc chloride, etc. However, the use of these catalysts has complicated operations and low selectivity. , corrosiveness, toxicity and other problems, and cannot meet the requirements of environmental protection. In response to the above problems, researchers have developed solid acid catalysts for the synthesis of diphenylmethane. They mainly include supported metal chlorides, zeolite molecular sieves, solid super acids, etc. These catalysts have certain effects on the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction of benzene and benzyl chloride. The catalytic activity can also avoid problems such as equipment corrosion. However, most of these catalysts require the conversion rate of benzyl chloride to reach more than 90%, the reaction time exceeds 2 h, and the utilization efficiency of benzene is low.
In recent years, some supported solid acid catalysts reported at home and abroad have shown excellent catalytic performance in Friedel-Crafts alkylation reactions. A new solid-supported AlCl3 catalyst was developed and used in low-degree polymerization of isobutylene, benzene and Conducted research on reactions such as long-chain olefin alkylation and α-olefin polymerization, and found that the solid-supported AlCl3 catalyst can not only maintain the characteristics of traditional AlCl3 catalysts with high activity and low reaction temperature, but also has good selectivity, reproducibility, and ease of use. Product separation and other advantages.
Since the solid acid catalyst required for alkylation reaction should have appropriate acidity and pore structure, people have done more research on how to prepare the required solid acid catalytic material, but less research on reaction kinetics. At the same time, because solid acid catalysts mostly use microporous materials, the molecular sizes of reactants and products are relatively large, which easily generates internal diffusion resistance in the catalyst pores during the reaction process. Through the study of reaction kinetics, it can be found that the effects on alkylation Some factors of the reaction and understanding the characteristics of the catalyst can provide certain guidance for the further development of the catalyst. Therefore, it is of great practical significance and economic value to find new catalytic systems to catalyze the synthesis of diphenylmethane.
Properties[3]
Diphenylmethane is a white oblique needle-shaped crystal with an orange aroma. It is insoluble in water and liquid ammonia and soluble in ethanol, ether, chloroform, benzene and cyclohexane. Relative density (d104) 1.3421 (solid), melting point 25.9°C, boiling point 264.5°C, flash point 130°C, refractive index 1.576~1.578. Minimum lethal dose (rat, oral) 5000mg/kg.
Apply[1][2]
Diphenylmethane is usually used in the fragrance industry. It is an important raw material for manufacturing fragrance preservation agents, soaps and perfume essences. It is also an important intermediate for the production of dyes and medicines. It is used in the pharmaceutical industry to produce diphenhydramine hydrochloride. Diphenylmethane can be used as a substitute for geranium oil and is suitable for preparing soap essences and perfumes. Also used in dye production. Its derivatives such as diphenyl halomethane can be used in the synthesis of drugs such as paclixin, cinnarizine, and oxamid.
Preparation[5][1][4]
Method 1: The specific process of alkylation of benzene and benzyl chloride to synthesize diphenylmethane, taking the optimal conditions as an example:
Add 0.1g catalyst and 60 mmol benzene in sequence to a three-necked flask (50 mL) equipped with a reflux condenser, and pass in nitrogen to take out the air in the three-necked flask and the hydrogen chloride gas generated after the reaction. Use 3 mol for the tail gas. /L of sodium hydroxide solution, heated to 80°C with magnetic stirring, then added 10 mmol of benzyl chloride, stopped the reaction after 1 hour, cooled the reaction solution to room temperature, filtered to separate the catalyst, and took the filtrate for gas chromatography analysis .
The catalyst is prepared as follows: under magnetic stirring and pH meter monitoring, first add 25 mL of sodium dihydrogen phosphate (0.01 mol) aqueous solution to 75 mL of sodium metavanadate (0.01 mol) aqueous solution, and add dropwise Adjust the pH of the solution to 4.00 with V(H2SO4):V(H2O) =1:1, then add 50 mL of sodium molybdate (0.08 mol) aqueous solution, add the above sulfuric acid solution dropwise again to adjust pH = 3.8, and reflux at 99°C for 8 hours.
After cooling, move the solution into a separatory funnel, add 80 mL of anhydrous ether, and add V(H2SO4):V(H2O) =1:1 sulfuric acid, shake and let stand, the red oil in the lower layer is the etherate of heteropoly acid. Place the oily substance in a fume hood for 1 to 2 days until the crystalline particles precipitate. Then add a small amount of distilled water and recrystallize to obtain an obvious crystal form. After drying in a vacuum drying oven at 60°C, the orange-red powdery substance obtained is H8P2Mo16 V2O62 ·41H2 O catalyst, recorded as HPA, set aside.
