Background and overview[1]
Benzophenobarbital (Benzophenobarbital) is the prodrug of the sedative drug phenobarbital. Compared with phenobarbital, it has the characteristics of less toxicity, less side effects, and lower dosage. There are few reports on the synthesis of benzoyl phenobarbital. Literature reports use phenobarbital silver salt and benzoyl chloride to react and synthesize under catalyst-free conditions, with a yield of about 20%. Benzoylphenobarbital was synthesized using phenobarbital and benzoyl chloride as raw materials, 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DM AP for short) as catalyst, and triethylamine as acid binding agent. The yield was 64%, w (Benzoylphenobarbital) = 99%.
Preparation [1-2]
Method 1: Using phenobarbital and benzoyl chloride as raw materials, the efficient catalyst 4-dimethylaminopyridine is used to catalyze the synthesis of benzoylphenobarbital:
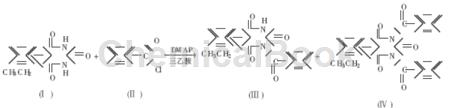
In a 250 mL three-neck flask, add 0.10 mol phenobarbital (Ⅰ), 3% DMAP, 125 mL benzene, and 0.102 mol triethylamine, stir and raise the temperature to 30 to 40 ℃, add 0.102 mol benzoyl chloride (Ⅱ) dropwise, and finish the addition in about 0.5 hours; raise the temperature to 50~55℃ for reaction, and TLC (thin layer chromatography) detects that the raw material point no longer decreases, and ends the reaction for 1.5 hours. Pour in dry hydrogen chloride to pH = 4~5 while maintaining temperature, filter while hot, and extract the solid with 2 × 100 mL benzene reflux twice; add 40 mL ethanol to dissolve the insoluble matter, and add water to recover phenobarbital. Combine the filtrate and distill under normal pressure to recover benzene to dryness (t≤90℃). Add 10 mL 95% ethanol,
After refluxing for 2 hours, add 70% ethanol to 100 mL, stir at normal pressure for 3 hours, filter the crystals and dry them to obtain 26.5 g of a mixture of (Ⅲ) and (Ⅳ). Add the above mixture to an appropriate amount of 5°C 0.1mol/L NaOH solution, stir for 5 min, and filter to obtain compound (IV). The filtrate was added to the measured 70°C, 20% hydrochloric acid solution, stirred for 10 minutes, filtered to obtain the crude product (Ⅲ); recrystallized with ethyl acetate, and dried to obtain 21.5 g of the refined product (Ⅲ), with a yield of 64%. The mass fraction is 99%, and the melting point is 134~136℃ (literature value 134~137℃). After testing, the mass fraction of impurities (I) in the refined product does not exceed 0.8%, and (IV) does not exceed 0.4%.
Method 2: Using DMAP to catalyze the synthesis of benzoylphenobarbital, the reaction time is short, the temperature is low, and the yield of the product is significantly improved:
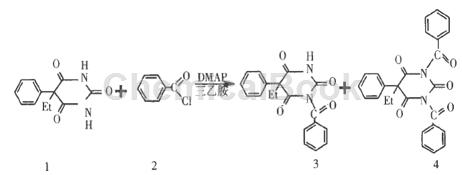
In a 250 ml three-neck flask, add 0.10 mol phenobarbital 1, 3% DMAP, 125 ml benzene, 0.102 mol triethylamine, stir to raise the temperature, and add 0. 102 mol benzoyl chloride 2, added in about 0.5 h. The temperature was raised to 50-55°C and the reaction was carried out for 1.5 hours. TLC detected that the reaction was completed. While maintaining temperature, pass dry hydrogen chloride to pH = 4 ~ 5, filter while hot, and extract the solid with 2 × 100 ml benzene reflux twice. Add 40 ml of ethanol to dissolve the insoluble matter, and add water to recover phenobarbital. The filtrates are combined and distilled under normal pressure to recover benzene to dryness (T ≤90 ℃).
Add 10 ml of 95% ethanol, reflux for 2 hours, then add 70% ethanol to 100 ml, stir at normal pressure for 3 hours, filter and dry the crystals to obtain 26.5 g of a mixture of 3 and 4. Divide the above mixture Add an appropriate amount of 0.1 mol/L NaOH solution at 5°C, stir for 5 min, and filter to obtain compound 4. FilterThe solution was added to the measured 70°C, 20% hydrochloric acid solution, stirred for 10 minutes, and filtered to obtain crude product 3. Recrystallized with ethyl acetate, and dried to obtain product 3, which was 21.5 g, with a yield of 64% and a content of 99%. , melting point 134 ~ 136 ℃ (literature value 134 ~ 137 ℃). After TLC testing, the content of impurities 1 in the product does not exceed 0.8%, and the content of 4 does not exceed 0.4%, which complies with the Soviet Pharmacopoeia XI standard.
Main reference materials
[1] Catalytic synthesis of benzoylphenobarbital using 4-dimethylaminopyridine
[2] Application of DMAP in the synthesis of benzoylphenobarbital

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

