Silk black is the general name for white amorphous powdery silicic acid and silicate products, mainly referring to precipitated silica, vapor phase silica, ultra Fine silica gels and aerogels, including powdered synthetic aluminum silicate and calcium silicate, etc. According to the production method, silica is generally divided into precipitation silica and fumed silica (scientific name: fumed silica).
Vapor-phase silica is normally white amorphous flocculent translucent solid colloidal nanoparticles. It is non-toxic and has a huge specific surface area (100-400m2/ g). Vapor-phase silica is all nanoscale silica, with a product purity of more than 99.8% and a primary particle size of 10-40nm; precipitation silica is divided into traditional precipitation silica and special precipitation silica. The former refers to silica produced using acid (sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid, etc.), CO2 and water glass as basic raw materials, while the latter refers to silica produced using hypergravity technology, sol-gel method, chemical crystal method, secondary crystallization method or reverse crystallization method. Silica produced by special methods such as phase micelle microemulsion method.

Vapor phase silica
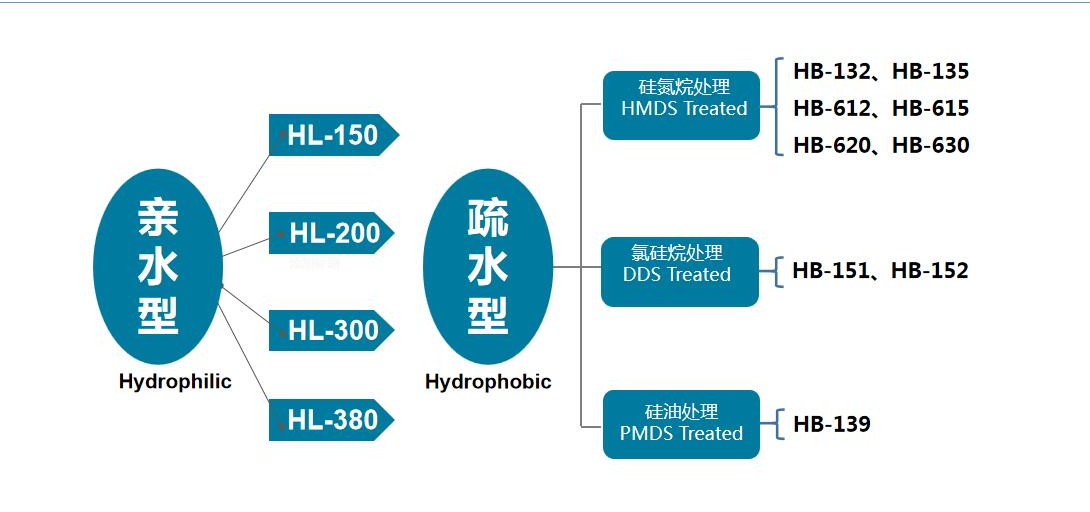
Vapor silica product classification
Comparison between gas phase silica and precipitation silica
1. The structural difference between gas phase silica and precipitation silica
Vapor phase silica is neither produced through simple crushing nor special drying. In any case, the smallest particle is the primary particle, but it will more or less agglomerate (because there are a large number of silanol groups on the surface), and the special surface is its most important property. Silica gel has a large internal surface area, which is why it has extremely strong adsorption capacity. In contrast, the primary particles of fumed silica are hydrolyzed by flames and have only an outer surface area. This also explains why the rheology of many systems is greatly improved after combining with fumed silica, such as the application of fumed silica in powder coatings. Table 1 gives the particle size of gas phase silica particles.
