Background and overview[1-2]
3,5-Dihydroxypentylbenzene is an important pharmaceutical intermediate, which was first obtained by degrading lichenic acid (also known as D-usroleic acid and amylyliscolic acid) extracted from lichen plants.
3,5-Dihydroxyalkylbenzene has a variety of biological activities and has killing effects on a variety of pathogenic fungi and bacteria. In recent years, people have discovered that high concentrations of 3,5-dihydroxyalkylbenzene can break DNA in the presence of copper chloride and oxygen. Therefore, it is used to inhibit and treat human immunodeficiency, cancer and other malignant tumors caused by retrovirus, with remarkable effects. 3,5-Dihydroxyalkylbenzene can also be used to synthesize cannabinoids. Cannabinoids are a general name for a class of substances with similar chemical structures in cannabis that are related to the physiological activity of the human body. There are more than 60 types and can be used for Analgesic, sedative, anti-inflammatory, digestive and anti-hypertensive. The representative of this type of compound is 3,5-dihydroxypentylbenzene (Olivetol).
Preparation[1]
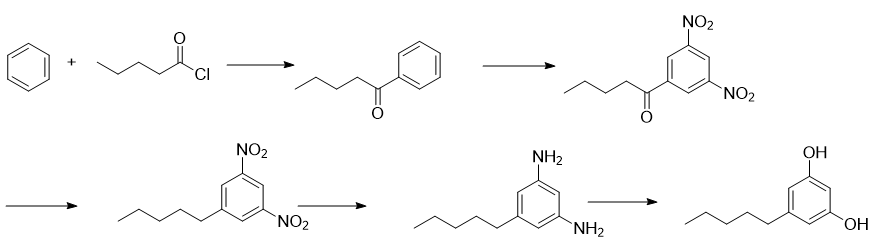
Add 156g benzene, 900mL dichloromethane and 146.5g anhydrous aluminum trichloride into a 2L three-necked flask. After cooling to 0-5°C, slowly add 120.5g n-valeryl chloride dropwise, maintaining the internal temperature during the dropwise addition. 0-10℃. After the dropwise addition is completed, the temperature is raised to 40°C, and the reaction is stirred for 2 hours. Under ice bath cooling, slowly add 500 mL of 1N hydrochloric acid solution dropwise. After the dropwise addition is completed, separate the liquids. The aqueous phase was extracted with 400 mL DCM. The organic phases were combined, concentrated and distilled under reduced pressure to obtain 142g of phenylpentanone, with a yield of 87%.
In a 1L three-necked flask, mix 200 mL fuming nitric acid and 200 mL 5% sulfuric acid into a mixed acid within 20°C, then cool the temperature to within 10°C, slowly add 129.6g phenylpentanone, and control the internal temperature during the dropwise addition to 0- 10℃. After the dropwise addition, the heat preservation reaction was completed for 2 hours, then the temperature was raised to 50°C, and the reaction was continued for 5 hours. After cooling to 20°C, the reaction solution was poured into crushed ice to precipitate the solid, which was filtered. The filter cake was dissolved in DCM and separated, and the organic phase was concentrated again to obtain a crude product. The crude product was mixed with PE and EA to dissolve, crystallize and dry to obtain 156.5g of 3,5-dinitrobenzene, with a yield of 78% and a purity of 98.3%.
Add 151.3g of 3,5-dinitrobenzene and 900mL of ethylene glycol dimethyl ether into a 2L three-necked flask. Cool the temperature to 0-5°C and then slowly add 159.6g of trifluoroacetic acid dropwise. The addition is completed. Finally, add 56g NaBH4 in batches at 0-5°C and keep overnight. After the reaction is completed, 500 mL 2N hydrochloric acid is added dropwise at 20°C. After the addition is completed, stir for 2 hours at 20-30°C and separate the liquids. The aqueous phase was extracted with 400 mL of DCM, and the organic phases were combined and concentrated to dryness to obtain 144.3g of crude 3,5-dinitropentylbenzene. The crude product was directly used in the next step of the reaction without purification.
Add 700mL water, 144g ammonium chloride and 700mL ethanol into a 2L three-necked flask, stir to dissolve, then add 160g iron powder, stir and control the temperature to 25-35°C, then add 144.3g of the synthesized 3,5-bis in batches For the crude nitropentylbenzene, after the dropwise addition, keep the reaction temperature for 2 hours, then raise the temperature to reflux and react for another 5 hours, then cool to 25-30°C and filter. The filtrate was concentrated to dryness and crystallized with a mixed solvent of ethanol: water = 1:1 to obtain 86.6g of 3,5-diaminopentylbenzene, with a purity of 96.7% and a total yield of 81% in two steps.
Dissolve 71.3g of 3,5-diaminopentylbenzene with 300mL of 40% sulfuric acid solution prepared in advance, and add 100mL of DCM to extract impurities. Transfer the aqueous phase to a 1L three-necked flask, stir and cool down to within 5°C. Insert the dropping funnel below the liquid level through the lower opening and add sodium nitrite solution dropwise (60g sodium nitrite dissolved in 160mL water). Control the temperature during the dripping process at 5°C. Next, after the addition is completed, stir for 5 minutes, then add 3g of urea, and store the diazonium salt solution in an ice bath for later use.
Add 300g anhydrous sodium sulfate, 400g sulfuric acid and 400mL water into another 2L three-necked flask equipped with a dropping funnel and a distillation condensation device. After heating to reflux, slowly add the above-mentioned diazo solution in the ice-water bath. After the addition, the reaction was incubated for 1 hour, 300 mL of DCM was added for extraction, and the organic phase was backwashed once with 100 mL of water. Add 200 mL of water to the organic phase, then adjust the pH to 10-11 with NaOH, separate the liquids, extract the organic phase with 50 mL of water, combine the aqueous phases and adjust the pH to 1 with hydrochloric acid, and solids will gradually precipitate during the acid adjustment process. Filter, rinse the filter cake with 50 mL of water, and blow-dry at a controlled temperature of 20-30°C until the moisture content is within 1.0% to obtain 56.4g of 3,5-dihydroxypentylbenzene (Olivetol), with a purity of 98.7% and a yield of 78%.
Apply[3]
CN201611230150.7 discloses a synthesis method of cannabinoid compounds. The steps are to use 3,5-dihydroxypentylbenzene as the starting material, phenolic hydroxybenzyl protection, 2-pyridylsulfonyl protection, acetic acid Palladium is used as the catalyst, oxygen is the oxidant, and two aryl carbon-hydrogen bonds are directly coupled to synthesize 6H-benzo[c]chromene compounds in one step, and then oxidized, deprotected, and methylated to synthesize cannabinol with high yield. . The method of the present invention realizes direct oxidative aryl coupling through -C-H-bond activation as a key step in the synthesis of cannabinol, and can synthesize cannabinol efficiently and concisely. Compared with traditional methods, it is simple to operate, has higher reaction yield, is environmentally friendly, and has high atom utilization rate.
References
[1][China Invention] CN201711345526.33, Synthesis method of 5-dihydroxypentylbenzene
[2][Chinese invention] CN201210511883.3 A synthesis method of alkyl-protected 3,5-dihydroxyalkylbenzene
[3][China invention, China invention authorization] CN201611230150.7 A synthesis method of cannabinoid compounds

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

