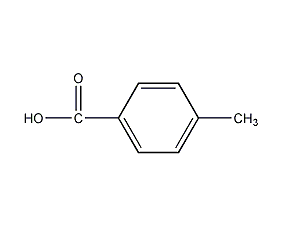
Structural formula
| Business number | 02GU |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H8O2 |
| Molecular weight | 136.15 |
| label |
4-methylbenzoic acid, 4-Methylbenzoic aicd, 4-Toluic acid, Aromatic aldehydes, ketones and their derivatives, Raw materials and intermediates used in ink, acidic solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:99-94-5
MDL number:MFCD00002565
EINECS number:202-803-3
RTECS number:XU1575000
BRN number:507600
PubChem number:24889293
Physical property data
1. Properties: White or yellowish powder.
2. Density (g/mL, 25℃): 1.23
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): Undetermined
4. Melting point (ºC): 180~182
5. Boiling point (ºC): 274~275 (sublimation)
6. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ· mol-1): -3959.28
7. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -332.08
8. Flash point (ºC): 181
9. Crystal phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3862.17
10. Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -429.24
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, ºC): Not available Determined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, ºC): Undetermined
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical Temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
p>
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
18. Explosion lower limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Dissolution Properties: Easily soluble in methanol, ethanol, and ether, insoluble in hot water, and evaporates with the evaporation of water.
Toxicological data
Acute toxicity: Rat peritoneal cavity LD50: 874mg/kg; Mouse oral LD50: 2340mg/kg; Mouse peritoneal cavity LD50: 916mg/kg;
Ecological data
This substance is harmful to the environment and can cause pollution to water bodies and the atmosphere. Organic acids can easily form acid rain during atmospheric chemistry and atmospheric physical changes. Therefore, when the pH value drops below 5, it will cause serious harm to animals and plants. The reproduction and development of fish will be seriously affected. Metals in the soil and water sediments in the watershed can be dissolved into the water.�Poisoning fish. Acidification of water bodies will also lead to changes in the composition and structure of aquatic organisms. Acid-resistant algae and fungi will increase, while root plants, bacteria and vertebrates will decrease, and the decomposition rate of organic matter will decrease. Acidification will seriously lead to the reduction or death of fish in lakes and rivers.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 38.00
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 118.2
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 307.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 45.4
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 15.06
Compute chemical data
1. Hydrophobic parameter calculation reference value (XlogP): 2.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers:
6. Topological molecular polar surface area (TPSA): 37.3
7. Number of heavy atoms: 10
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 123
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters Number: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. It does not decompose under normal temperature and pressure. Avoid contact with strong oxidants, strong alkalis, and strong acids.
2. See benzoic acid (C145).
3. Exist in flue-cured tobacco leaves, burley tobacco leaves, and smoke.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills. The packaging is lined with plastic bags and iron drums outside.
Synthesis method
1. It is produced by catalytic oxidation of paraxylene with air. When using the normal pressure method, xylene and cobalt naphthenate can be added to the reaction pot. When it is heated to 90°C, air can be introduced. The temperature is controlled at 110-115°C. After reacting for about 24 hours, about 5% of paraxylene will be converted into p-Toluic acid. Cool to room temperature, filter, wash the filter cake with p-xylene, and dry to obtain p-toluic acid. And paraxylene is recycled. The yield is 30-40%. When using the pressure oxidation method, the reaction temperature is 125°C, the pressure is 0.25MPa, the ventilation volume is 250L per hour, and the reaction is for 6 hours. Then, unreacted xylene is distilled off with water vapor, and the oxidized material is acidified to a pH value of 2 with concentrated hydrochloric acid. Stir, cool, and filter. The filter cake is soaked in paraxylene and then filtered and dried to obtain p-toluic acid with a content of more than 96%. The single-pass conversion rate of paraxylene is 40% and the yield is 60-70%.
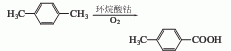
2. By p-isopropyl Toluene is produced by oxidation with nitric acid. Mix 20% nitric acid and p-isopropyltoluene, stir and raise the temperature to 80-90°C, react for 4 hours, and then raise the temperature to 90-95°C for 6 hours. Cool, filter, and recrystallize the filter cake with toluene to obtain p-toluic acid, with a yield of 50-53%. In addition, p-xylene can also be obtained by oxidizing p-xylene with concentrated nitric acid and reacting for 30 hours, with a yield of 58%.
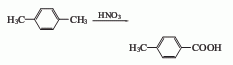
3. Tobacco: BU, 26 ;FC,40.
Purpose
In the pharmaceutical industry, it is used as a hemostatic drug, hemostatic aromatic acid, and an anti-tumor drug, procarbazine, etc.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