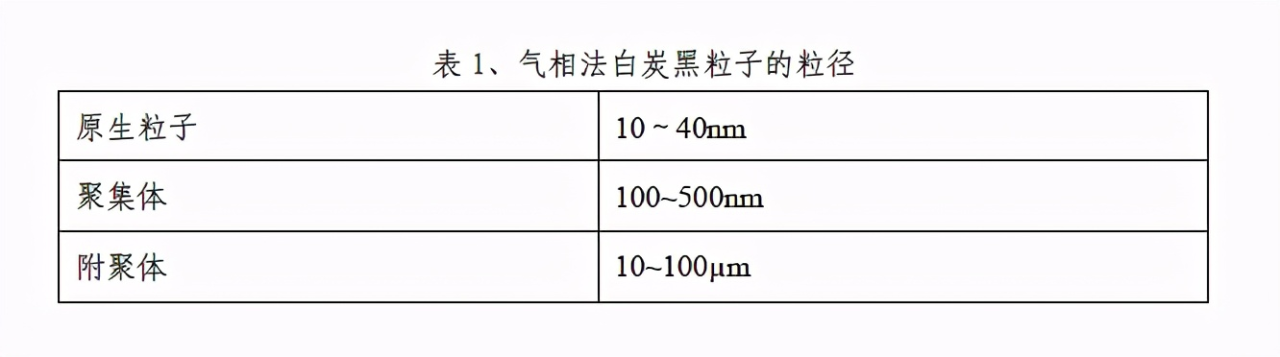
Table 1
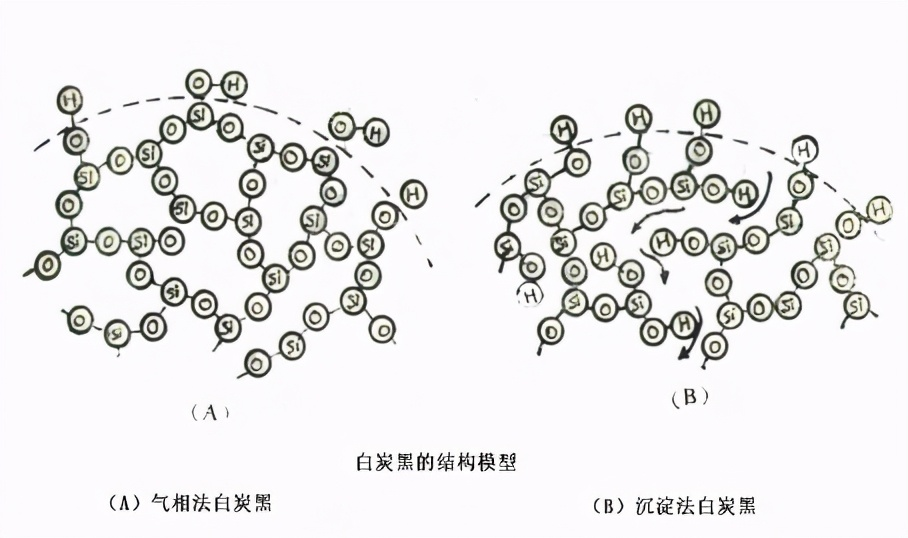
Figure 1 Comparison of the structural models of gas phase silica and precipitation silica
2. The difference in the number of silica hydroxyl groups between gas phase silica and precipitation silica
The difference in drying loss of silica has a great impact on product characteristics and product application performance. The lower the drying loss requirement of silica, the better. For example, the lower the drying loss, the better the insulation properties of the silicone rubber used to make cables. It has low drying loss and can increase the stability of single-component adhesives and sealants containing silica during storage. In fact, the main difference between white carbon blacks is that their silanol numbers are different (that is, SiOH/nm2). The number of silanol groups of hydrophilic vapor phase silica is between 2 and 3. In contrast, the silanol content of precipitation silica is about 6. Surface-modified silica (hydrophobic silica) ) has a silanol content below 1.
3. The difference in silicon purity between gas phase silica and precipitation silica
The difference in purity of silica is also worth noting. In terms of anions, vapor phase silica contains only trace amounts of chloride ions and metal oxide impurities. The anions of precipitation silica include acid ions, alkaline ions and alkaline earth metal ions (about 1000ppm). Differences in process technology lead to differences in product purity.
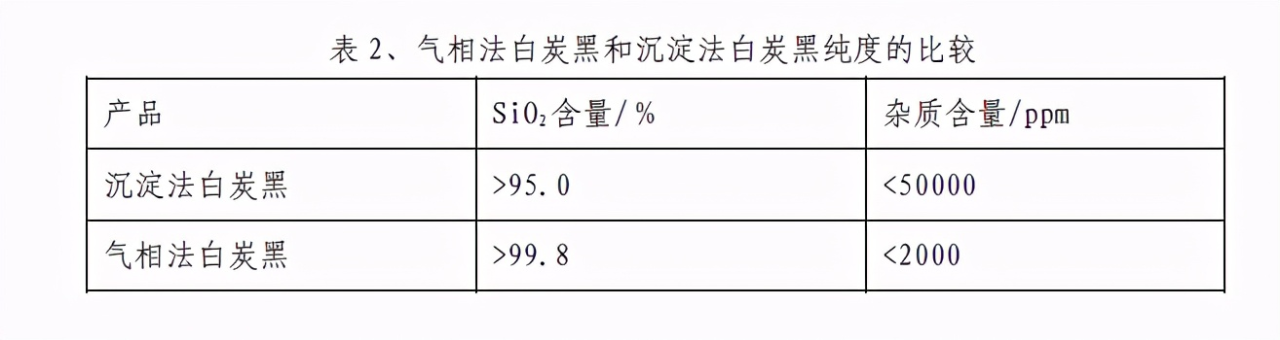
Table 2

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

