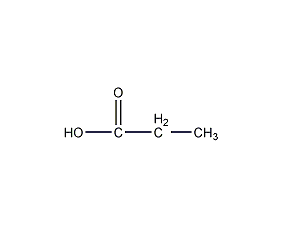
Structural formula
| Business number | 01PA |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H6O2 |
| Molecular weight | 74 |
| label |
Oleic acid, Methyl acetic acid, Ethyl formic acid, Methyl acetic acid, Ethylformic acid, Propanoic acid, Ethanecarboxylic acid, acidic solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:79-09-4
MDL number:MFCD00002756
EINECS number:201-176-3
RTECS number:UE5950000
BRN number:506071
PubChem number:24845375
Physical property data
1. Properties: colorless oily liquid with pungent odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -21.5[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 141.1[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.99[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 2.56[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 1.33 (39.7℃)[6]
7. Heat of combustion (kJ/mol): -1525.8[7]
8. Critical temperature (℃): 339[8]
9. Critical pressure (MPa): 4.53[9]
10. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 0.25~0.33[10]
11. Flash point (℃): 54 (CC) [11]
12. Ignition temperature (℃): 485[12]
13. Explosion upper limit (%): 14.9[13]
14. Lower explosion limit (%): 3.0[14]
15. Solubility: miscible with water, miscible with ethanol, ether, and chloroform. [15]
16. Refractive index (n20ºC): 1.3848
17. Refractive index (n25ºC): 1.3843
18 . Viscosity (mPa·s, 15ºC): 1.175
19. Viscosity (mPa·s, 30ºC): 0.958
20. Flash point (ºC): 51
21. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 54.93
22. Heat of evaporation (KJ/mol, b.p.): 32.31
23. Heat of fusion (KJ/ mol): 7.54
24. Heat of formation (KJ/mol, 25ºC, liquid): -511.29
25. Specific heat capacity (KJ/(kg·K), 20ºC, constant pressure ): 2.08
26. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K), 20ºC): 28.8854
27. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K), 60ºC ): 23.4337
28. Thermal conductivity (W/(m·K), 100ºC): 19.0204
29. Volume expansion coefficient (K-1, 20ºC): 1.10×10-3
30. Body expansion coefficient (K-1, 55ºC): 1.14×10 -3
31. Body expansion coefficient (K-1, 100ºC): 1.62×10-3
32. Critical density (g·cm-3): 0.318
33. Critical volume (cm3·mol-1 ): 233
34. Critical compression factor: 0.219
35. Eccentricity factor: 0.2536
36. Solubility parameter (J·cm -3)0.5: 19.459
37. van der Waals area (cm2·mol-1 ): 6.530×109
38. van der Waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 43.420
39. Gas phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1</sDirect oxidation of low-carbon hydrocarbons: When low-carbon hydrocarbons are oxidized to produce acetic acid, formic acid and propionic acid can be co-produced, and propionic acid can be obtained after separation. See acetic acid.
2. Reppe method: Ethylene reacts with carbon monoxide and water under the catalysis of nickel carbonyl to synthesize propionic acid in one step. The reaction conditions are 250~320℃ and 10~30MPa. ![]()
3. Propanaldehyde oxidation method: Propanaldehyde reacts with air or oxygen in the presence of manganese propionate catalyst to generate propionic acid. 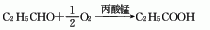
4. Propylonitrile hydrolysis method is produced by hydrolysis of propionitrile under the catalysis of concentrated sulfuric acid. The reaction formula is as follows:![]()
5. The acrylic acid method is produced by hydrogenation and reduction of acrylic acid. The reaction formula is as follows: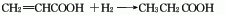
6. Ethanol carbonylation method is produced by reacting ethanol with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst.
Purpose
1. Mainly used as food preservatives and antifungal agents. It can also be used as an inhibitor for medium-viscous substances such as beer. Used as nitrocellulose solvent and plasticizer. It is also used in the preparation of nickel plating solutions, the preparation of food flavors and the manufacture of medicines, pesticides, antifungal agents, etc.
2. Organic synthetic raw materials, used to synthesize propylene salt, propionate ester, vinyl propionate, propylene ester cellulose, etc. Propionic acid is a safe food preservative that inhibits bacterial growth. It is also an effective organic acid preservative in grain and feed storage, and has strong antibacterial effects on various types of molds, aerobic bacilli or gram-negative bacilli. Propionic acid is used in aerosol form to prevent bread and other foods from becoming moldy. It is also used as a solvent and plasticizer for nitrocellulose. It can also be used as a reagent for the determination of aromatic diamines and an acidifying agent.
3. Cosmetics can be used as hair conditioners, anti-dandruff and anti-itching agents.
4. Propionic acid is used as an additive substance in electroless plating and electroplating.
5. Used in baked goods, cheese, and imitation dairy products.
6. Used as esterification agent, solvent for nitrocellulose, plasticizer, chemical reagent and raw material for food preparation. [25]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

