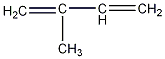
Structural formula
| Business number | 01NK |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C5H8 |
| Molecular weight | 68.12 |
| label |
2-Methyl 1,3-butadiene, isoprene, Diethyl disodium, 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, chemical composition of isoprenoid, Double B double sodium, Wave Vita Cola, Aliphatic hydrocarbons |
Numbering system
CAS number:78-79-5
MDL number:MFCD00008600
EINECS number:201-143-3
RTECS number:NT4037000
BRN number:969158
PubChem number:24881389
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless and volatile liquid [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -146[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 34.0[3]
4. Relative density (water=1): 0.68[4]
5. Relative vapor density (air=1): 2.35[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 62.1 (20℃ )[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -2986.4[7]
8. Critical Temperature (℃): 211.1[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 3.79[9]
10 .Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.42[10]
11. Flash point (℃): -54 (CC)[11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 427[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 10.0[13] sup>
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.5[14]
15. Solubility: insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol, ether, etc. Most organic solvents. [15]
16. Solubility parameter (J·cm-3)0.5:15.455
17.van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1): 7.410×109
18. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 51.250
19. Gas phase standard heat of combustion (enthalpy) (kJ·mol -1): -3186.7
20. Gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 75.8
21. Gas phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 314.67
22. Gas phase standard free energy of formation (kJ ·mol-1): 146.3
23. Gas phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 102.69
24. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -3159.9
25. Liquid phase standard Claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): 49.0
26. Liquid phase standard entropy (J·mol-1·K-1): 228.28
27. Liquid phase standard free energy of formation (kJ·mol-1): 150.2
28 .Liquid phase standard hot melt (J·mol-1·K-1): 151.05
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity
Inhalation LC50 in rats: 180mg/m3/4H; Inhalation LC50 in mice: 139mg/m3/2H;
2. Other multi-dose toxicity:
Rat caliber TDLO: 157mg/kg/9W-C; rat inhalation LC50: 3400mg/m3/22W-I; mouse inhalation LC50: 3400mg/m3/17W-I; pigTwo distillation towers remove light components and heavier components to further concentrate isoprene to obtain 97% crude isoprene, which is then separated through an acetonitrile extraction distillation tower to separate C5 alkane and olefins; followed by distillation, Metal sodium treatment removes impurities such as alkynes, trace cyclopentadiene, and sulfides, and finally the polymer grade isoprene is separated from the top of the isoprene degravity tower. The product content is ≥99%, and the isoprene recovery rate is Up to 95%. A high-grade alcohol polymerization inhibitor is used in the process.
Consumption quota: 7.4t of C5 fraction containing 15% isoprene, 0.2t of steam (1.08MPa), 12.3t of steam (0.44MPa), 635t of cooling water (△t10℃), sodium 1-6( Generally 1) kg, electricity 5.4×100000KJ/t.
(2) Dehydrogenation method This method is divided into catalytic dehydrogenation method and oxidative dehydrogenation method. Among them, isopentane and isopentene dehydrogenation methods have been used in industrial production. Oxidative dehydrogenation has not yet been industrialized.
1. Isopentane dehydrogenation method This method is divided into one-step method and two-step method. The two-step method uses industrial isopentane or n-pentane directly distilled from gasoline and isomerized isopentane fraction as raw materials, and isoprene is produced through two-step dehydrogenation. In the first step, the dehydrogenation of isopentane to isopentene occurs in a fluidized bed using a particulate aluminum-chromium catalyst (most dehydrogenation catalysts for hydrocarbons are also effective). The reaction temperature is 540-610℃, the space velocity is 100-300h-1, and the pressure is ≤63.74KPa. The overall yield of isoprene and a small amount of isoprene is 28%-33%, and the overall selectivity is 66%-73%. The reaction system includes a reactor and a regenerator. The two reactors are connected by a U-shaped tube. The regeneration temperature is 610-650°C. The catalyst acts as a heat carrier. After circulating in the two reactors, the reaction product is washed, compressed, absorbed and separated to obtain the content. Isoprene fraction of isoprene. In the second step, isoprene is dehydrogenated to produce isoprene, using a phosphate composite catalyst containing tungsten, chromium, etc., the reaction temperature is 550-650°C, the pressure is 39.23-98.06KPa, and the isopenten to steam ratio is 1:20 ( mol), the gum hydrogen product passes through two extractive distillation towers and is extracted and distilled with anhydrous DMF solvent to obtain crude isoprene. The crude isoprene is then chemically treated with cyclohexanone and butanol in the presence of caustic alkali solution. Remove cyclopentadiene. Then, in the presence of a catalyst, the alkyne is removed through a hydrogenation reaction, and the isoprene product is obtained after separation, with a content of >99%.
