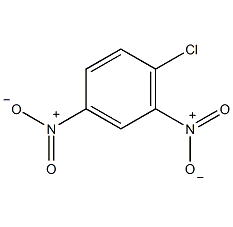
Structural formula
| Business number | 02BS |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H3ClN2O4 |
| Molecular weight | 202 |
| label |
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene, 4-Chloro-1,3-dinitrobenzene, 2,4-dinitrobenzene chloride, 1,3-dinitro-4-chlorobenzene, 6-Chloro-1,3-dinitrobenzene, Chlorodinitrobenzene, 2,4-diazochlorobenzene, 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene, 4-Chloro-1,3-dinitrobenzene, Aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:97-00-7
MDL number:MFCD00007075
EINECS number:202-551-4
RTECS number:CZ0525000
BRN number:613161
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Characteristics: light yellow or yellow-brown needle-like crystals with a bitter almond smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 52~54[2]
3. Boiling point (℃) : 315[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.69[4]
5. Relative Vapor density (air = 1): 6.98[5]
6. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.17[6]
7. Flash point (℃): 194 (CC) [7]
8. Explosion limit (%): 22.0[8]
9. Lower explosion limit (%): 2.0[9]
10. Solubility: insoluble in water, easily soluble in ethanol and ether. [10]
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation: Standard Dresser test: human skin contact, 30μg; starting irritation test: rabbit skin contact, 100μg/24H; standard Dresser test: rabbit skin contact, 2mg/24HREACTION SEVERITY, strong reaction; Standard Dresser test: rabbit eye contact, 50μg/24 HREACTION SEVERITY, strong reaction; 2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 780mg/kg; rat peritoneal cavity LD50: 280mg/kg; rabbit skin contact LD50: 130mg/kg kg; 3. Other multiple dose toxicity: Rat oral TDLo: 2340mg/kg/30D-I; Rat inhalation TCLo: 200 μg/m3/4H/17W-I; 4. Mutagenicity: Mutant microbial test: Bacteria -Salmonella typhimurium, 3μg/plate; Mutant microorganism test: bacteria-Salmonella typhimurium, 50μg/plate; DNA damage test: rat liver, 5μmol/L; DNA damage test: mouse peritoneal cavity, 30mg/kg; Morphological transformation test: hamster kidney, 10mg/L; 5. It is a highly toxic substance. The time-weighted average allowable concentration of toxic substances in the air in the workplace is 0.6mg/m3, and the allowable concentration for short-term exposure is 1.8mg/m3. Toxic if taken orally, inhaled or in contact with skin, and has cumulative hazards.
6. Acute toxicity[11] LD50: 640mg/kg (rat oral); 130mg/kg (rabbit dermal )
7. Irritation[12]Rabbit transdermal: 100mg (24h), causing irritation (open stimulation test)
8. Mutagenicity[13] Microbial mutagenicity: Salmonella typhimurium 3μg/dish. DNA damage: 30mg/kg in mouse abdominal cavity.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradable[14] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 750d (theoretical).
4. Other harmful effects[15] This substance is harmful to the environment, and special attention should be paid to the pollution of water bodies. .
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 44.23
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 125.0
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 354.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 64.2
5. Polarizability: 17.53
Calculate chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 91.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 224
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. This product is toxic, more toxic than mononitrochlorobenzene. It has a significant irritating effect on the skin and mucous membranes, causing severe dermatitis. It can cause blood poisoning, damage the liver and kidneys, and damage nerves, causing neuralgia and neuritis. Ventilate the maximum allowable concentration in the air. Operators should wear protective equipment. It is prohibited to drink alcohol before or after work. This product can explode when heated to high temperatures. Toxic when inhaled, swallowed or in contact with skin, and has cumulative hazards.
2. Stability[16] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[17] Strong oxidizing agent, strong alkali, strong reducing agent
4. Conditions to avoid contact [18] Vibration, heat
5. Polymerization hazard[19] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products[20] Nitrogen oxides, hydrogen chloride
Storage method
1. Storage precautions [21] Store in a cool, well-ventilated special warehouse, and implement the “two people to send and receive, and two people to keep” system. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The packaging is sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, reducing agents, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
2. Packed in iron drums, with a net weight of 200kg or 300kg. Store in a ventilated, cool, dry place. Avoid mixed storage and transportation with inorganic oxidants and acids. Store and transport according to regulations for flammable and toxic substances.
Synthesis method
1. Obtained from nitrification of chlorobenzene twice with mixed acid. The two-step nitrification process realizes continuous production, and the production device mainly consists of four reaction towers. The mixed acid (nitric acid accounts for 33.1%, sulfuric acid accounts for 62.88%, and the rest is water) is continuously passed through four reaction towers at a flow rate of 11.3kg/min and chlorobenzene at a flow rate of 3.18kg/min. The reaction temperatures are controlled at 75-85°C and 100°C respectively. ℃, 120±20℃ and 125±2℃. After reacting for about 3 hours, the reaction product is washed with water to obtain a qualified product.
