Overview[1]
4-Nitrophenylboronic acid is an organic intermediate that can be prepared from 4-nitrobromobenzene in one step.
Preparation[1]
In polar solvents, at a temperature of 80~100℃, the action of dicatechol and 4-nitrobromobenzene on potassium acetate and Pd(dppf)Cl2 React for 2 to 3 hours, lower to room temperature, filter, extract with ethyl acetate, concentrate the organic layer, and filter the crude product with a non-polar hydrocarbon solvent to obtain 4-nitrobenzene boric acid;
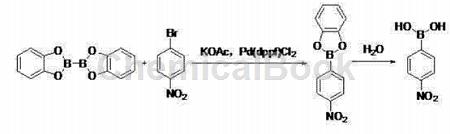
Apply[1-3]
1. Used to prepare 4-aminobenzene borate hydrochloride
4-Nitrophenylboronic acid is catalytically hydrogenated in ethyl acetate with palladium on carbon, and hydrogenated at 60~80°C, 0.8~1.0MPa for 6~8 hours. After the reaction is completed, filter at 15~25°C and keep at 0~10°C. Add concentrated hydrochloric acid to the filtrate, filter to obtain a crude product, use acetone to beat the crude product, filter, and dry to obtain 4-aminobenzene borate hydrochloride.
2. Used to prepare 3-(4-nitrophenyl)pyridine
Some oral drugs that target ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP), such as niraparib, are mainly targeted at cancer patients with BRCA-1/2 gene mutations, such as ovarian cancer and breast cancer patients. . In the synthesis of many such drugs, 3-(4-nitrophenyl)pyridine is one of the important intermediates.
A synthesis method of 3-(4-nitrophenyl)pyridine, including the following steps:
S1 Under the protection of inert gas, mix 4-nitrobenzene boric acid, 3-chloropyridine, nitrogen heterocyclic carbene-palladium complex, basic substances, and reaction solvent, and then react at room temperature for 48 hours to obtain a reaction solution; S2 The reaction solution obtained in step S1 is post-treated to obtain a product, which is 3-(4-nitrophenyl)pyridine.
3. Used to prepare 4-aminophenylboronic acid derivatives
As a reactive intermediate, 4-aminophenylboronic acid derivatives play a very important role in the fields of organic synthesis and medicine. This is mainly due to its good stability, low price, electrophilic group and It is environmentally friendly and has many advantages. At the same time, it can be used to prepare fluorescent chromophore molecules that adapt to physiological environments, such as anthracenes, naphthalenes, heterocyclics and other phenylboronic acid compounds, and its application in chromatographic analysis, mold detection and new pH sensors It is also widely used in .
A method for preparing 4-aminophenylboronic acid derivatives, which includes the following steps: first, 4-nitrobenzeneboronic acid undergoes a hydrogenation reduction reaction under the action of a hydrogen atmosphere and a palladium carbon catalyst to obtain 4-aminophenylboronic acid, and then 4-Aminophenylboronic acid is mixed with an acylation reagent in a solvent and undergoes an acylation reaction to obtain the 4-aminophenylboronic acid derivative.
Main reference materials
[1][Chinese invention] CN201210557943.5 Method for preparing 4-aminophenyl borate hydrochloride
[2]CN201811274330.4 A synthesis method of 3-(4-nitrophenyl)pyridine
[3][Chinese invention] CN201710218099.6 Preparation method of 4-aminophenylboronic acid derivatives

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

