Background and Overview
2-Bromo-3-methylphenol is a phenol derivative that can be used as an organic raw material for the preparation of pharmaceutical intermediates.
Preparation[1]

Dissolve 2-amino-m-cresol 8a (5.7g, 46.3mmol) in H2O (30mL) and 1,4-dioxane (15mL). The mixture was heated to reflux, then HBr (48%, 17 mL, 0.31 mol) was added dropwise over 20 min. After the addition is complete, maintain reflux for an additional 15 minutes. The reaction was cooled to 0°C and a solution of NaNO2 in H2O (20 mL) was added over 30 minutes. Stirring was continued at 0 °C for 15 min, then the mixture was transferred in one portion to stirred Cu(1)Br (7.64 g, 53.2 mmol) in HO (20 mL) and HBr (48%, 17 mL, 0.31 mol) in a mixture. At 0°C (no light). The reaction was stirred at 0°C for 15 minutes, warmed to 60°C, stirred for an additional 15 minutes, cooled to room temperature, and then stirred overnight. The reaction mixture was then transferred to a separatory funnel and extracted with EtOAc (3x). The organic layers were combined, washed with brine, dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered and concentrated over silica to give a mixture that was purified using a CombiFlash Companion (20% EtOAc/Hexane) to give the desired The bromide 2-bromo-3-methylphenol 8b (1.46 g, 17% yield) was a reddish-brown oil.
Apply [2]
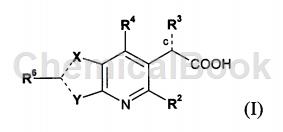
WO 2009062288 provides a series of new compounds with anti-HIV replication inhibitory activity. Representative compounds of the present invention have activity as inhibitors in cell-based HIV replication assays. The compounds of the invention have affinity for HIV integrase. Therefore, the compounds of the present invention can be used to inhibit the activity of HIV integrase and can be used to reduce HIV replication. Other objects of the present invention can be obtained by those skilled in the art from the following description and examples. The present invention provides isomers, racemates, enantiomers or diastereomers of the compound of formula (I):
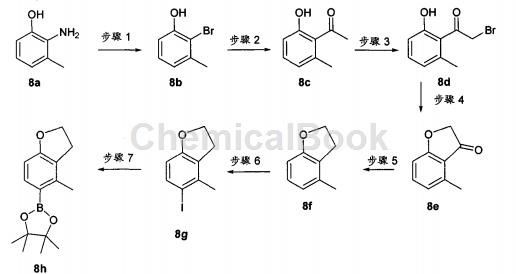
Synthesis of boronic acid ester fragment 8h (which can be coupled to the thienopyridine skeleton to obtain the compound of the present invention)
Step 1
2-Amino-m-methylphenol 8a (5.7 g, 46.3 mmol) was dissolved in H2O (30 mL) and 1,4-dioxane (15 mL). The mixture was heated to reflux, then HBr (48%, 17 mL, 0.31 mol) was added dropwise over 20 minutes. After the addition is complete, reflux for another 15 minutes. The reaction was cooled to 0°C and NaNO2 in H2O (20 mL) was added over 30 min. Stirring was continued at 0°C for 15 min, then the mixture was transferred in one injection to Cu(I)Br (7.64 g, 53.2 mmol) in H2O (20 ml) and HBr (48%, 17 ml, 0.31 mol) in the stirring mixture (protected from light). The reaction was stirred at 0°C for 15 minutes, warmed to 60°C, stirred for an additional 15 minutes, cooled to room temperature, and then stirred overnight. Next, the reaction mixture was transferred to a separatory funnel and extracted with EtOAc (3x). The organic layers were combined, washed with brine, dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated on silica gel to give a mixture that was purified using Companion (20% EtOAc/Hexane) to give the desired bromide 2-bromo-3- Methylphenol 8b (1.46 g, 17% yield) was a reddish-brown oil.
