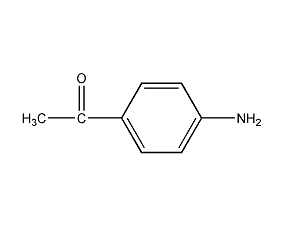
Structural formula
| Business number | 02GS |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H9NO |
| Molecular weight | 135.16 |
| label |
p-Aminobenzylketone, p-aminoacetophenone, Para-aminoacetophenone, 4-Aminoacetophenone, p-aminophenyl methyl ketone, Acetanilide, 4′-Aminoacetophenone, 4-Acetylaniline, 1-(4-Aminophenyl)-ethanon, 1-(4-Aminophenyl)ethanone[qr], 4’-Amino-acetophenon, 4’-Aminoacetophenone[qr], Acetophenone, p-amino-, Acetophenone,4’-amino-, Acetophenone,4-amino-[qr], Acetophenone,p-amino-[qr], Reagent |
Numbering system
CAS number:99-92-3
MDL number:MFCD00007896
EINECS number:202-801-2
RTECS number:AM5500000
BRN number:471493
PubChem ID:None
Physical property data
1. Properties: light yellow needle-like crystals or powder. Has a pleasant special smell. The color becomes darker after exposure to light.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): Undetermined
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 106
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 293-295
6. Boiling point (ºC, 5.2kPa): Not available Determined
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (kPa, 25ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturation Vapor pressure (kPa, 60ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (% , V/V): Undetermined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Easily soluble in hot water, soluble in…Alcohol, ether and hydrochloric acid, slightly soluble in cold water and benzene.
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 381mg/kg; rat peritoneal cavity LD50: 260mg/kg; mouse oral LC50: 596mg/kg; mouse peritoneal cavity LC50: 300mg/kg; dog oral LD: >70mg /kg; Oral LD50 of wild birds: 133mg/kg;
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 40.51
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 123.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 318.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 44.4
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 16.06
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: 7
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 43.1
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 125
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with oxidants.
2. It is irritating and harmful if taken orally. Avoid inhaling the dust of this product and avoid contact with eyes and skin.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. 2. They should be stored separately from acidic substances, acidic chlorides, acid anhydrides and chloroformates, and avoid mixed storage. 3. Equip with corresponding varieties and quantities of fire-fighting equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
(1) Reduction from p-nitroacetophenone: Put stannous chloride and concentrated hydrochloric acid into the reaction tank, cool, stir and add p-nitroacetophenone. When the temperature naturally rises to 90°C, cool it quickly to 85°C, continue to cool to room temperature, stir for 1 hour, filter, and add excess sodium hydroxide solution to the filter cake to decompose the complex. After filtration, crude p-aminoacetophenone is obtained. When dilute ethanol is used, recrystallization is obtained to obtain fine product with a melting point of 105-106°C. The yield is 61%. The reduction reaction can also be carried out by using iron powder and sodium chloride instead of stannous chloride.
(2) Acetamidoacetophenone is prepared from acetanilide and acetic anhydride, and then hydrolyzed and neutralized. Mix acetic anhydride, acetophenone and anhydrous zinc chloride and keep it at a slight boil for 5 hours. Cool slightly, pour in concentrated hydrochloric acid, reflux and hydrolyze for 5 hours, let it come to room temperature, add 25% sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH to 7-8, and add steam. Remove the aniline, filter with decolorizing carbon, concentrate under reduced pressure, and cool to obtain orange-yellow crystals. Drain to get the crude product. Then use water for recrystallization and purification.
(3)Mix acetic anhydride and acetanilide evenly with the catalyst amount of anhydrous zinc chloride in a ratio of 1:1 (molar ratio) , heated to reflux for 5h, add concentrated hydrochloric acid and continue refluxing for 5h:
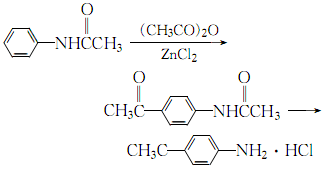
After the reaction is completed, let it cool to room temperature, add 25% sodium hydroxide solution until the oil and water are clearly separated, and then separate Add water to the resulting oil layer, then use 25% sodium hydroxide to adjust the pH value to 7-8, and then use steam distillation to evaporate the aniline. The residue is decolorized with activated carbon, and the filtrate obtained is filtered and concentrated under reduced pressure. The cooled orange-yellow crystals are recrystallized with water to obtain pure p-aminoacetophenone.
Purpose
1. Sensitive reagent for precipitating palladium. Photometric reagent for cerium. Determination of vitamin B1. Colorimetric determination of sulfonamides. Organic Synthesis.
2. Used as a chromogenic reagent for the determination of palladium by photometric turbidimetry. It is also used as a chromogenic agent for the photometric determination of several organic compounds, such as thiamine and sulfonamides.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

