Background and overview[1][2]
4-methoxyphenylacetic acid is usually a white flaky crystal with a melting point of 84-86°C. It is easily soluble in hot water, ethyl acetate, ethanol, ether, etc., and is soluble in cold water. p-Methoxyphenylacetic acid is an intermediate in the synthesis of a new generation of antidepressant drug Venlafaxine, and is also a key intermediate in the synthesis of various cardiovascular drugs such as puerarin and isoflavones. Regarding its synthesis method, reports at home and abroad mainly include the following: a) Cyanation method, generally using p-methoxybenzyl chloride and sodium cyanide to react to generate p-methoxyphenylacetonitrile, which is hydrolyzed to obtain p-methyl Oxyphenylacetic acid, this method uses highly toxic cyanide, so there are serious safety risks; b) Acetophenone rearrangement method, this method often uses p-methoxyacetophenone as raw material, together with sulfur and hexahydrate Piperazine reaction, after rearrangement and hydrolysis, p-methoxyphenylacetic acid is obtained, but the hydrogen sulfide generated by this method is highly toxic and smelly, and the yield is not high; c) Oxo synthesis method, which uses p-methoxybenzyl chloride As raw material, it reacts with CO under the action of a catalyst to generate p-methoxyphenylacetic acid. The disadvantage of this method is that the catalyst used is expensive and CO is also more harmful.
Structure[2-5]
P-Methoxyphenylacetic acid is an important pharmaceutical intermediate and is widely used in medicine, dyes, etc. For example, p-methoxyphenylacetic acid is an important raw material for the synthesis of dextromethorphan intermediate 1-(4-methoxybenzyl)-1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8-octahydroisoquinoline ; It is also an important raw material for the synthesis of a new generation of antidepressant drug Wenlafaxin; it is also an important raw material for the synthesis of α, β-diaryl-substituted acrylic acid, an important intermediate for the synthesis of anti-tumor, antifungal and antibacterial drugs phenanthrobiridine alkaloids ; In addition, p-methoxyphenylacetic acid is also a key intermediate in the synthesis of puerarin, isoflavones and other cardiovascular drugs. Other applications are as follows:
1. Prepare levorphan tartrate. The method uses p-methoxyphenylacetic acid and 2-(cyclohexenyl)ethylamine as starting materials and undergoes acylation condensation, Bischler-Napieralski cyclization reaction, imine reduction, ether bond hydrolysis, resolution, and N-alkane There are nine steps in total including tylation, Grewe cyclization reaction and salt formation. This method obtains levorphan tartrate and various intermediates with high yield and high purity, and can be used as an industrial method for large-scale production.
2. Preparation of formononetin. Condensate first, add resorcinol, p-methoxyphenylacetic acid, and boron trifluoride ether in a dry reactor, heat the reaction. After the reaction is completed, add water, heat to reflux, cool to precipitate crystals, filter, and wash with water until neutral. , dry to obtain the intermediate; then cyclize, add the intermediate, triethyl orthoformate, morpholine, DMF and glacial acetic acid to a dry reaction tank, separate the reaction by-product ethanol, heat to reflux, complete the reaction, and reduce the pressure Recover the DMF reagent, cool it, add saturated sodium bicarbonate solution to the residue, reflux, cool down, precipitate and crystallize, obtain crude formononetin through conventional treatment, and obtain fine formononetin through methanol refinement. The present invention solves the current problem of formononetin. The problem of lack of resources of phosphorus is that it has the advantages of easy availability of raw materials, efficient reaction and convenience, and has high application value.
3. A method for preparing 2,4-dihydroxy-4-methoxydeoxybenzoin, including the following steps: (1) Add resorcinol, zinc chloride, and p-methoxybenzene to a dry container Acetic acid, vacuum to within -0.06Mpa, stir and react at 120℃~140℃ for 30~120min; (2) After the reaction, cool down to below 100℃, add water to dissolve the material, stir for 30~100min, and cool to 5~30℃, crystallize; (3), filter, wash the filter cake with water until neutral, and dry to obtain the product. The invention is reasonably designed and uses zinc chloride as a catalyst. By adjusting the temperature and pressure, that is, the reaction conditions are mild and under negative pressure, the key intermediate of formononetin can be prepared. No special equipment is required and it will corrode the equipment. It has low toxicity, fast safety, easy operation, small waste liquid and low pollution.
