Background and overview[1][2]
In recent years, hypervalent iodine reagent has been favored by the majority of scientific research work as a mild, low-toxic, and highly selective oxidizing reagent, and has been used in many synthetic transformations. In some research works, hypervalent iodine reagents have replaced transition metal reagents well and demonstrated mild oxidation properties. Therefore, hypervalent iodine compounds have become a multifunctional reagent in organic synthesis. Iodophenyl diacetic acid is an organic hypervalent iodine compound. It is a mild, non-toxic oxidant and a strong electrophilic reagent. Compared with previous heavy metal oxides such as KMnO4, CrO3, etc., it has the advantages of non-polluting and non-toxic. Traditional heavy metal oxidants produce pollution after use, affecting the environment and causing a waste of resources.
Apply[2-5]
Iodophenylacetic acid is used in pharmaceutical and other industries. It has good selective oxidation properties and has been increasingly widely used in recent years. For example, the synthesis of the latest oral lung cancer treatment drug topotecan, the anti-inflammatory analgesic drug naproxen, the antidepressant fluoxetine, the influenza drug oseltamivir (Tamiflu) to deal with avian influenza, and the anti-tumor drug Aranorosin, in addition to Used for Hofmann degradation, such as the synthesis of unnatural amino acids L-2, 3-diaminopropionic acid and L-2, 4-diaminobutyric acid, catalytic halogenation, and ring formation of heterocyclic compounds such as benzimidazole. Oxidation of phenol, oxidation of porphyrinogen, etc. The products have wide uses, stable properties, and are easy to store. The by-product of the reaction is usually the relatively expensive organic raw material iodobenzene, which can be recycled and used, or used to synthesize other compounds. , does not pollute the environment and is a very ideal oxidizing reagent. If there is a study on using iodophenylene diacetic acid to promote the chlorination reaction of aryl ketone enol silyl ethers, acetophenone-derived enol silyl ether 1a (0.5 mmol), iodophenylene diacetic acid and trimethylchlorosilane are used as template reactions :
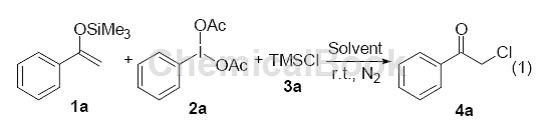
Utilizing iodophenylacetic acid and trimethylsilyl chloride as the chlorine source, a method for preparing α-chloroaryl ketones from aryl ketone enol silyl ethers was realized. This method has the characteristics of simple operation and mild reaction conditions. Through this reaction, the product α-chloroaryl ketone can be obtained with medium or good yield. And by using trimethylsilyl bromide instead of trimethylsilyl chloride, this reaction can also be used to prepare α-bromoaryl ketones.
In addition, iodobenzene diacetic acid can also be used to prepare iodobenzoic acid derivatives. The specific method is to first add 6 mmol of iodobenzene diacetic acid, benzoic acid, benzoic acid derivatives or tetrapentyl in a 25mL round-bottomed flask. 12 mmol of acid, add 5 ml of methanol until benzoic acid or benzoic acid derivatives and iodophenylene diacetic acid are all dissolved in methanol; place the round-bottomed flask on a rotary evaporator and heat to 45°C for reaction for 0.5 h; Distill the solvent under reduced pressure and spin it dry, and a large amount of white solid can be seen precipitating; pour the solid obtained from the reaction solution into a Buchner funnel, wash it three times with 15 ml of methanol, and dry the remaining white solid; an iodobenzene dibenzoate is obtained. Derivatives; the benzoic acid derivatives are 4-methoxybenzoic acid, 4-methylbenzoic acid, 4-chlorobenzoic acid, 4-fluorobenzoic acid or 4-nitrobenzoic acid.
Iodophenyl diacetic acid can also be used to prepare the cationic photoinitiator (2-hydroxytetradecyloxyphenyl) benzene iodonium hexafluoroantimonate. The specific method is to dissolve iodobenzene diacetic acid in p-toluene in a solvent. It is prepared by a one-step reaction with 2-hydroxytetradecyloxybenzene in the presence of sulfonic acid. The reaction temperature is room temperature and the reaction time is 4-24 hours. After the reaction is completed, the solvent is concentrated to remove (2-hydroxytetradecyloxybenzene). base) benzene iodonium p-toluenesulfonate, and finally perform ion exchange with sodium hexafluoroantimonate in acetone to obtain the product. Compared with the existing technology, the above process is reasonable, simple to operate, safe to produce, suitable for industrial large-scale production, and provides favorable conditions for the industrial production of (2-hydroxytetradecyloxyphenyl)phenyliodonium hexafluoroantimonate
Preparation [1, 3]
Method 1: A method for preparing iodobenzene diacetic acid. This method uses sodium perborate tetrahydrate as raw material, and undergoes an acylation reaction with iodobenzene in the presence of glacial acetic acid/acetic anhydride mixture, in which sodium perborate tetrahydrate is used. The molar ratio of sodium borate to iodobenzene is 3-10:1, the reaction temperature is 30℃-45℃, and the reaction time is 4-24 hours. After the reaction, add ice waterThe crude product of iodophenylene diacetic acid is obtained, and then recrystallization is performed to obtain iodophenylene diacetic acid.
Method 2: Preparation method of highly efficient and environmentally friendly iodobenzene diacetic acid: use iodobenzene as the starting material, acetic acid as the solvent, react with peracetic acid, and add water to precipitate iodobenzene diacetic acid. The specific steps include: adding iodobenzene and acetic acid to the reaction bottle, controlling the temperature to 30-40℃, adding peracetic acid dropwise, stirring for 5 hours after the drops are completed, and cooling to 5-10℃ >, centrifuge, wash the filter cake with water and n-heptane in sequence, and dry it to obtain iodophenylene diacetic acid.
Main reference materials
[1] CN200910049332.8 A kind of preparation method of iodophenylene diacetic acid
[2] Iodophenylacetic acid promotes the chlorination reaction of aryl ketone enol silyl ethers
[3] CN201711043495.6 Efficient and environmentally friendly preparation method of iodophenylene diacetic acid and mother liquor recycling method
[4] CN201610674608.1 Preparation method and device of iodobenzoic acid derivatives
[5] CN201410257994.5 Preparation method of cationic photoinitiator (2-hydroxytetradecyloxyphenyl) benziodonium hexafluoroantimonate

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

