Background and overview[1][2]
4-Carboxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride is an important intermediate, especially a pharmaceutical intermediate. The existing technology uses p-aminobenzoic acid as raw material, and is prepared through diazotization reaction, sodium sulfite reduction, and hydrolysis. The synthesis method of the obtained 4-carboxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride requires a long reaction time, generally requires a yield of only 63-72%, and has high production costs.
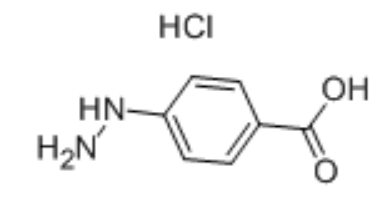
4-Carboxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride
Apply[3]
4-Carboxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride is an important intermediate, mainly used to prepare indole and pyrazolone derivatives, and can also be used to prepare other chemical products.
Preparation[2]
The traditional preparation process of carboxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride includes a two-step process of diazotization of aniline and reduction of diazobenzene chloride. Among them, the diazotization of aniline is mostly in hydrochloric acid medium, under the condition of pH equal to 2, at 0 Add sodium nitrite to react at a low temperature of ~5℃ to generate diazobenzene chloride. The reduction of diazobenzene chloride generally uses sodium sulfite and sodium bisulfite as reducing agents. Ammonium bisulfite and ammonium hydroxide are also used as reducing agents. The reduced phenylhydrazine disulfonate material liquid enters the acid precipitation kettle through a filter press. , phenylhydrazine hydrochloride is obtained through acid precipitation operation. This traditional synthesis method of phenylhydrazine hydrochloride has a reaction time of 3 to 4 hours, and the yield is only between 63-72%. In addition, when the reducing agents used are sodium sulfite and sodium bisulfite, the cost It is higher and increases production costs; when ammonium bisulfite and ammonium hydroxide are used as reducing agents, because they are liquids, they are difficult to transport and store. In addition, this process requires the use of a reduction kettle, a filter press and an acid precipitation kettle, which requires a lot of equipment and a large investment.
Specific method one:
Add 150ml of water into a 600ml beaker, stir, add 27.4g of para-aminobenzoic acid, 57.5ml of 10N hydrochloric acid, cool the solution to 0°C and slowly add sodium nitrite solution (made from 15g of sodium nitrite and 30ml of water) into), complete the addition, adjust the pH of the system to 1-2, control the temperature of the reaction system to 5°C, and after reacting for 20 minutes, filter and retain the filtrate.
Add 200 ml of water into a 1000 ml beaker, add 64 grams of sodium metabisulfite and 78 grams of sodium hydroxide while stirring. At this time, the pH of the solution is 7 and the temperature of the solution is 35°C. After the solution cools to 15-18°C, slowly Add the above filtrate. When the addition is complete, the solution temperature is 20°C and the pH is 7. After 30 minutes of reaction, the temperature is raised to 50-60°C, 115ml of hydrochloric acid is added, and the temperature is continued to be raised to 97-100°C, and the reaction is carried out at this temperature for 30 minutes. Finally, add 7 grams of activated carbon, decolorize and filter at 90°C to retain the filtrate, cool to 15°C, add hydrochloric acid, the material precipitates, filter, and drain to obtain 4-carboxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride product. The purity of 4-carboxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride measured by high performance liquid chromatography was 98.92%.
Specific method two:
(1), Diazotization reaction
Add 200ml of water and 27.4g of 4-aminobenzoic acid into an 800ml beaker, stir, add 57.5g of 10N hydrochloric acid, and stir thoroughly for 30 minutes. After the 4-aminobenzoic acid is completely dissolved, slowly cool the solution to below 0°C. Then slowly add sodium nitrite aqueous solution (made by dissolving 15g sodium nitrite and 30ml water). After the addition, the temperature of the material in the beaker is 5°C, and the potassium iodide iodine powder test paper is slightly blue. Control the temperature of the material at 0 to 5°C, continue to stir the reaction for 20 minutes, and filter to obtain a brown solution of 400 to 450 ml, which is the diazobenzene chloride solution.
(2), reduction reaction
Add 200ml of water to a 1000ml beaker, stir and add 64g of sodium metabisulfite. After all is dissolved, add 56.3g of sodium hydroxide. At this time, the temperature is about 30~35°C and the pH is 7. Add ice and cool to 15~18°C. Add slowly After adding the diazobenzene chloride solution above, control the temperature to 18-20°C and keep the reaction for 30 minutes to obtain a solution containing the reduction product.
(3), hydrolysis reaction
Add 115g of 10N hydrochloric acid to the solution containing the reduction product obtained from (2), heat to 97-100°C, and keep the reaction for 30 minutes to obtain a light brown solution containing 4-carboxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride. Add 7g of activated carbon, react for 5 minutes, filter to obtain a light yellow solution, cool the light yellow solution to 5-10°C, white material precipitates, filter and drain to obtain 40g of white filter cake, and dry to obtain 27.43g of 4-carboxybenzene. Hydrazine hydrochloride finished product. Based on 4-carboxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride, the molar yield is 73%, and the purity detected by high performance liquid chromatography is 98.80%.
Main reference materials
[1] Chen Chongya, & Pan Fuyou. (2007). Research on the synthesis process of o-carboxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 34(4), 32-33.
[2] Yu Jinlong, & Shen Yunhan. (0). A preparation method of 2-carboxyphenylhydrazine hydrochloride.
[3] Jin Wenhu, Zhang Pengzhi, & Ji Yafei. (2010). 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-4-methylpyrazole-3-carboxylic Synthesis of acids. Synthetic Chemistry(03), 131-133.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

