Background and overview[1][2]
2,6-Dibromotoluene can be obtained by bromination of p-nitrotoluene and can be used to prepare 2,6-dibromobenzyl.
Preparation[1]

1,3-Dibromo-2-methyl-5-nitrobenzene: To a solution of 1-methyl-4-nitrobenzene (30.0g, 218.8mmol) in CHCl3 (120mL), add iron powder (3.6g, 64.5mmol) and stir mechanically. Then bromine (124.8g, 40mL, 780.9mmol) was slowly added while increasing the temperature to 40°C. After addition of bromine, the mixture was heated to reflux for 48 hours. After cooling, wash the solution with saturated Na2SO3 solution, saturated Na2CO3 solution, and brine. , and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. After removal of the solvent, the residue was recrystallized from MeOH to obtain 26.5 g of the title compound as yellow crystals. An additional 12.3 g of the title compound were obtained by silica column chromatography. Overall yield: 60%. 1,3-Dibromo-2-methyl-5-nitrobenzene, yield 12.3g, 60%. 1H NMR (400MHz, CDCl3) δ2.67 (s, 3H), 8.38 (s, 2H).
5-(3,5-Dibromo-4-methylphenyl)amine: Dissolve 1,3-dibromo-2-methyl-5-nitrobenzene (11.3g, 38.3mmol) in THF / EtOH (100mL / 100mL), then add SnCl2 2H2O (43.2g, 191.6mmol). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 3 hours. After removing the solvent, add NaOH solution (25g/200mL) and stir the mixture for 1.5 hours. The solution was extracted with EtOAc (200 mL×2) and dried over anhydrous Na2SO4. After removal of EtOAc, CH2Cl2 was added, followed by concentrated HCl (7 mL) to form the hydrochloride salt, which was collected by filtration. The solid was used in subsequent reactions without further purification. (3,5-Dibromo-4-methylphenyl)amine. 1 H NMR (400MHz, D2O) δ2.43 (s, 3H), 3.61 (br, 2H), 6.86 (s, 2H).
1,3-Dibromo-2-methylbenzene: Stir a solution of (3,5-dibromo-4-methylphenyl)amine in water (80 mL) and concentrated HCl (7.5 mL) 20 minutes, then cool the mixture and add NaNO2 (3.4g/40mL H2O) solution at 0-5°C. The reaction mixture was stirred at 0-5 °C for 2 h, then the suspension was added to a solution of hypophosphorous acid (50%, 27.9 g) and the mixture was cooled to 0 °C. The mixture was stirred at room temperature overnight. Then extract with CH2Cl2 (100mL×2). The organic layer was washed with brine (30 mL) and dried over Na2SO4. After silica column chromatography (eluting with petroleum ether), 3.57 g of product were obtained as a colorless liquid. 1,3-dibromo-2-methylbenzene, yield 3.57g. 1H NMR (400MHz, CDCl3) δ2.57 (s, 3H), 6.89 (t, J = 8.0Hz, 1H), 7.50 (d, J = 8.0Hz, 2H).
Apply[2]
2,6-Dibromobenzyl is an important pharmaceutical intermediate. Leukotrienes and prostaglandins are important mediators of inflammation and can respectively promote the development of inflammation in different pathways. Patent WO2006128142A2 uses 2,6- Cytoplasmic phospholipase (cPLA2) synthesized from benzyl dibromide as raw material can be used as a chemical inhibitor of leukotriene and prostaglandin activity to achieve the effect of treating inflammation; Adri et al. synthesized it from benzyl dibromide as raw material. Ropinirole is a drug used to treat Parkinson’s syndrome; the tetrahydroquinoline compound synthesized by Thomas et al. using 2,6-dibromobenzyl as raw material is a new cholesterol ester transfer protein inhibitor.
The synthesis of 2,6-dibromobenzyl is based on 2,6-dibromotoluene as raw material and prepared through bromination reaction. This reaction uses N-bromosuccinimide as the bromination reagent, benzoyl peroxide as the initiator, and carbon tetrachloride as the solvent. The yield is 89.0%. Although this method has a higher yield, there are problems such as N-bromosuccinimide being more expensive, the solvent being highly toxic, and benzoyl peroxide introducing impurities.
CN201110000564.1 provides a simple and economical preparation method of 2,6-dibromobenzyl. This method uses hydrobromic acid and hydrogen peroxide to replace the traditional bromination reagent N-bromosuccinimide; uses light to replace the initiator benzoyl peroxide; uses non-toxic or less toxic solvents to replace the highly toxic tetrachloride carbon.
Hydrobromic acid reacts with hydrogen peroxide to produce bromine, and bromine free radicals are generated under light triggering.The methyl hydrogen is taken to generate 2,6-dibromobenzyl radical, which finally reacts with bromine to generate 2,6-dibromobenzyl and bromine radicals, which continue to participate in the next round of radical substitution reactions. The traditional bromine substitution method generates a molecule of bromine product and a molecule of highly corrosive hydrogen bromide, which has low raw material utilization and is not conducive to environmental protection. In the present invention, hydrogen bromide is always in the reaction cycle, which greatly improves the utilization rate of the bromination reagent and reduces the production cost.
The reaction process is as follows:
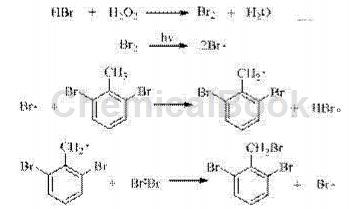
Because the Br atom has a strong electron-withdrawing ability, the reactivity of methyl hydrogen is low; at the same time, the steric hindrance of the reaction is large, making the reaction extremely high selectivity for monobromination.
The preparation method of 2,6-dibromobenzyl involved in the present invention is to use 2,6-dibromotoluene as raw material and prepare it through bromination reaction. The reaction formula is as follows:
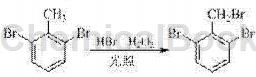
It is characterized by including the following steps:
(1) In the presence of organic or inorganic solvents, add compound 2,6-dibromotoluene and 40% hydrobromic acid, and add 30% hydrogen peroxide dropwise under light conditions, reaction 6 ~24h;
(2) The reaction solution was washed with saturated sodium sulfite solution, water, and dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate, and then the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure. Compound 2,6-dibromobenzyl was obtained by silica gel column chromatography.
Main reference materials
[1] PCT Int. Appl., 2009100169, 13 Aug 2009
[2] CN201110000564.1 A kind of preparation method of 2,6-dibromobenzyl

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

