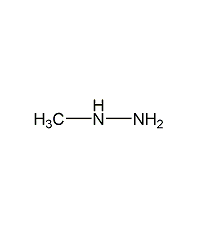
Structural formula
| Business number | 01BC |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | CH6N2 |
| Molecular weight | 46 |
| label |
None |
Numbering system
CAS number:60-34-4
MDL number:MFCD00007621
EINECS number:200-471-4
RTECS number:MV5600000
BRN number:635645
PubChem number:24885277
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless and transparent liquid with ammonia smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -52.4[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 87.5[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.874[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 1.6[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 4.8 (20℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): -1304.2[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 312[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 8.24[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: -1.05[10]
11. Flash point (℃): -8.3 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 194[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 97±2[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 2.5[14]
15. Solubility: soluble in water, ethanol, and ether. [15]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[16]
LD50: 32mg/kg (rat oral); 183mg/kg (rat transdermal); 95mg/kg (rabbit transdermal)
LC50: 34ppm (rat inhalation, 4h)
2. Irritation No data yet
3. Subacute and chronic toxicity[17] Rats, dogs and monkeys Inhalation of 0.4~9.4 mg/m3, 6 hours a day, for 6 months, the growth of rats was retarded, dogs and monkeys had hemolysis, and the number of bone marrow myeloid blast cells changed.
4. Mutagenicity[18] DNA adduct: human fibroblasts 116 pmol. Unprogrammed DNA synthesis: rat lung 1μmol/L.
5. Teratogenicity[19] The lowest toxic dose ( TDLo) 50mg/kg, causing eye and ear developmental malformations.
6. Others[20] The lowest oral toxic dose for mice (TDLo): 100mg/kg (pregnant 8~12d), positive for teratogenesis.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[21] LC50: 3.54mg/L (96h) (channel catfish); 2.27mg/L ( 96h) (Golden American Bream)
2. Biodegradability[22]
Aerobic biodegradation (h): 312~576
Anaerobic biodegradation (h): 1248~2304
3. Non-biodegradability [23] Photooxidation half-life in air (h): 0.06~0.37
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 13.81
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 57.5
3.�� Zhang specific volume (90.2K): 128.9
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 25.2
5. Polarizability (10-24 cm3): 5.47
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): -0.9
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
p>
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 0
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 38
7. Number of heavy atoms: 3
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 2.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It will cause combustion and explosion when exposed to open flame or high heat. It can spontaneously ignite when exposed to air or the dry product can spontaneously ignite after long-term storage and deterioration.
2. Stability[24] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[25] Strong oxidants, oxygen, peroxides
4. Conditions to avoid contact[26] Heat
5. Polymerization hazard[27] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products[28] Ammonia
Storage method
Storage Precautions[29] Stored in a cool, well-ventilated special warehouse, implementing a “double person to receive and receive, double person to keep” system . Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 37°C. The packaging must be sealed and must not come into contact with air. They should be stored separately from oxidants, peroxides, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Using hydrazine hydrate and benzaldehyde as raw materials, it is obtained through condensation and methylation reactions. Add 39% hydrazine hydrate into the reaction pot, add benzaldehyde dropwise with stirring at 20-30°C, complete the addition in about 7 hours, continue stirring for 2 hours, and leave overnight. Filter the next day, wash with water until it is nearly neutral, and dry to obtain granular solid benzyridazine, with a melting point of 90-93°C and a yield of about 95% or more. Add benzene; benzylidene azide; dimethyl sulfate into the reaction pot, stir and reflux for 5 hours. Cool and precipitate the solid, add water, the solid will dissolve, separate into layers, and perform steam distillation until benzaldehyde cannot be evaporated. Add absolute ethanol to precipitate solid, cool and filter to obtain methylhydrazine sulfate. The yield is 60%-70%.
Purpose
1. Used in organic synthesis. N-methyldicarboxylhydrazide can be produced by acylation reaction of methylhydrazine sulfate. Add formic acid, sodium formate, and methylhydrazine sulfate into the glass-lined reaction pot, slowly raise the temperature to 110-115°C, and stir for 1.5 hours. Cool to 5°C, filter, and wash with absolute ethanol. Combine the filtrate, concentrate under reduced pressure, and extract with chloroform. Filter to remove sodium sulfate and wash with chloroform. Evaporate the chloroform from the feed liquid under reduced pressure, let it cool, and add absolute ethanol and ether. The solid is precipitated, filtered, washed with a small amount of diethyl ether, and dried in the air to obtain N-methyldicarboxylic acid hydrazide. Melting point 50-51℃. The yield is 70%-80%. Used in the production of the drug methylphenylhydrazine. Methylhydrazine is also used in rocket fuel and as a solvent.
2. Used as organic synthesis intermediates and solvents. [30]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

