Overview[1][2]
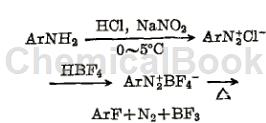
Fluorobenzene is a colorless liquid with a benzene smell. Boiling point 84.7℃, 275℃ (3850kPa), 200℃ (1317kPa), relative density 1.024, refractive index 1.4677, 1.463625, -40℃ solidification. Insoluble in water, miscible with ethanol and ether. Toxic and irritating, the limit allowable content in the air is 2.5mg/m3. Preparation method: derived from the action of diazobenzene hydrochloride and HF. Usage: Identification reagent for plastics or resins, pesticide intermediates.
Water removal method[2]
Fluorobenzene is an important organic solvent in industry and has a wide range of applications. In recent years, with the continuous advancement of science and technology, the use of fluorobenzene has been continuously developed. At present, high-purity non-aqueous fluorobenzene has been successfully used in lithium-ion battery electrolytes. Compared with the usual carbonate-containing electrolytes, more fluorobenzene is added. A large content of fluorobenzene can improve the performance of the battery. It has obvious advantages in terms of the low-temperature performance, battery life and high-temperature discharge capability of the battery. Fluorobenzene may bring moisture during production, transportation, and storage. If the moisture is too high, it will affect the moisture of the lithium-ion battery electrolyte. Excessive moisture will have a certain impact on the electrochemical performance of the battery. Usually, the electrolyte contains Moisture is controlled within 30ppm or lower. With the traditional production process, the moisture in fluorobenzene is too high and cannot meet the requirements of high-quality battery grade.
CN201010598746.9 provides a method for removing water from fluorobenzene, which is characterized by adding a water removing agent that is insoluble in fluorobenzene and can absorb moisture into fluorobenzene. The water-removing agent is aluminosilicate oxide, activated carbon, silica gel, barium sulfate or activated alumina. The amount of water-removing agent added is 1~10% of the weight of fluorobenzene. Preferably, the amount of water removal agent added is 5 to 10% of the weight of fluorobenzene. Further preferably, the added amount of water removing agent is 8% by weight of fluorobenzene. The process flow of the present invention: remove water from fluorobenzene in an argon-filled glove box (moisture content <10 ppm, oxygen content <10 ppm): place fluorobenzene into a stainless steel cylinder in proportion (the cylinder is filled with high-purity argon) After vacuuming and replacing three times), add 1 to 10% of the weight of fluorobenzene as a dewatering agent. After sealing, shake for 5-10 minutes to fully contact the fluorobenzene and the dewatering agent. Let it stand for 3-5 hours and then shake for 5 minutes. -10 minutes, take a sample to test the moisture of fluorobenzene after treatment; the temperature of the above process is controlled at 20~30℃, and the time is 3~5 hours. After the sampling and testing meet the requirements, the dehydrating agent and fluorobenzene are filtered to obtain high-quality fluorine. benzene. The beneficial effects of the present invention are: adding one or several water-removing agents to fluorobenzene can simply and quickly remove the moisture in fluorobenzene, thereby reducing the negative consequences of adding it to the lithium-ion battery electrolyte. Influence. The method of the invention is simple, can effectively reduce the moisture content in fluorobenzene, and meets the requirements of high-quality electrolyte for fluorobenzene.
Main reference materials
[1] Compound Dictionary
[2] CN201010598746.9 Fluorobenzene water removal method

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

