Background and overview[1]
P-Bromophenylacetylene can be used as a pharmaceutical synthesis intermediate. Halogenated phenyl acetylene is an important type of electronic chemical raw materials and organic synthesis intermediates. It is widely used in drugs, pesticides, catalysis, liquid crystal intermediates, polymerization inhibitors, electrode materials, luminescent coatings, corrosion inhibitors, etc. Currently, the methods commonly used to synthesize halogenated phenyl acetylene include synthesis methods from substituted acetophenones, substituted styrenes, heterocyclic compounds, etc. as raw materials, and synthesis methods through Vilsmerier reaction.
Preparation[1]
The synthesis steps of p-bromophenylacetylene include:
The first step: Preparation of: (E)-3-(4-bromophenyl)acrylic acid
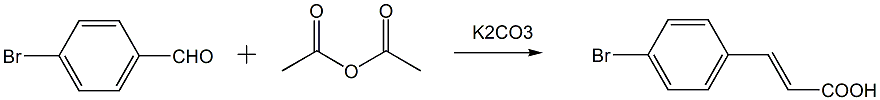
In a three-necked flask equipped with a reflux condenser and a drying tube, add 4-bromobenzaldehyde, acetic anhydride and anhydrous potassium carbonate (or anhydrous sodium carbonate, anhydrous hydrogen carbonate) with an equivalent ratio of 1:4:1.5 Sodium), stir and reflux at 130~140°C. Stop the reaction after the raw material 4-bromobenzaldehyde has reacted. Prepare 20% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution. When the system cools to 80~90°C, adjust the pH to 8~10 After the system is cooled to room temperature, add a little activated carbon, boil and filter while hot to obtain filtrate 1. Transfer the filter cake to the three-necked flask of the original reaction and add water. Add sodium hydroxide solution to adjust the pH to 8~10. Heat at 100°C for 2 hours and then filter while hot to obtain filtrate 2; combine filtrate 1 and filter cake 2, cool, slowly add concentrated hydrochloric acid dropwise to the filtrate, adjust the pH to 4, let it stand overnight until it is fully separated, and filter with suction. The filter cake is washed with water, dried and weighed to obtain (E)-3-(4-bromophenyl)acrylic acid;
Step 2: Preparation of 2,3-dibromo-3-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid
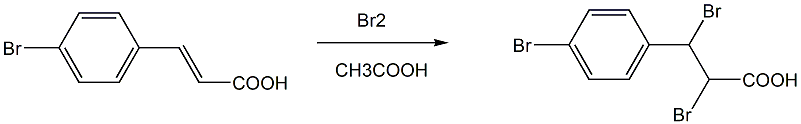
Add (E)-3-(4-bromophenyl)acrylic acid and one of acetic acid or ethanol or methanol into a three-necked flask equipped with a dropping funnel, a reflux condenser and an exhaust gas absorption device, and add magnetic stirring Submers, add 1.5 equivalents of Br2 dropwise at 60°C, detect that (E)-3-(4-bromophenyl)acrylic acid has completed the reaction, stop the reaction; evaporate the solvent under reduced pressure and recover it; wait for the reaction mixture to cool and add to Add an appropriate amount of water to precipitate a light yellow solid, let it stand until it is fully precipitated, filter with suction, wash the filter cake with water, dry and weigh to obtain 2,3-dibromo-3-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid;
The third step: Preparation of: (Z)-1-(4-bromophenyl)-2-bromethylene
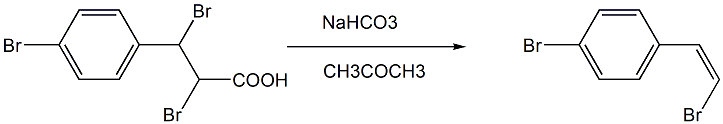
Add acetone, 2,3-dibromo-3-(4-bromophenyl)propionic acid and sodium carbonate (or sodium bicarbonate) with an equivalent ratio of 1:3 in a single-necked flask, and heat at 55 to 60°C. Stir and reflux, stop the reaction, cool, evaporate acetone under reduced pressure, add water to the system, extract with ether, and dry with anhydrous Na2SO4; after evaporating ether under reduced pressure, the crude product (Z)-1-(4-bromo) is obtained Phenyl)-2-ethyl bromide;
Step 4: Preparation of p-bromophenylacetylene
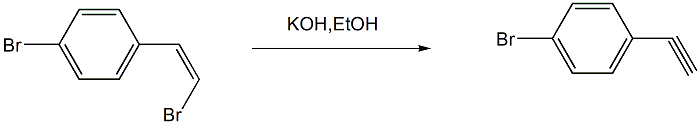
Add absolute ethanol (or anhydrous methanol) and (Z)-1-(4-bromophenyl)-2-bromethylene and potassium hydroxide (or hydrogen Sodium oxide), heat to 70°C for reaction, and stop the reaction after monitoring until the reaction is complete; cool the reaction mixture to room temperature, remove the ethanol under reduced pressure, add ice water to the system, seal it and leave it in the refrigerator overnight until the target product is fully After precipitation, suction filtration, and water washing of the filter cake, the product is sublimated to obtain p-bromophenylacetylene.
Main reference materials
[1]CN201410523075.8 A new synthesis method of 4-halogenated phenyl acetylene

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

