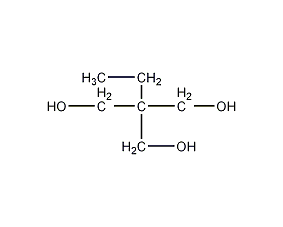
Structural formula
| Business number | 01ML |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H14O3 |
| Molecular weight | 134.17 |
| label |
trimethylolpropane, 1,1,1-Trimethylolpropane, 2,2-Dihydroxymethylbutanol, CH3CH2C(CH2OH)3, Trimethylolpropane, 1,1,1-Tris(hydroxymethyl)propane, 2,2-Bis(hydroxymethyl)-1-butanol, plasticizer, alcohol solvents, surfactant raw materials, Electronic materials raw materials and intermediates |
Numbering system
CAS number:77-99-6
MDL number:MFCD00004694
EINECS number:201-074-9
RTECS number:TY6470000
BRN number:1698309
PubChem number:24889859
Physical property data
1. Properties: Odorless white crystals with a sweet taste.
2. Relative density (g/mL, 70/4℃): 1.0889
3. Melting point (ºC): 58.8
4. Boiling point (ºC) , normal pressure): 295
5. Boiling point (ºC, 0.67kPa): 160
6. Flash point (ºC, open): 180
7 . Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): 193
8. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol): 600.0
9. Heat of fusion (KJ/mol): 183.5
p>
10. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): 3617.4
11. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 31ºC, constant pressure): 2.43
12 . Solubility: Easily soluble in water, low alcohol, glycerin, N,N-dimethylformamide, partially soluble in acetone, ethyl acetate, slightly soluble in carbon tetrachloride, ether and chloroform, insoluble in aliphatic hydrocarbons , aromatic hydrocarbons and chlorinated hydrocarbons.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 14100 mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 13700 mg/kg;
2. High boiling point and flash point, not absorbed by the skin. The maximum allowable concentration in the atmosphere is 50mg/m3.
Ecological data
May cause pollution to the environment. Harmful to water bodies.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 34.41
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 120.1
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 316.1
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 47.9
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 13.64
Compute chemical data
1.Hydrophobic parametersCalculation reference value (XlogP): -0.8
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 3
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: None
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 60.7
7. Number of heavy atoms :9
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 60.4
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11 .Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Combustible solids. It is hygroscopic, with high boiling point and flash point, and its hygroscopicity is about 50% of that of glycerin. It has the chemical properties of general aliphatic alcohols and can undergo esterification, etherification, acetalization, halogenation and other reactions.
2. Slightly toxic. It is non-irritating to the skin and the LD50 tested on rats is 14.1g/kg.
Storage method
1. This product should be kept sealed.
2. Lined with plastic bags and packed in wooden or iron drums. It should be stored in a cool, dehumidified, sun-proof, heat-insulated place and away from fire sources. Store and transport according to general chemical regulations.
Synthesis method
N-butyraldehyde and formaldehyde undergo an aldol condensation reaction under alkaline conditions. The reaction solution is concentrated and desalted, and then decolorized and purified with ion exchange resin. Finally, it is evaporated, cooled, and rolled with a thin film evaporator to obtain the finished product. . Raw material consumption quota: n-butyraldehyde (≥95%) 950kg/t, formaldehyde (37%) 3400kg/t.
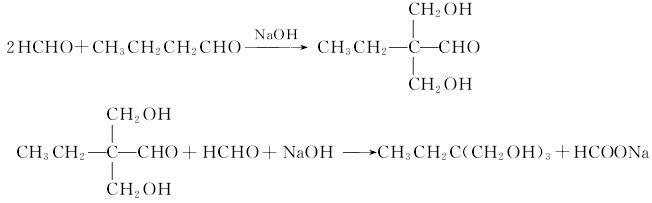
Refining method: generally refined by vacuum distillation. Since sodium formate is mixed during manufacturing, pyrolysis is likely to occur. It needs to be removed with ion exchange resin first, and ammonium salt, hydroquinone or α-naphthol is added as a stabilizer during distillation. If further purification is required, recrystallization with diethyl ether-acetone (1:1) can be used.
Condensation disproportionation method using triethylamine as catalyst. This method uses n-butyraldehyde and formaldehyde as raw materials and triethylamine as catalyst to perform aldol condensation reaction. 2,2-dimethylolbutyraldehyde is generated, and then the Cannizzaro reaction occurs with excess formaldehyde and alkali to generate trimethylolpropane. The amine salt is decomposed to recover the catalyst triethylamine, and then purified in a distillation tower to obtain Trimethylolpropane. The reaction formula is as follows:
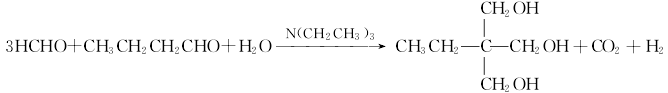
The condensation hydrogenation method uses n-butyraldehyde and formaldehyde as raw materials, and uses triethylamine as the catalyst to perform an aldol condensation reaction to generate 2,2-dihydroxymethylbutyraldehyde. Then, catalytic hydrogenation is performed to generate trimethylolpropane, and the hydrogenated reaction liquid is distilled under reduced pressure to obtain the product trimethylolpropane. Catalysts for hydrogenation are generally divided into two categories: one is a palladium-carbon catalyst with mild reaction conditions, the general reaction temperature is 140°C and the reaction pressure is 0.98MPa, but the price is relatively expensive; the other is a copper-based catalyst with a carrier of γ Aluminum trioxide, operating conditions are reaction temperature 130°C and pressure 3.0MPa.
Purpose
Widely used in the production of polyester and polyurethane foams, as well as in the manufacture of alkyd coatings, synthetic lubricants, plasticizers, surfactants, fiber processing agents, rosin esters and explosives. It is also directly used as a textile auxiliary and thermal stabilizer of PVC resin. When used in alkyd resin, it can improve the firmness, color tone, weather resistance, chemical resistance and sealing of the resin. Polyvinyl alcohol and polyformaldehyde resin can be dissolved in polymer substances. Therefore, it can be used as a plasticizer for these resins. Used as raw material for synthetic polyurethane adhesives, polyester and polyurethane foam

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

