Overview[1]
Bis- or polymethoxy-substituted phenylacetic acid is an important organic synthesis intermediate and is widely used in medicine and dyes. For example: (3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetic acid is used as raw material to synthesize pterostilbene with anti-cancer activity; 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenylacetic acid is used as raw material to synthesize highly active anti-tumor drug CA4; 2,4-Dimethoxyphenylacetic acid is a key intermediate in the synthesis of new quinolinone derivatives with the effect of preventing and treating osteoporosis; it is synthesized using 3,4-dimethoxyphenylacetic acid and prolinol as raw materials Hainan crude toreprisonine analogs with antitumor activity.
Preparation[1]
Method 1: (3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetic acid is prepared as follows: add 3,5-dimethoxybenzaldehyde to a 100ml three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer, reflux condenser and dropping funnel. 3.32g (0.02mol), 0.5g tetrabutylammonium chloride and 25ml chloroform, stir to dissolve and then heat up to 80°C. Start slowly adding 5ml of 50% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution dropwise. Stop the reaction after 6 hours. Naturally cool to room temperature, add an appropriate amount of water to dissolve all the solids, pour into a separatory funnel to remove the organic layer, wash the aqueous layer with chloroform until the organic layer is basically colorless, add 1:1 hydrochloric acid to acidify to PH=2~3, and use ethyl acetate to The ester was extracted, the combined organic layers were dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate, concentrated, and then recrystallized from ethanol-water to obtain a slightly yellow solid, which was 2.66g of 3,5-dimethoxymandelic acid, with a yield of 62.7%. In a 50ml three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer and a reflux condenser, add 2.12g of 3,5-dimethoxymandelic acid (0.01mol), 3.39g of stannous chloride dihydrate (0.015mol), and 10ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid, and heat to 85°C, react for 2 hours, add an appropriate amount of water while hot, cool and crystallize, and obtain white crystals by suction filtration, which is 0.76g of 3,5-dimethoxyphenylacetic acid, with a yield of 38.7%.
Method 2: (3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetic acid is prepared as follows
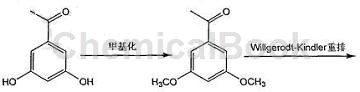
1) Add 1.52g (0.010mol) 3,5-dihydroxyacetophenone and 10ml water into the reaction bottle, and add 6.36g (0.060mol) about 20% mass of carbonic acid while stirring at a constant temperature of 0°C. Sodium aqueous solution and 1.68 ml (0.020 mol) of dimethyl carbonate solution were added dropwise for about 3 hours. After the stirring was completed, the reaction was continued for 2 hours. Pour the reaction solution into 20 ml of ice water and let it stand to cool. Filter it with suction to obtain a brown solid 3,5-bis Methoxyacetophenone 1.16g, yield 64.44%.
2) Add p-toluenesulfonic acid and 1.74ml (0.02mol) morpholine into the reaction bottle, heat to 120°C, stir at constant temperature and react for 5 hours. After the reaction is completed, cool to room temperature. Add 1.60g (0.040mol) of 20% mass sodium hydroxide aqueous solution and 0.161g (0.5mmol) tetrabutylammonium bromide to the reaction solution, heat to 100°C, and react at a constant temperature for 5 hours. TLC thin layer chromatography detects the reaction to completely. Pour the reaction solution into water, add acid to acidify it to PH=7, remove oily impurities by suction filtration, add acid to the filtrate and continue acidifying it to PH=2. At this time, a large amount of white solid will be generated. Let it stand and cool and filter it to obtain crude product 3,5. -Dimethoxyphenylacetic acid, the crude product was recrystallized from water.��White needle-like crystals (3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)acetic acid 1.59g, yield 81.12%.
Main reference materials
[1] CN200810027888.2 Preparation method of bis- or multi-methoxy-substituted phenylacetic acid
[2] CN200910041790.7 Preparation method of (Z)-3’-hydroxy-3,4’,5-trimethoxystilbene

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

