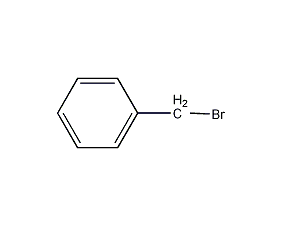
Structural formula
| Business number | 02HS |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C7H7Br |
| Molecular weight | 171.03 |
| label |
α-bromotoluene, benzyl bromide, Toluene bromide, Bromomethylbenzene, benzyl bromide, benzyl bromide, benzyl bromide, 1-Bromotoluene, α-Bromo-toluene, Bromophenylmethane, foaming agent, Halogenated hydrocarbon solvents |
Numbering system
CAS number:100-39-0
MDL number:MFCD00000172
EINECS number:202-847-3
RTECS number:XS7965000
BRN number:385801
PubChem number:24848056
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless liquid with aromatic odor and tear-inducing properties. [10]
2. Melting point (℃): -4.0[11]
3. Boiling point (℃): 198[12]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 1.44[13]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 5.8[14]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.133 (32℃)[15]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -4278.2[16]
8. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 2.92[17 ]
9. Flash point (℃): 79 (CC) [18]
10. Solubility: insoluble in water, Soluble in ethanol, ether and benzene. [19]
Toxicological data
1. Mutagenicity: Mutant microorganism test: bacteria – Salmonella typhimurium, 300 μmol/L; Non-qualitative DNA comprehensive test: bacteria – Escherichia coli, 1300 μmol/L; Sister chromatid exchange test: hamster ovary, 30 μmol/L L;
2. It has a strong irritating effect on the eyes and mucous membranes. There is the possibility of irreversible damage to the body.
3. Others[20] LCLo: 2000mg/m3 (rabbit inhalation, 30min)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3. Non-biodegradability[21] In the air, when the concentration of hydroxyl radicals is 5.00×105/cm3, the degradation half-life is 7.1d (theoretical). At 25°C, the hydrolysis half-life is 79 minutes (theoretical).
4. Bioconcentration[22] BCF: 35 (theoretical)
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 38.90
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 118.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 296.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 38.4
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 15.42
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 0
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 0
7. Number of heavy atoms: 8
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 55.4
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemically active, the bromine atom is easily replaced by hydroxyl, amino, etc. to form benzyl alcohol, benzyl amine, etc.
2. Stability[23] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[24] Alkalis, amines, strong oxidants, alcohols
4. Conditions to avoid contact [25] Heating
5. Polymerization hazard[26] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products[27] Hydrogen bromide
Storage method
Storage Precautions[28] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, amines, alcohols, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Originated from bromination of toluene. Heat toluene to 50°C, add bromine for reaction, the reaction temperature is 75-80°C, react for 6 hours, fractionate under normal pressure to remove the fractions before 140°C, then distill under reduced pressure, collect the 112-114°C (2.0kPa) fraction, Obtain benzyl bromide.
Purpose
1. The greatest use of benzyl bromide is as a benzylation reagent for heteroatom functional groups. It can effectively benzylate various heteroatom functional groups under various conditions, thus having a wide range of uses in organic synthesis ( Mainly used as a protecting group)[1].
Alcohols and phenols can react with benzyl bromide under alkaline conditions. For example, in ether or DMF solvents, the alcohol is treated with NaH or KH to obtain an alkoxy compound, which then undergoes Williamson reaction with benzyl bromide[2]. At low temperatures, primary alcohols can be benzylated more preferentially than secondary alcohols. In addition to NaH and KH alkaline systems, the use of KF/Al or Ag2O can also be used as an alkaline system to induce the benzylation reaction of alcohols.
The application of benzylation reaction in carbohydrate compounds is very successful. First, the sugar derivatives are pretreated with tin reagents, and then a benzylation reaction occurs, so that the protection of the equatorial hydroxyl groups can be selectively achieved in the presence of axial hydroxyl groups (Formula 1)[3].
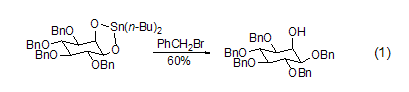
For those with larger steric hindrance For the benzylation reaction of alcohol compounds, a catalyst amount of iodine reagent such as (n-Bu)4NI can be used as an iodine source to convert benzyl bromide into a more active form. of benzyl iodide, making it easier to achieve the benzylation reaction. Since phenolic compounds are more acidic than fatty alcohol compounds, the benzylation reaction of phenol only requires a weak base such as potassium carbonate [4].
Benzyl bromide can also protect the nitrogen-containing groups of amine compounds. The reaction also needs to be completed under alkaline conditions, and the main product of the reaction for primary amines is the bisbenzylation product [5]. In addition, amides, lactams, sulfonamides and nitrogen-containing heterocycles can react with benzyl bromide.
Sulfur-containing compounds such as mercaptans, silicon sulfides, etc. can also react with benzyl bromide under alkaline conditions, such as the reaction between L-cysteine and benzyl bromide in sodium hydroxide alkali solution. reaction (Formula 2). Under the action of DMF solvent or zinc carbonyl, benzyl bromide can also react with carboxylic acid anions to prepare benzyl carboxylate compounds [6].
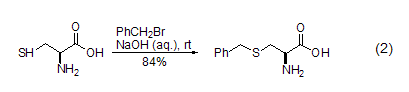
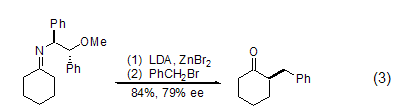
Benzyl bromide can also react with Alkylation occurs with methylene compounds such as enol ketones, esters, 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds, amides, lactams, and nitro-stabilized carbanions. For example, the benzylation reaction between benzyl bromide and metal enamine under the action of chiral imine can obtain better enantioselectivity (formula 3)[7].
Prepared by the reaction of benzyl bromide and active metals Benzyl metal compounds (such as benzyl lithium) are difficult to realize, mainly because the resulting compounds can easily undergo Wurz coupling reaction[8]. But there are exceptions, such as benzylmagnesium bromide, benzylzinc bromide and BnCu(CN)ZnBr, which are all successful examples.
Benzyl bromide tends to undergo coupling reactions with organometallic compounds such as alkyl lithiums, Grignard reagents, alkyl ketones, etc. For example, the coupling reaction between benzyl bromide and N-methylphthalimide occurs under the action of Li (Formula 4)[9].
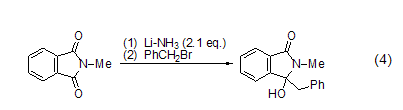
2. Used in organic synthesis and Manufacture of foaming agents. [29]
p>[29]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