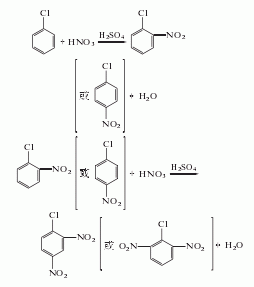
2. By pair, neighbor The by-product co-fusion oil of chlorobenzene is nitrated with mixed acid, separated waste acid, neutralized, washed with water and purified by crystallization to obtain the finished product, and 2,6-oil is a by-product.
3.Chlorobenzene is nitrated twice with mixed acid, and the reaction product is washed with water and separated to obtain the product.
4.Place a mixed acid solution with a nitric acid content of 33.1% and a sulfuric acid content of 62.88% and chlorobenzene at 11.3kg/min respectively. and 3.18kg/min flow continuously through 4 reactors. The reaction temperatures are controlled at 75~85℃, 100℃, (120±2)℃ and (125±2)℃ respectively, and the residence time of the reactants is controlled to 3h. , the obtained product is poured into crushed ice to solidify, and after standing, filtering, washing with water, dissolving in hot ethanol, cooling, and filtering to dryness, the finished product is obtained. The process reaction is:
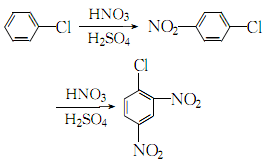
5. It is produced from chlorobenzene and mixed acid through two-step nitration batch reaction. In the first step of nitrification, first use 1400kg chlorobenzene to extract the previous batch of nitrification waste acid, separate the waste acid after stratification, and then add the previous batch of second-step nitrification waste acid 1500kg and 830kg of 98% nitric acid and the previous batch of second-step nitrification waste acid. The mixed acid consists of 770kg of waste acid, and the feeding temperature is controlled at about 55°C. After the addition is completed, raise the temperature to 80°C for 30 minutes. After the mixture is completely separated, the waste acid is separated. The mixed acid composed of 2000kg of 98% sulfuric acid and 880kg of 98% nitric acid is slowly added to the obtained p-nitrochlorobenzene. The feeding temperature is controlled at 65°C. After the addition, the temperature is raised to 100°C. ℃ for 1 hour, let it stand for stratification, and separate the waste acid layer. The crude dinitrochlorobenzene obtained can be washed with water and treated with ethanol to obtain the pure product.
Purpose
1. Identify nicotinic acid, nicotinamide and other pyridine compounds. Identification of Thiol Compounds Thiols. Standard for the determination of carbon, hydrogen and chlorine by organic microanalysis. Molecular polymerization inhibitors commonly used in industry, dosage 0.10% ~ 0.001%. This product is used to manufacture dyes, pesticides, medicines, and can also be used to prepare sulfate black dye, ice dye, saccharin, dinitroaniline, picric acid, p-nitroanthralide and other products.
2. Molecular polymerization inhibitor commonly used in industry, dosage 0.001% ~ 0.10%. It can be used to manufacture dyes, pesticides, medicines, and can also be used to prepare sulfur black dye, ice dye, saccharin, dinitroaniline, picric acid, p-nitroanthralide and other products.
3. Used as a chromogenic reagent for the detection of nicotinic acid, nicotinamide and pyridoxal (vitamin B6) by thin layer chromatography.
4. Used as raw materials for synthetic dyes, pesticides and medicines. [22]
The obtained p-nitrochlorobenzene is then slowly added with a mixed acid composed of 2000kg of 98% sulfuric acid and 880kg of 98% nitric acid. The feeding temperature is controlled at 65°C. After the addition is completed, the temperature is raised to 100°C for 1 hour, and the mixture is left to stratify and separate the waste. Acid layer, the obtained crude dinitrochlorobenzene is washed with water and treated with ethanol to obtain the pure product.
Purpose
1. Identify nicotinic acid, nicotinamide and other pyridine compounds. Identification of Thiol Compounds Thiols. Standard for the determination of carbon, hydrogen and chlorine by organic microanalysis. Molecular polymerization inhibitors commonly used in industry, dosage 0.10% ~ 0.001%. This product is used to manufacture dyes, pesticides, medicines, and can also be used to prepare sulfate black dye, ice dye, saccharin, dinitroaniline, picric acid, p-nitroanthralide and other products.
2. Molecular polymerization inhibitor commonly used in industry, dosage 0.001% ~ 0.10%. It can be used to manufacture dyes, pesticides, medicines, and can also be used to prepare sulfur black dye, ice dye, saccharin, dinitroaniline, picric acid, p-nitroanthralide and other products.
3. Used as a chromogenic reagent for the detection of nicotinic acid, nicotinamide and pyridoxal (vitamin B6) by thin layer chromatography.
4. Used as raw materials for synthetic dyes, pesticides and medicines. [22]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

