Background and overview[1][2]
Diphenylbromobutyric acid, also known as 4-bromo-2,2-diphenylbutyric acid, is a key intermediate for the preparation of loperamide. Loperamide is similar to morphine in that it can significantly inhibit intestinal peristalsis and stop diarrhea, but it does not have the same central inhibitory effect as morphine, nor does it affect the transport of solutes and water in the intestinal lumen. The antidiarrheal effect is fast and long-lasting. It can effectively and safely control acute and chronic diarrhea, and can reduce the outflow and increase the hardness of ileostomy patients.
Preparation[1]
After the action of benzene acetonitrile and sodium amide, ethylene oxide is introduced for reaction, and 36% hydrogen bromide in glacial acetic acid solution is added to the resulting compound to obtain 4-bromo-2,2-diphenyl Butyric acid.
Apply[1-2]
1. Used to prepare loperamide: After the action of diphenyl acetonitrile and sodium amide, ethylene oxide is introduced for reaction, and 36% hydrogen bromide in glacial acetic acid solution is added to the resulting compound to obtain 4 -Bromo-2,2-diphenylbutyric acid, then chlorinated acid chloride with ammonium sulfoxide, and then in toluene and water, passed in dimethylamine for acylation, and finally with 4-hydroxy-4-p-chlorophenyl Piperidine reaction yields loperamide.
2. Used in the preparation of loperamide derivatives:
CN201610545435.3 Based on the study of the pathogenesis of MLL leukemia and the targetability of the menin-MLL interaction interface in the treatment of MLL leukemia, through the virtual screening method of skeleton transition and combined with experimental verification at the molecular and cellular levels, it was discovered that Loperamide hydrochloride, a marketed drug originally used for antidiarrhea, and its multiple derivatives have promising applications in the treatment of MLL leukemia. Experiments have shown that loperamide and its derivatives can bind to menin protein, disrupt the menin-MLL interaction system, down-regulate highly expressed HOX series genes, and cause MLL leukemia cells to produce G0/G1 cycle arrest and tend to differentiate and undergo apoptosis. , thereby inhibiting the proliferation of MLL leukemia cells. Compound 30 was prepared from diphenylbromobutyric acid (compound D) using the following method:
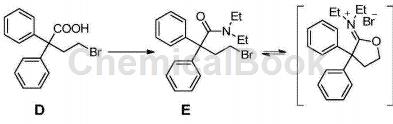
Add thionyl chloride (2mL) to the chloroform solution (15mL) of compound D (2g), react under reflux conditions for 4 hours, spin the solvent to dryness, add toluene (7mL) to dissolve, and transfer to a dropping funnel. Add diethylamine (0.77mL), sodium carbonate (1.59g), and water (10mL) to another reaction bottle. Slowly add the toluene solution in the dropping funnel at 0°C. After 2 hours of reaction, add chloroform and water for extraction. , the organic layer was dried and concentrated to obtain E, and then the next step was continued.
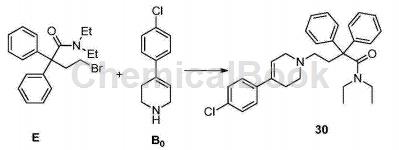
Add compound E (373 mg), compound B0 (229 mg), sodium carbonate (318 mg), and acetonitrile (5 mL) into the reaction flask, and react at 80 degrees for 4 hours. After the reaction is completed, extract with ethyl acetate, and the organic layer is dried and concentrated. Compound 30 (398 mg, 82%) was obtained after column chromatography.
Main reference materials
[1] CN201310732844.0 Preparation method of loperamide
[2] CN201610545435.3 Roperamide derivatives and their application in preparing drugs for treating mixed lineage leukemia

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

