Overview[1]
Methoxyphenylacetic acid, such as o-, p- and m-methylphenylacetic acid, is an important class of organic chemical fine chemical intermediates and is mainly used in the manufacture of pesticides, medicines and corresponding esters. In the existing technology, there are not many reports on the preparation methods of methoxyphenylacetic acid, but there are many synthesis and preparation methods of its analogue phenylacetic acid, and its synthesis process routes mainly include the following:
(1) Phenyl acetonitrile hydrolysis method: first use chloride and sodium cyanide in the presence of a solvent to generate phenylacetonitrile, then further react to obtain aryl acetonitrile, and finally hydrolyze in dilute sulfuric acid into aryl acetic acid. This method has a high yield in the hydrolysis step, but the synthesis yield of phenylacetonitrile is low, and sodium cyanide is highly toxic.
(2) Phenylacetamide hydrolysis method: Using styrene as raw material, it reacts with ammonia and sulfur to generate phenylacetamide, and continues the reaction to obtain arylacetamide, which is then hydrolyzed to generate arylacetic acid. This method has a simple process, easy to control operating conditions, and low toxicity of raw materials and intermediate products. However, the by-product of the reaction between styrene, ammonia, and sulfur, phenethyl mercaptan, has a strange smell and pollutes the environment, and the reaction needs to be carried out under pressure, which is limiting. application of this reaction.
(3) Carbon-based synthesis method: Under the action of a carbonation catalyst, chlorinated arylmethane undergoes a carbonation reaction in a two-phase system of sodium hydroxide and organic solvent at lower pressure and mild temperature to generate Sodium arylacetate is then acidified to arylacetic acid. The product of this method has high purity and mild reaction conditions. However, it has the disadvantages of high technical requirements during the process and careful operation to prevent catalyst deactivation or loss. The yield still needs to be improved.
Preparation[1]
Method 1: In a 500m1 four-necked flask, first add 100g of water, then slowly add 240g of 98% concentrated sulfuric acid (2.40mo1) while stirring. Later, the temperature was raised to 90°C, and 200 grams (98%, 1.50mol) of m-toluene acetonitrile was slowly added dropwise at 90°C-150°C. Other operations were the same as in Example 1. When the reaction is completed, cool down to 80°C, then add 300ml of toluene, stir for 10 minutes, separate the organic phase, extract the aqueous phase twice with 100ml of toluene, combine the organic phases, and wash twice with distilled water or clean water. Stir the organic phase and slowly cool it to 3-5°C to precipitate flaky white crystals; filter and air-dry at room temperature to obtain 180.3g of m-methoxyphenylacetic acid product, with a yield of 80.14% and a melting point of 120-122°C.
Method 2: Synthesis of m-methoxyphenylacetic acid (VI)
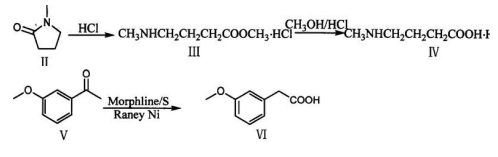
Add 33g sublimated sulfur, 96.5ml 3-methoxyacetophenone (V) and 92ml morpholine into a 1000ml three-necked flask, and reflux for 15 hours under mechanical stirring. Cool the temperature to about 30°C, add a mixed solution composed of 350ml glacial acetic acid, 105ml distilled water and 70ml concentrated sulfuric acid under mechanical stirring, and continue to reflux for 5.5 hours. Pour the reaction mixture into ice water (400g ice + 100ml water), stir mechanically until a yellow-brown solid precipitates (add crushed ice if necessary), quickly cool and filter in an ice bath. Dissolve the solid with 300 ml of 20% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution and filter. Add the brown insoluble matter to 100 ml of 20% sodium hydroxide aqueous solution, heat and reflux for half an hour, and filter while it is hot.
Combine the filtrate, add 10g of activated powdered activated carbon and reflux for half an hour for decolorization. filter. Add 15g RaneyNi as a catalyst, reflux and stir for 2 hours, remove the Ni after reaction, and add 15g RaneyNi and heat and reflux for 2 hours. Filter, and the filtrate is acidified to pH 1-2 with 2N hydrochloric acid under ice bath and mechanical stirring to obtain a pinnaceous white precipitate. Place it in an ice bath for half an hour, filter, and dry to obtain 58g of m-methoxyphenylacetic acid, with a yield of 49.8%. , melting point 68-71℃.
Main reference materials
[1] Preparation method of CN201210087394.X methoxyphenylacetic acid
[2] CN200410017499.3 A method for preparing 1-methyl-3-ethyl-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-hexahydro-1H-azepine hydrochloride

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

