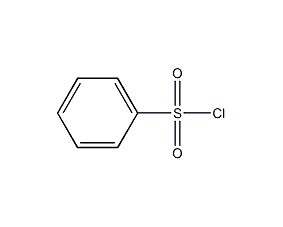
Structural formula
| Business number | 02DA |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H5ClO2S |
| Molecular weight | 176.62 |
| label |
benzene sulfonyl chloride, chlorosulfobenzene, Benezenesulfochloride, Benzenesulfchloride, Benzenesulfonchloride, aromatic sulfur compounds, Sulfonating reagent |
Numbering system
CAS number:98-09-9
MDL number:MFCD00007426
EINECS number:202-636-6
RTECS number:DB8750000
BRN number:606926
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and transparent oily liquid with pungent odor. [9]
2. Melting point (℃): 14.5[10]
3. Boiling point (℃): 251 (Decomposition) [11]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.384[12]
5. Relative vapor density (air = 1): 6.0[13]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 1.33 (120℃)[14]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.940[15]
8. Flash point (℃): >110[16 ]
9. Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ether, easily soluble in ethanol and benzene. [17]
10. Refractive index: 1.551
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[18]
LD50: 1960mg/kg (rat oral); 828mg/kg (mouse oral) Oral); 828mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
2. Irritation No information available
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[19] LC50: 3mg/L (48h) (1-year-old grayling, static)
2. Biodegradability No information available yet
3. Non-biodegradability[20] At 10℃, the hydrolysis half-life is 12.9min (theoretical).
Molecular structure data
None
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 1.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 34.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 186
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters Number: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Toxic, can irritate eyes, skin, mucous membranes and cause inflammation. used in productionThe raw material chlorosulfonic acid is extremely irritating and corrosive. Rat oral LD501960mg/kg, inhalation for 1 hour LC5032×10-6. Protective equipment should be worn during operation and the equipment should be sealed. The maximum allowable concentration in the air is 0.3 mg/m3.
2. This reagent is highly irritating and will cause harm to humans if absorbed through the skin or ingested; it is highly hygroscopic, sensitive to air and moisture, and easily interacts with nucleophilic solvents reacts and releases hydrogen chloride. It is generally stored in an inert environment and should be operated in a fume hood.
3. Stability[21] Stable
4. Incompatible substances[22] Strong oxidants, strong alkalis, water, alcohols
5. Conditions to avoid contact [23] Humid air
6. Polymerization hazard[24] No polymerization
7. Decomposition products[25] Nitrogen oxides, hydrogen chloride
Storage method
Storage Precautions[26] Stored in a cool, dry and well-ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature does not exceed 30°C and the relative humidity does not exceed 80%. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, etc. and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
The preparation method is to react benzene and chlorosulfonic acid at a ratio of 1:3 (mol) at 20-30°C for 2 hours to obtain crude benzene sulfonyl chloride, which can be refined to obtain the finished product.
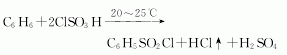
Purpose
1. Benzenesulfonyl chloride is a commonly used sulfonation reagent, mostly used to prepare sulfonamides, sulfonated esters and sulfones.
1. Sulfonamide
Protection of amino groups(Formation of sulfonamide) Benzenesulfonyl chloride is mostly used to protect amines and indoles. Indoles and other nitrogen-containing functional groups (Formula 1)[3]. Other aryl or alkyl sulfonyl chlorides (such as p-toluenesulfonyl chloride and methylsulfonyl chloride) can also be used as protecting groups for amino groups. The choice of base and solvent in the reaction depends on the reaction substrate.
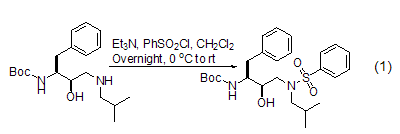
2. Sulfonation Esters
The formation of sulfonated esters Benzenesulfonyl chloride can react with alcohols [4] and N– The hydroxyl compound [5] reacts to form a sulfonated ester, and the resulting sulfonated ester group is a better leaving group. For example, in the presence of tertiary amines, benzene sulfonyl chloride reacts with 1,4- or 1,5-diol to form cyclic ethers. This reaction can also be used to prepare cyclic tertiary amines. Such as the protection of alcoholic hydroxyl groups by benzenesulfonyl chloride (Formula 2).
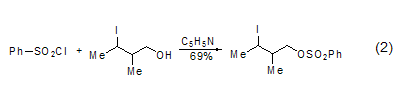
3. Sulfone
Addition of unsaturated bonds Under light or Cu(I) catalytic conditions, benzene sulfonyl chloride can undergo free radical addition reactions with alkenes and alkynes[6], for example, conjugated diene compounds can undergo an addition reaction with benzenesulfonyl chloride to obtain sulfone (formula 3).
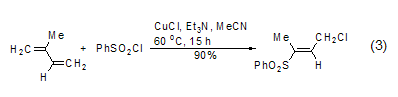
Reacts with aromatic hydrocarbons Under the action of aluminum trichloride or ferric chloride, benzene sulfonyl chloride reacts with aromatic hydrocarbons to form diaryl sulfone (formula 4)[7].
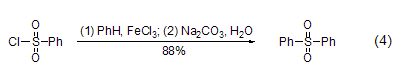
React with phenylboronic acid Under the action of a catalyst such as PdCl2, benzene sulfonyl chloride can react directly with phenylboronic acid to form diaryl sulfone. This reaction is compared with the direct reaction between benzene sulfonyl chloride and aromatic hydrocarbons to form diaryl sulfone. The reaction conditions of base sulfone are milder, and the reaction yield is also higher (Formula 5)[8].

2. Used in organic synthesis, Preparation of sulfonamides and identification of various amines. [27]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