Step 2:
To a solution of bromide 8b (1.36 g, 7.27 mmol) and (PPh3)2PdCl2 (766 mg, 1.09 mmol) in DMF (12 mL) was added 1-ethoxyvinyl-tris- n-Butyltin (2.7 mL, 8.0 mmol). The mixture was covered and heated in the microwave at 160°C for 15 minutes. HPLC and LC-MS analysis showed approximately 70% conversion. More 1-ethoxyvinyl-tri-n-butyltin (2.7 mL; 8.0 mmol) and catalyst (PPh3)2PdCl2 (380 mg, 0.05 mol%) were added and the solution was again subjected to the same microwave conditions. The reaction was quenched with 6N HCl (1.5 mL) and stirred at room temperature for 1 hour until hydrolysis of the intermediate was achieved. The mixture was poured into EtOAc (150 mL), washed with brine (3x), dried over MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated on silica gel to give a mixture which was purified using Companion to afford the desired ketone 8c (947 mg, 87% Yield), as orange oil.
Step 3:
Methyl ketone 8c (1.02 g, 6.8 mmol) was dissolved in EtOAc (15 mL) and CHCl3 (15 mL) and treated with Cu(II)Br2 (3.03 g, 13.6 mmol). The mixture was heated to reflux for 16 hours. The mixture was cooled to room temperature and the product was filtered and washed with EtOAc (1x). The solution was concentrated on silica gel to give a mixture which was purified using Companion (10% EtOAc/hexanes) to give α-bromoketone 8d (710 mg, 46% yield) as an orange oil. This material was used as such in the next step without purification.
Step 4:
To a solution of bromoketone 8d (710 mg, 3.1 mmol) in anhydrous DMF (12 mL) was added KF (400 mg, 6.95 mmol). The reaction was stirred at room temperature for 16 hours. The mixture was dissolved in EtOAc (150 mL), washed with brine (3x), dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated on silica gel to give a mixture which was purified using Companion (20% EtOAc/Hexane) to give cyclo Ketone 8e (280 mg, 61% yield) as a light orange solid.
Step 5:
Zn powder preactivation method: Place zinc powder (20 grams, 350 mesh) in a round-bottomed flask, and add 1N HCl (50 ml). The suspension was sonicated for 1 minute and the liquid was decanted. This step was repeated twice, then the solid was washed with EtOH (2x), Et2O (2x) and dried under high vacuum. To a solution of ketone 8e (280 mg, 1.89 mmol) in AcOH (10 mL) was added preactivated Zn powder (1.24 g, 18.9 mmol). The reaction mixture was then heated to 75°C for 2 hours. The reaction mixture was filtered (solids washed with EtOAc). The solvent was evaporated on silica gel and the mixture was purified directly using Companion (10% EtOAc/Hexane) to afford the desired dihydrobenzofuran 8f (174 mg, 69% yield) as a colorless oil.
Step 6:
To a solution of dihydrobenzofuran 8f (240 mg, 1.8 mmol) in MeOH (5 mL) was added AgNO3 (304 mg, 1.79 mmol), followed by iodine (453 mg, 1.79 mmol) ). The yellow mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1 hour. To the reaction mixture, 10% Na2S2O3 solution was added, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 15 minutes. The mixture was diluted with EtOAc (100 mL) and the organic layer was washed with brine (3x) and 10% Na2S2O3 (2x). The organic phase was dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and concentrated on silica gel to give a mixture. The mixture was purified using Companion (10% EtOAc/Hexane) to afford 8 g (400 mg, 86% yield) of the iodo derivative as a white amorphous solid.
Step 7:
Dissolve 8g of iodo derivatives (400 mg, 1.54 mmol), bis(pinacol)diborane (585 mg, 2.31 mmol), and potassium acetate (511 mg, 5.4 mmol) in DMF (20 ml) was deoxygenated (Ar balloon and sonicated for 5 min); the catalyst (PdCl2dppf, 188 mg, 0.23 mmol) was then added with subsequent degassing (Ar balloon and sonicated for 2 min). Next, the mixture was heated to approximately 95°C for 4 hours. The mixture was cooled, EtOAc (200 mL) was added, washed with brine (3x), water (2x), dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and solvent evaporated on silica gel to give a mixture which was purified using Companion (10% EtOAc/ Hexane), the desired boronic acid ester was obtained for 8 h (315 mg, 79% yield) as a yellow oil.
Main reference materials
[1] PCT Int. Appl., 2009062285, 22 May 2009
[2] PCT Int. Appl., 2009062288, 22 May 2009
p>[1] PCT Int. Appl., 2009062285, 22 May 2009
[2] PCT Int. Appl., 2009062288, 22 May 2009

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