Fe2H2P2Mo16V2O62·41H2O: According to the stoichiometric ratio, weigh 2 mmol of HPA and dissolve it in a three-necked flask containing 20 mL of distilled water, and then replace the three-necked flask with nitrogen. Using the air in the flask, add 4 mmol of ferric chloride to the HPA solution under nitrogen protection and magnetic stirring. At this time, ferric chloride quickly dissolves and reacts in the heteropoly acid solution, and stirs for 2 h. Then, use suction filtration and vacuum distillation to dry, and grind to obtain orange powdery phosphorus molybdenum vanadium iron salt, namely Fe2H2P2 Mo16V2O62·41H2O is recorded as FeHPA.
Method 2: A catalytic synthesis process of diphenylmethane with simple reaction process, green environmental protection, clean and efficient:
The specific technical plan is as follows: Benzene and formaldehyde are used as raw materials, and their dosage weight ratio is 20/1 2/1. The reaction conditions are: at a temperature of 100-200°C, the reaction time is 18 hours, and the reaction time is 18 hours. It is synthesized by a batch one-step condensation reaction under the action of a catalyst. The weight ratio of the amount of catalyst and reactants is 1/50 1/5.
The reaction steps are: 1) Add benzene and formaldehyde into the reactor, the molar ratio of benzene and formaldehyde is 20/1 2/1; 2) Add the catalyst, the molar ratio of catalyst to formaldehyde is 1/50 1/5, use high-purity nitrogen as a protective atmosphere, stir, and react at a temperature of 100 to 200°C for 18 hours. The obtained product is added with nitrobenzene as an internal standard, and the conversion rate is analyzed on GC; reaction The final catalyst is centrifugally separated, and the catalyst can be reused after recovery; 3) The reaction product is distilled, and the unreacted benzene can be recovered and reused; 4) Add absolute ethanol to dissolve the solid product after distillation, and then repeatedly distill under reduced pressure , the product diphenylmethane can be obtained.
Method 3: An environmentally friendly catalytic synthesis of diphenylmethane:
It is characterized by adding HCl with a concentration of 10% to 16% to Hangjin 2# clay mineral at a solid-liquid ratio of 1:2.5~3, heating and activation at 90~100°C for 3.5~4 hours, and washing with water until pH=6 , suction filtration, dry the filter cake at 100℃~105℃, roast at 250~300℃ for 2~3h, cool to room temperature to obtain clay-SA01 for later use, use clay-SA01 as the carrier, first mix ZnCl2 at 0.135~0.27g:1ml Dissolve ZnCl2 in methanol at a ratio of ~2ml to obtain a ZnCl2-methanol mixture, and then mix the mixture with the carrier clay-SA01 in a ratio of loading 0.135-0.27g active component ZnCl2 per gram of clay-SA01 and soak it for 24-36h to form a paste sample.
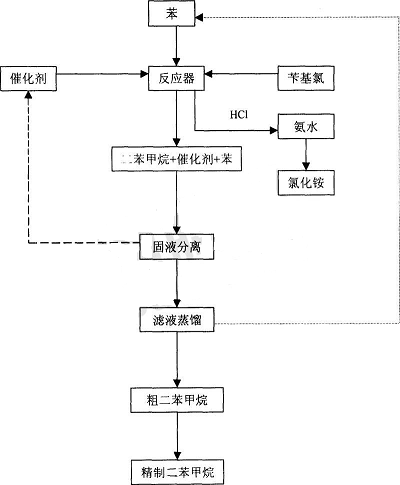
Dry the sample in vacuum at 70~80℃ for 3~4h, recover methanol, and prepare ZnCl2/Clay-SA01 solid sample. Under N2 gas protection, roast the clay-SA01 solid sample at 250-300℃ for 3 The ZnCl2/clay-SA01 catalyst is prepared in ~4h, and then the catalyst is cooled to room temperature in a N2 atmosphere. The catalyst and benzene are added to a reactor equipped with a calcium chloride drying device and an HCl gas absorption device, and slowly heated to 40 ~ 50°C, after stirring for 10 to 15 minutes, slowly add benzyl chloride, the ratio of benzene: benzyl chloride: catalyst is 25ml: 2.6ml: 1g, then increase the reaction temperature to 65 to 70°C, after reacting for 3 to 4 hours, Stop heating and cool to room temperature to separate the solid and liquid, recover the catalyst, distill the mixture to separate benzene and diphenylmethane, and recover the solvent benzene.
Main reference materials
[1] Fan Zongliang, Wei Huijuan, Li Guixian, et al. Catalytic synthesis of diphenylmethane by Dawson-type phosphomolybdenum vanadium heteropolyacid salt[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2015, 32(5): 543-547.
[2] Ji Min, Wu Haiming, He Min, et al. Study on reaction kinetics of solid-supported AlCl3 catalyzed synthesis of diphenylmethane [J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology, 2008, 48(2): 168-172.
[3] Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry analysis of diphenylmethane
[4] CN201310217853.6 Diphenylmethane catalytic synthesis process
[5] CN200310109813.6 An environmentally friendly catalytic synthesis method of diphenylmethane

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

