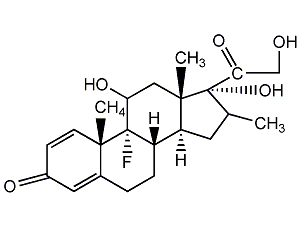
Structural formula
| Business number | 0133 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C22H29FO5 |
| Molecular weight | 392.46 |
| label |
9-Fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methyl(11β,16α)-pregnant-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, Prednisolone F, (11β,16α)-9-Fluoro-11,17,21-trihydroxy-16-methylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, 9α-Fluoro-16α-methyl-11β,17α,21-trihydroxy-1,4-pregnadiene-3,20-dione, 9α-Fluoro-11β,17α,21-trihydroxy-16α-methylpregn-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, glucocorticoids, anti-inflammatory drugs, antiendotoxin, immunosuppressants, anti-shock drugs, stress response enhancer |
Numbering system
CAS number:50-02-2
MDL number:MFCD00064136
EINECS number:200-003-9
RTECS number:TU3980000
BRN number:2066651
PubChem number:24893536
Physical property data
1. Properties: white powder
2. Melting point (℃): 255~264
3. Specific optical rotation (º, C=1, DIOXANE): 75
4. Solubility: soluble in water, 10mg/100mL, 25℃; ethanol, 1mg/mL.
Toxicological data
None
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 100.23
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 296.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 812.3
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 56.5
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 39.73
Compute chemical data
None
Properties and stability
The chemical structure of dexamethasone is that a fluorine atom is introduced at the 9α position of the B ring of prednisolone, and a methyl group is introduced at the 16α position of the D ring; both the 9α fluorine and the 16α methyl group significantly enhance its anti-inflammatory activity, while the 16α methyl group significantly enhances its anti-inflammatory activity. Reduces the water and sodium retention side effects of dexamethasone. The clinical bioequivalent dose ratio of dexamethasone and prednisolone is 0.75:5, and the biological half-life is 36-54 hours. It is classified as a long-acting glucocorticoid.
Storage method
None
Synthesis method
A new production process of dexamethasone 21-hydroxy compound, using the intermediate 21-acetate as the substrate, using an appropriate amount of methanol containing 0 to 10% chloroform as the solvent to semi-solubilize the substrate, and using alkali as the catalyst Carry out a hydrolysis reaction, neutralize with acetic acid after the reaction is complete, concentrate the reaction solution under reduced pressure to an appropriate volume, cool down, filter, rinse the filter cake with water, and dry to obtain 21-hydroxyl material. This process can shorten the production cycle, improve the quality and yield of 21-hydroxy compounds, and reduce the amount of impurities in 21-hydroxy compounds.Quantity.
Purpose
Dexamethasone, like other glucocorticoids, has pharmacological effects such as anti-inflammation, anti-endotoxin, immune suppression, anti-shock, and enhancement of stress response. Therefore, it is widely used in various departments to treat a variety of diseases, such as autoimmune diseases, allergies, etc. , inflammation, asthma and dermatology, ophthalmology diseases. Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate Injection is an indispensable emergency medicine for rescuing critically ill patients. In the past decade, clinicians have used Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate to treat and prevent drug allergies caused by various Chinese and Western medicines and to treat fever caused by viral colds. disease, the clinical dosage of dexamethasone has increased year by year. So far, my country has become the largest dexamethasone market in the world. Glucocorticoids such as dexamethasone have no obvious adverse reactions when physiological doses are used for replacement therapy. Adverse reactions mostly occur when pharmacological doses are used, and are closely related to the course of treatment, dosage, type of medication, usage and route of administration. Common adverse reactions include the following categories: 1. Long-term use can cause the following side effects: iatrogenic Cushing’s syndrome, face and posture, weight gain, lower limb edema, purple lines, easy bleeding tendency, poor wound healing, acne, menstrual disorders, Avascular necrosis of the humeral or femoral head, osteoporosis and fractures (including vertebral compression fractures, pathological fractures of long bones), muscle weakness, muscle atrophy, hypokalemia syndrome, gastrointestinal irritation (nausea, vomiting), pancreas inflammation, peptic ulcer or perforation, growth inhibition in children, glaucoma, cataracts, benign intracranial hypertension syndrome, impaired glucose tolerance and exacerbation of diabetes. 2. Patients may experience psychiatric symptoms: euphoria, excitement, delirium, restlessness, disorientation, or depression. Psychiatric symptoms are more likely to occur in people suffering from chronic wasting diseases and those who have had mental disorders in the past. 3. Concurrent infection is the main adverse reaction of adrenocortical hormone. Mainly fungi, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Staphylococcus aureus, Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and various herpes viruses. 4. Glucocorticoid withdrawal syndrome. Sometimes patients experience dizziness, fainting tendencies, abdominal or back pain, low-grade fever, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, muscle or joint pain, headache, fatigue, and weakness after stopping the drug. After careful examination, if adrenal insufficiency and the original disease can be ruled out, If the disease relapses, it may be considered as a syndrome of dependence on glucocorticoids. The glucocorticoid dexamethasone is commonly known as “skin opium” and is an ingredient strictly prohibited in cosmetics. Consumers who use cosmetics containing dexamethasone will initially feel that their skin has improved significantly, but long-term use will not only cause dependence, but also lead to dermatitis Even various diseases.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

