Overview[1]
1,4-Benzoquinonedioxime is a cross-linking agent. In recent years, the main method for industrial production of 1,4-benzoquinonedioxime is: at 0℃, in the presence of a certain concentration of sulfuric acid, sodium nitrite Nitrate phenol dissolved in 30% NaOH solution to prepare p-benzoquinone monooxime, and then add the prepared p-benzoquinone monoxime to hydroxylamine oximation to prepare the final product 1,4-benzoquinonedioxime. The purity of the product is affected by this synthesis method. limit (≤95%) and contains many impurities, specifically reflected in: 1) In the process of preparing p-benzoquinone monoxime, the air in the reactor will oxidize part of p-benzoquinone monoxime to generate resin, It affects the quality of p-benzoquinone monoxime and indirectly affects the quality of 1,4-benzoquinonedioxime.
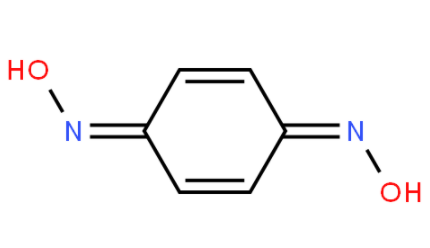
Apply[1]
1,4-Benzoquinonedioxime products are suitable for: butyl rubber, ethylene-propylene rubber, natural rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber, polysulfide rubber, etc., especially suitable for butyl rubber and ethylene-propylene rubber. Product performance: easy to disperse in the rubber, fast vulcanization speed, high elongation strength of the rubber, heat and weather resistance, ozone resistance and excellent electrical insulation properties. It can be used as a polymerization inhibitor for acrylic acid and can improve the heat resistance of polyester fiber tire cord. Resistance, hot-melt adhesive for metallic glass, regulator for olefin copolymer cross-linking, organic monomer stabilizer, self-vulcanizing adhesive, rubber products to prevent nuclear radiation, active against oxidants (such as Pb304, Pb02) Activation. However, the criticality is low and there is a tendency to scorch. Adding certain anti-scorch agents, thiuram, and thiazole accelerators can effectively improve operational safety. It pollutes rubber. Adding about five parts of titanium dioxide can prevent and greatly improve the safety of operations. Contaminating. It is especially suitable for butyl rubber, natural rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber, polysulfide rubber, ethylene-propylene rubber, etc. that have high tensile strength and fast vulcanization speed.
Preparation[1-2]
Method 1: Preparation method of 1,4-benzoquinonedioxime, follow the following steps: 1) Prepare sodium phenolate solution: Mix 5%-20% NaOH solution with phenol solution and sodium nitrite solution to prepare Obtain the sodium phenol liquid, and add soda ash to it. The weight of the soda ash added is 1/10 of the weight of NaOH; 2) Prepare p-benzoquinone monooxime, and introduce the sodium phenol liquid into the 28%-32% acidic liquid through the catheter. And add sodium nitrite solution to carry out nitrosation reaction. The whole process is carried out under the conditions of -3℃-5℃; 3) Washing liquid: Wash the prepared p-benzoquinone monoxime with pure water until it is neutral, and measure the decomposition Point; 4) Preparation of 1,4-benzoquinone dioxime: Add water to the prepared p-benzoquinone monooxime, stir, control the temperature at 45°C-62°C, and pour in hydroxylamine oxime to prepare it.
Method 2: Preparation method of 1,4-benzoquinonedioxime
In the first step, put 4.0g p-benzoquinone, 5.4g calcium carbonate, and 10.0g hydroxylamine chloride into the reactor, add 80ml ethanol and 20ml water, and stir evenly. React at 70°C for 3 hours. After the reaction is completed, the product is vacuum evaporated to remove the solvent.
In the second step, add 60ml of water and 11.3g of 36.5% hydrochloric acid to the container after removing the solvent, stir evenly for 5 minutes, then filter the product, wash with water, and dry to obtain 4.05g of product. After high-performance liquid chromatography analysis and comparison with standard samples, the purity of the product reached more than 99%. The yield of the target product was 79.2%.
Main reference materials
[1] Preparation method of CN200810156240.51,4-benzoquinonedioxime
[2] Preparation of CN200710047540.51,4-benzoquinonedioxime

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