2. Isopenten catalytic dehydrogenation method The raw material isopentene comes from catalytic cracking C5 fraction. The catalysts used are iron oxide, chromium oxide and carbonate. The reaction temperature is 550-650℃ and the pressure is 39.2-98.06KPa. Isoprene yield is 96%-98% (based on converted isoprene).
(3) Synthesis method There are many synthesis methods, mainly introducing the propylene dimerization method. The synthesis reaction is divided into three steps: propylene dimerization, isomerization and demethylation. Step 1: The propylene dimerization reaction catalyst is tripropylaluminum, the reaction temperature is 150-200°C, and the reaction pressure is 20MPa. ; The second step: the catalyst used in the isomerization reaction is solid phosphoric acid, the reaction temperature is 150-300°C; the third step: the catalyst used in the cracking reaction is hydrogen bromide, the reaction temperature is 650-800°C, and the contact time is 0.005-0.35.
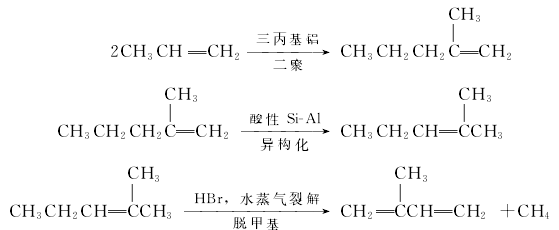
This method does not have high requirements for the purity of raw materials. 40% acrylic is enough. In the first step, the propylene conversion rate is 60%-95%, and the yield reaches 95%. In the second step, the yield can reach 99%. The final isoprene yield is 70% based on raw materials, and the product content is >99.4%.
Consumption quota: 1.52t of propylene, 27t of steam, 10,000 square meters of cooling water, and 300KW·h/t of electricity.
In addition, isoprene can also be produced by the propylene dimerization method, the acetylene-acetone method and the isobutylene-formaldehyde method.
(2) The isobutylene-formaldehyde method consists of a two-step reaction
(3) The acetylene-acetone method consists of a three-step reaction
The by-product C5 fraction of the ethylene unit separates isoprene and C5 fraction The yield is generally 5% to 8% (wt) of the cracked raw material, of which the isoprene content is 15% to 25%. The isoprene yield is 0.5% to 1.0% of the cracked raw material. It is difficult to obtain high-purity products with ordinary distillation methods. Extractive distillation and azeotropic distillation methods are generally used. Industrialized extractive distillation methods include acetonitrile method, N,N-dimethylamide method, N-methylpyrrolidone method, etc.
Purpose
1. Mainly used in the production of polyisoprene rubber and the second monomer of butyl rubber. It is also used in the manufacture of pesticides, medicines, spices and adhesives, etc.
2. Polymerization monomer, used to synthesize polyisoprene rubber, isoprene rubber, butyl rubber, and copolymerized with styrene to form SIS thermoplastic elastomers, etc. It is also an important raw material for the preparation of fine chemicals, used in the manufacture of adhesives, synthetic fragrances, pesticides, polymerization inhibitors, pharmaceuticals, etc.
3. Important organic chemical raw materials, used as synthetic rubber, butyl rubber monomer, etc. [29]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