Preparation [1, 6]
Method 1: Using anisole (2) as raw material, Friedel-C raft s acylation reaction occurs with ethyl oxalyl chloride under the catalysis of AlCl3 to generate ethyl p-methoxyacetophenonate (3) , the latter directly undergoes Wolff-Kishner-Huang reaction with hydrazine hydrate without separation to obtain the target product (1), with a total yield of 55.4%. The raw materials used in this synthesis route are cheap, there is no need to use expensive and highly toxic reagents, and the industrial prospects are good. The specific reaction formula is shown in the figure.

Step 1: Synthesis of ethyl p-methoxyacetophenonate (3)
Add 14.7 g (0.11 mol) anhydrous aluminum trichloride, 120 mL 1,2-dichloroethane and 10.8 mL (0.10 mol) anisole, stir evenly and heat to 45°C, add 12.3 mL (0.11 mol) oxalyl chloride monoethyl ester, and keep warm for 8 h. After the reaction is completed, cool in an ice-water bath, add 100 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid aqueous solution with a concentration of 10%, and separate the organic layer. Washed with 5% sodium bicarbonate solution (50 mL × 2) and water (80 mL × 2) in sequence, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and filtered, the filtrate was concentrated to dryness under reduced pressure to obtain 17.8 g of crude product (3). The rate is 85.5%. This product was directly used in the next step of synthesis without purification.
Step 2: Synthesis of p-methoxyphenylacetic acid (1)
Add 17.8 g (0.086 mol) of crude product (3), 110 mL ethylene glycol and 12 mL (0.24 mol) 85% hydrazine hydrate into a 250 mL three-necked flask, slowlyRaise the temperature to 130°C and react for 2 hours. Then cool the reaction solution to room temperature and add 13.4 g (0.24 mol) of solid potassium hydroxide. Heat the temperature to 180°C and react for 4 hours. While increasing the temperature, the low boiling matter (about 2 h), and then reflux for 4 h. After the reaction is completed, cool to room temperature and add 6 mol/L hydrochloric acid (about 55 mL) to adjust the pH to 1~2. Add 180 mL of water, extract with ethyl acetate (50 mL × 2), and combine the organic phases. The combined organic phases were washed with water (10 mL After suction filtration and drying the filter cake, 9.2 g of silver-white scaly crystals (1) were obtained. The yield in this step was 64.4%m.p.84~86°C.
Method 2: A method for synthesizing p-methoxybenzoic acid from anisole. The reaction formula and operating steps are as follows:
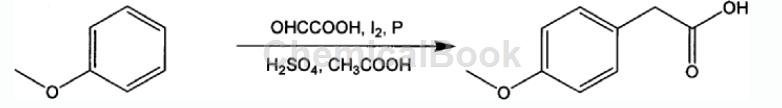
The steps are as follows:
1) Add the following materials into the round-bottomed flask in sequence according to the formula of 1 mol anisole, 0.3-1.5 mol glyoxylic acid, 1-20 mL concentrated acid, iodine, red phosphorus, and 100-1500 mL glacial acetic acid;
2) Stir the above materials at 50-100°C for 2-12 hours, and use high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) to take samples and monitor them. After the reaction is completed, reduce to room temperature, filter out the red phosphorus, and collect the filtrate;
3) Add 10-100mL of 10% sodium acetate aqueous solution to the above filtrate. After stirring, add concentrated hydrochloric acid dropwise to adjust the pH value of the mixture to 1-2. Wait until the precipitate precipitates, filter and collect the filter residue;
4) Dry the above filtrate to obtain crude p-methoxyphenylacetic acid, which is then distilled under reduced pressure to obtain pure p-methoxyphenylacetic acid;
Main reference materials
[1] Research on new synthesis process of p-methoxyphenylacetic acid
[2] CN201510111704.0 Preparation method of p-methoxyphenylacetic acid
[3] CN201610886326.8 A preparation method of levorphan tartrate
[4] CN201010600926.6 A kind of synthesis method of formononetin
[5] CN201610677984.62, preparation method of 4-dihydroxy-4-methoxydeoxybenzoin
[6] CN201310319288.4 A method for synthesizing p-methoxyphenylacetic acid from anisole

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

