Background and overview[1][2]
Optically active (1S, 2S)-(-)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine; (1R,2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine is an important chirality Reagents have been widely used in asymmetric synthesis and optical resolution, such as asymmetric hydroxylation reactions of alkenes, asymmetric aldol condensation reactions, asymmetric Diels-Alder reactions, asymmetric allylation reactions of carbonyl groups, optical activity The synthesis of allenyl alcohol and propynyl alcohol, the asymmetric epoxidation reaction of alkenes without functional groups, and the resolution of binaphthol, etc. It is a chiral reagent widely used in the chemical industry.
The current preparation method is to separate (1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine in an ethanol solvent using tartaric acid as a resolving agent. According to the needs, different separation conditions are used for separation. The required (1R,2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine or 1S,2S)-(-)–1,2-diphenylethylenediamine is obtained. The other half of the discarded chiral compounds are present in the mother liquor after separation, namely (1R, 2R)-(+)–1,2-diphenylethylenediamine or (1S, 2S)-(-) –1,2-diphenylethylenediamine mother liquor recovery product, it is necessary to racemize the chiral mother liquor recovery product to re-produce (1R,2R)-1,2-diphenylethane The diamine raw materials are then separated.
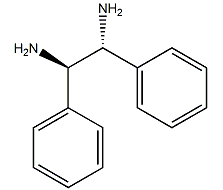
(1R,2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine
Apply[3]
The preparation method of (1R,2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine nickel azide complex ferroelectric material, the steps are as follows:
The dissolved nickel perchlorate [Ni(ClO4)2·6H2O, 37 mg, 0.1 mmol] and the chiral bidentate nitrogen-containing organic ligand (1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethylene di A 10 mL methanol solution of amine (22 mg, 0.1 mmol) was put into the test tube as the bottom layer, and 8 mL of a mixed solution of methanol and water (volume ratio 1:1) was added as an intermediate buffer layer, with azide dissolved in it. A 5 mL aqueous solution of sodium (NaN3, 6.5 mg, 0.1 mmol) was slowly added into the test tube as the top layer. After standing for 5 days, light blue crystals were obtained. Filter, wash with methanol and water respectively, and dry under vacuum. Calculate 1R, 2R)- The yield of 1,2-diphenylethylenediamine azide nickel complex ferroelectric material is 83% (calculated as nickel).
Perkin-Elmer 240C elemental analyzer was used to analyze the C, H and N contents of the one-dimensional chain nickel complex [Ni(L)2(N3)]nClO4·0.5H2O, and the calculated value was calculated according to the molecular formula (NiC28H32N7O9Cl) ( %): C, 47.72; H, 4.58; N, 13.91. Measured values (%): C, 48.05; H, 4.41; N, 13.79. Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer single crystal diffractometer was used to measure (1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine nickel azide complex ferroelectric material [Ni(L)2(N3)]∞ClO4 at room temperature. ·Molecular structure of 0.5H2O.
At room temperature, the ferroelectric testing system Precision Premier II (Radiant Technologies Inc.) was used to characterize the ferroelectric properties of the one-dimensional (1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine nickel azide complex. The test results show that the target material has good ferroelectric properties, its residual polarizability Pr = 2.37 μc/cm2, saturation polarizability Ps = 5.15 μc/cm2, and coercive electric field Ec = 20 kv/cm.
Preparation[2]
Add 1,2-diphenylethylenedionedioxime (48g, 0.20mol) and 260ml methanol into a 500ml four-necked flask equipped with a condenser, stir to completely dissolve, then add 2g activated carbon (120 mesh ), 0.5g Raney Nickel, raise the temperature to 60℃, slowly add 80% hydrazine hydrate (28.75g, 0.46mol) dropwise, keep the reaction temperature between 58℃-62℃, nitrogen will be released during the reaction, the dropping speed It is better to control the nitrogen release rate so that it is not too fast. Use liquid chromatography to track the reaction process. When the raw material 1,2-diphenylethylenedioxime disappears, end the reaction. Cool the mixture, filter Raney nickel and activated carbon, and add a small amount of it. Cover with water and save for reuse. The filtrate is distilled to recover methanol. Add 200ml petroleum ether to the remainder and heat it to completely dissolve it. Cool for 24 hours and filter to obtain 41.55g of the product (1R, 2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine. Collect The rate is 98% and the chemical purity is 99.57%.
Main reference materials
[1] Du Yu. Synthesis of a type of (1R,2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine suspended zirconium-supported ruthenium organophosphonate catalyst and its application in asymmetric transfer hydrogenation. ( Doctoral dissertation).
[2] Zhang Danxia. Preparation and performance study of (1R,2R)-1,2-diphenylethylenediamine molecularly imprinted polymer coated on silica gel surface. (Doctoral dissertation).
[3] Zhang Bangle, & Zhang Shengyong. (1999). Synthesis of optically pure (+)-(1r,2r) and (-)-(1s,2s)-1,2-bis using asymmetric dihydroxylation reaction Phenyl-1,2-ethylenediamine. Chemical Reagents (3), 133-134.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

