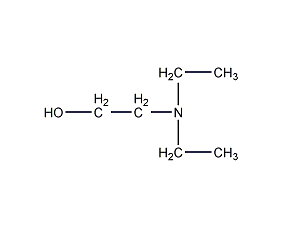
Structural formula
| Business number | 02HR |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H15NO |
| Molecular weight | 117.19 |
| label |
Hydroxytriethylamine, 2-diethylaminoethanol, N,N-diethylethanolamine, Diethylaminoethanol, 2-(diethylamino)ethanol, 2-Hydroxytriethylamine, Diethyl-2-hydroxyethylamine, 2-Hydroxytriethylamine, Diethylethanolamine, 2-(Diethylamino)ethyl alcohol, 2-(N,N-Diethylamino)ethanol, 2-Hydroxytriethylamine, beta-(Diethylamino)ethanol, beta-(Diethylamino)ethyl alcohol, beta-Hydroxytriethylamine, preservative, neutralizer, resin hardener, photographic developer, fixer additives, emulsifier, fiber treatment agent |
Numbering system
CAS number:100-37-8
MDL number:MFCD00002850
EINECS number:202-845-2
RTECS number:KK5075000
BRN number:741863
PubChem number:24859090
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless hygroscopic liquid with ammonia smell. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -70[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 163[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.88[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 4.03[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 2.8 (20℃)[6]
7. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.31[7]
8. Flash point (℃): 52 (CC); 60 (OC) [8]
9. Ignition temperature (℃): 320[9]
10. Explosion limit (% ): 11.7[10]
11. Lower explosion limit (%): 6.7[11]
12. Solubility : Miscible with water, soluble in most organic solvents such as ethanol, ether, benzene, acetone and so on. [12]
13. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.4412
14. Viscosity (mPa·s, 20ºC): 3.5
15. Viscosity (mPa·s, 25ºC): 4.05
16. Viscosity (mPa·s, 60ºC): 1.50
17. Vapor pressure (kPa, 55ºC): 1.33
18. Vapor pressure (kPa, 100ºC): 10.67
19. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): 4198.1
20. Heat of generation (KJ /mol): 309.8
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity[13]
LD50: 1300mg/kg (rat oral); 1260mg/ kg (rabbit transdermal)
2. Irritation[14]
Rabbit Transdermal: 500 mg, mild irritation (open irritation test).
Rabbit eye: 5mg, severe irritation.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[15] LC50: 1780mg/L (96h) (fathead minnow); >1000mg/L ( 96h) (Medaka)
2. Biodegradability No data available
3. Non-biodegradability No information available yet Information
4. Other harmful effects[16] This substance may be harmful to the environment, and special treatment should be given to water bodies. Notice.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 35.10
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 132.3
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 313.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 31.4
5. Polarizability: 13.91
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 0.3
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 23.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 43.8
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: It has chemical reactivity with tertiary amines and alcohols. When oxidized with hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate, etc., ethanol, acetic acid, acetohydroxamic acid, ammonia, glyoxal, and oxalic acid are generated. When oxidized with lead tetraacetate, diethylamine and glycol aldehyde are generated. Oxidation with potassium thiosulfate at room temperature generates acetaldehyde. And can form hydrochloride C6H15NO·HCl (melting point 135~136℃), picrate [C6H15NO·C6H3N3O7 (melting point 79℃)].
2. Stability[17] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[18] Strong oxidants, strong acids
4. Polymerization hazard[19] No polymerization
Storage method
Storage Precautions[20] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. The storage temperature should not exceed 37℃. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
1. React chlorohydrin and sodium hydroxide at 105°C to generate ethylene oxide, pass it into a diethylamine solution for reaction, separate low boilers under normal pressure, and then fractionate under reduced pressure to obtain N,N-diethylethanolamine finished product. At present, most production plants directly use ethylene oxide as raw material.
Refining method: normal pressure or vacuum distillation and refining.
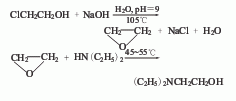
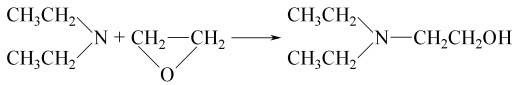
2. Use diethylamine and As raw material of ethylene oxide, add ethylene oxide to diethylamine and react at a certain temperature. The crude product obtained will be distilled under reduced pressure into pure product. The reaction formula is as follows:
Purpose
1. Used as pharmaceutical intermediates, softeners, emulsifiers, curing agents, etc. In addition to being used as a pharmaceutical raw material such as procaine, 2-(diethylamino)ethanol can also be used as a preservative, neutralizer, resin curing agent, photographic developer and fixer additive, etc. Amine soap generated with higher fatty acids can be used as emulsifier and fiber treatment agent.
2. It is an effective oxygen scavenger and passivator. It can be used in combination with diethylhydroxylamine in boiler water treatment. Diethylaminoethanol can also be used as a synthetic resin curing agent, textile softener, acidic medium, emulsifier, and rust inhibitor component.
3. Used in organic synthesis and as fabric softener. [21]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

