Background and overview[1][2]
Chiral compounds are widely used in the fields of drugs, food, pesticides, materials, feed and other fields. Optically active (1S, 2S)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine is an important chiral reagent that has been widely used in asymmetric synthesis and optical resolution, such as asymmetric hydroxylation of alkenes, Asymmetric aldol condensation reaction, asymmetric Diels-Alder reaction, asymmetric allylation reaction of carbonyl group, synthesis of optically active allenyl alcohols and propynyl alcohols, asymmetric epoxidation reaction of alkenes without functional groups And the resolution of binaphthol, etc. It is a chiral reagent widely used in the chemical industry. The current preparation method is to separate (±)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine in an ethanol solvent using tartaric acid as a resolving agent. According to the needs, different separation conditions are adopted to obtain or (1S ,2S)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine or (1R,2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine.

Racemization method[1]
Add 40g (189mmol) (1S, 2S)-(-)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine, 190ml of water, 20g of benzaldehyde (198mmol), and react at 60-100°C for 2 hours to form Schiff base is then decomposed by adding hydrochloric acid to adjust pH 1 to produce (±)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine 34.8, [α] = 0°, M.P. 80-81°, racemization yield 87%. 48% (1R, 2R)-(+)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine and 46% (1S, 2S)-(-)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine and 3% internal elimination Spin body.
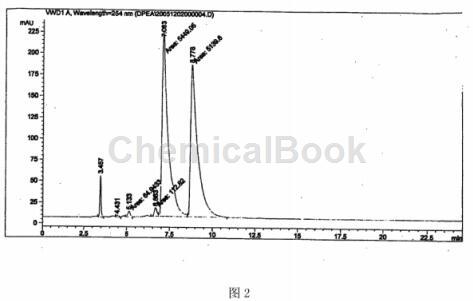
Figure 2: HPLC chiral analysis chart of (±)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine prepared after racemization; peak time 7.048 is (1S, 2S)-(-)-1, 2-diphenylethylenediamine;
The peak time 8.778 is (1R2R)-(+)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine;
The peak time of 3.414 is meso 1,2-diphenylethylenediamine.
Main reference materials
[1]CN200610023518.2(1S,2S)-(-)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine; (1R,2R)-(+)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine Racemization method

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

