Background and overview[1][2]
2-Thiobenzothiazole zinc salt has the characteristics of fast vulcanization acceleration, low vulcanization flatness, and no early vulcanization during mixing. It is widely used in the rubber processing industry and is essential for natural rubber and synthetic rubber. Highly efficient rubber vulcanization accelerator. At present, the commonly used method in industrial production is the aniline method, but its waste gas hydrogen sulfide seriously pollutes the environment, has high recovery costs, low production efficiency, no recovery of the by-product benzothiazole, and low product purity.
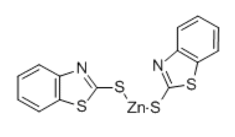
2-Thiobenzothiazole zinc salt
Apply[3]
2-Thiobenzothiazole zinc salt can effectively promote the vulcanization speed of rubber products, improve the performance of rubber products, and improve the quality of rubber products. However, the traditional 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt is a powder, which can easily cause dust and environmental pollution during production, transportation and use. Secondly, the powder product has poor compatibility with rubber and requires prolonged mixing. Mixing time, increasing mixing temperature and other methods.
Preparation[2]
At present, the commonly used method in industrial production is the o-nitrochlorobenzene method:
Use sodium polysulfide, o-nitrochlorobenzene and carbon disulfide to condense into M sodium salt at a temperature of 110~130℃ and a pressure of 3.5atm. After purification, drying, crushing, screening and other post-processing, the finished product M is obtained. This low-temperature and low-pressure M process is produced by Lanzhou Chemical Company Organic Factory and Chongqing Dongfeng Chemical Factory. But the quality is poor, the uses are limited, and the amount of waste is high
The existing industrial production process of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt adopts the traditional air flow drying process. In the production of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt, the wet material of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt after reaction contains water, methanol solution and a small amount of CS2. When drying the salt, it is necessary to remove methanol and CS2 in the wet material of 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt. The process method is: dry the 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt through an airflow dryer after heating the air. All moisture, methanol and CS2 evaporate and are taken out by dry air and discharged.
The disadvantage of this process technology is that the process uses an air open circuit system. Since the 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt wet material contains a small amount of CS2, flash explosions often occur during the drying process and CS2 is irritating and Toxic, endangering personal safety and affecting the environment; the methanol solvent in the 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt wet material is seriously wasted, and is discharged with the hot air during the drying process, affecting the environment and causing waste; the wet material uses air flow Drying, heating the air through steam, has low thermal efficiency and high energy consumption.
Specific method:
Step 1. Preparing the dissolved sulfur solution: Add 600kg/t of 98% carbon disulfide solution and 250kg/t of 98% sulfur powder into the reactor, and dissolve it into a dissolved sulfur solution at 35°C; then add the dissolved sulfur solution The liquid metering tank is insulated and stored for later use;
Step 2. Ingredients: During production: drying of the synthetic kettle: the newly opened kettle is heated up or the hot kettle is filled with materials; 1) steam blowing out the kettle; 2) air pressure blowing out water vapor; 3) vacuuming; closing Kettle; add 95% aniline 440kg/t into the synthesis kettle, then add the prepared dissolved sulfur solution, and finally add the remaining aniline, close the feed port of the synthesis kettle, and raise the temperature;
Step 3. Reaction: Wait for the temperature in the synthesis kettle to rise to 200°C, keep the temperature constant between 200 and 210°C, and control the pressure between 80 and 81Mpa. React for 2.5 hours to generate 2-mercaptobenzene. Thiazole zinc salt solution;
Step 4: Exhaust: When the reaction is complete, the temperature of the kettle and the pressure of the kettle begin to decrease, stop heating, open the exhaust valve to discharge hydrogen sulfide to the treatment process, when the kettle pressure returns to zero, close the exhaust valve;
Step 5. Discharging: Use the upper discharging method, open the steam valve, press out the 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt solution, and discharge the material from the discharging pipe that runs through the top of the kettle. Press in and stir in real time. and pre-passed into the alkali solution tank of caustic soda;
Step 6. Alkali dissolution: Put the 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt solution into an alkali solution tank and dissolve it in caustic soda at 40°C to form a crude 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt sodium solution. , filter and stack alkali-soluble resin;
Step 7. Change: Add the crude 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc sodium salt solution treated in step 6 into the change tank, add dilute sulfuric acid dropwise at 35°C to change, filter and stack the change resin, and collect 2-Thiobenzothiazole zinc sodium salt solution;
Step 8. Neutralization: Add the 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc sodium salt solution treated in step 7 into the neutralization tank and stir. Add dilute sulfuric acid dropwise at 35°C to precipitate 2-mercaptobenzene. When pH 9 is reached, the upper solution of benzothiazole zinc salt is extracted or released to the recovery tank for treatment; the remaining 2-mercaptobenzothiazole zinc salt is filtered, washed and dried in a centrifuge, and then dried by airflow at 100°C to become the finished product 2 -Thiobenzothiazole, after crushing and screening, the larger particles are the first ones. 2-Thiobenzothiazole zinc salt is used to produce 2,2′-dithiodibenzothiazole, which meets the screening grade 2 -Thiobenzothiazole zinc salt enters the packaging room for packaging.
Step 9. Resin treatment: mix the alkali-soluble resin produced in step 6 and the modified resin produced in step 7, and then go through multiple cycles of alkali dissolution, modification and neutralization to recover 2-mercaptobenzoyl Thiazole zinc salt is used to produce 2,2′-dithiodibenzothiazole, and the resin is filtered out and sent to the garbage dump.
Main reference materials
[1] Tang Cuifang. (2002). Effect of vulcanization system on the quality of natural latex condoms. World Rubber IndustryIndustry, 029(005), 8-10,4.
[2] Lin Xinhua, Chen Zhaohui, & Wang Dizhen. (2008). Effects of three zinc salt accelerators on vulcanization of natural rubber%. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 036(011), 153-156,161.
[3] Wei Weimei. Effects of non-amine accelerators ZDTP and ZIX on the properties of natural latex. (Doctoral dissertation).

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

