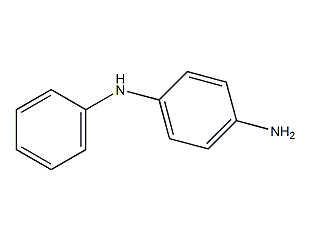
structural formula
| business number | 02kr |
|---|---|
| molecular formula | c12h12n2 |
| molecular weight | 184.24 |
| label |
n-phenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine, n-phenyl-p-phenylenediamine, variamine blue rt base, n-phenyl-1,4-phenylenediamine, azoic diazo component 22, c6h5nhc6h4nh2, dyes and auxiliary intermediates |
numbering system
cas number:101-54-2
mdl number:mfcd00007850
einecs number:202-951-9
rtecs number:st3150000
brn number:908935
pubchem number:24854480
physical property data
1. properties: gray needle crystals are obtained from ethanol.
2. density (g/ml, 25/4℃): 1.09
3. relative vapor density (g/ml, air=1): undetermined
4. melting point (ºc): 66
5. boiling point (ºc, normal pressure): 354
6. boiling point (ºc, 5.2kpa): undetermined
p>
7. refractive index: undetermined
8. flash point (ºc): 193
9. specific rotation (º): undetermined
10. autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºc): undetermined
11. vapor pressure (kpa, 25ºc): undetermined
12. saturated vapor pressure (kpa , 60ºc): undetermined
13. heat of combustion (kj/mol): undetermined
14. critical temperature (ºc): undetermined
15 . critical pressure (kpa): undetermined
16. log value of oil-water (octanol/water) distribution coefficient: undetermined
17. explosion upper limit (%, v/v ): undetermined
18. lower explosion limit (%, v/v): undetermined
19. solubility: easily soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and ether, and also soluble in acid, alkaline solution, slightly soluble in water.
toxicological data
1. skin/eye irritation: standard dresser test: rabbit eye contact, 100mg/24h reaction severity, moderate reaction; 2. acute toxicity: rat oral ld50: 464mg/kg; mouse oral lc50: 244mg/kg ; mammalian-cat oral ldlo: 100mg/kg; rabbit oral ld50: >5mg/kg; rabbit skin contact ld50: >5mg/kg; 3. other multiple dose toxicity: rat oral tdlo: 13500mg/kg/90d-c; 4. mutagenicity: mutant microbial test: bacteria – salmonella typhimurium, 150μg/plate;
ecological data
this substance may be harmful to the environment and it is recommended not to let it enter the environment.
molecular structure data
1. molar refractive index: 59.86
2. molar volume (cm3/mol): 157.7
3. isotonic specific volume (90.2k ): 426.4
4. surface tension (dyne/cm): 53.4
5. dielectric constant:
6. dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. polarizability: 23.73
compute chemical data
1. reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (xlogp): none
2. number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. number of tautomers: none
6. topological molecule polar surface area 38
7. number of heavy atoms: 14
8. surface charge: 0
9. complexity: 156
10. number of isotope atoms: 0
11. determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. number of covalent bond units: 1
properties and stability
avoid light. avoid contact with strong oxidants and acids.
poisonous. operators should wear protective equipment to avoid direct contact with the human body.
storage method
store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. keep away from fire and heat sources. protect from direct sunlight. the packaging is sealed. they should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
synthesis method
1. the production routes adopted at home and abroad include 4-nitrodiphenyl gum reduction method and 4-nitrosodiphenylamine reduction method. the former is divided into aniline and formamide methods according to the raw materials used. the 4-nitrosodiphenylamine method is also called the diphenylamine method because it uses diphenyl gum as raw material. there is also a method of soap yellow reduction. (1). aniline method p-nitrochlorobenzene and aniline (molar ratio 1:1.78) are combined in the presence of copper catalyst (such as copper oxide and acid binding agent potassium carbonate) at 170-215°c under normal compression for 14 hours to obtain 4 – nitrodiphenylamine, based on p-nitrochlorobenzene, the yield is 90.6%. raw material consumption quota: p-nitrochlorobenzene 1100kg/t, aniline 820kg/t, formic acid 500kg/t, potassium carbonate 650kg/t, alkali sulfide 1950kg/t. (2). formanilide method: formic acid and aniline are condensed to obtain formanilide, which is then mixed with p-nitrochlorobenzene (the amount of formanilide is 0%-100% excess than the theoretical amount), in the presence of the acid-binding agent potassium carbonate. , react at 120-195°c to obtain 4-nitrodiphenylamine. the 4-nitrodiphenylamine obtained by the above two methods can be reduced by alkali sulfide or hydrogenation, or electrochemically reduced at 20-50°c, with a yield of 96%. (3).4-nitrosodiphenylamine method: diphenylamine is nitrosated with nitrite in a solvent in the presence of acid to obtain n-nitrosodiphenylamine, which is then translocated and rearranged with anhydrous hydrogen chloride. that is, 4-nitrosodiphenylamine is obtained, with a yield of 98%-99%. the temperature of nitrosation, translocation and rearrangement is 17-30℃. 4-nitrosodiphenylamine can be reduced with alkali sulfide at 50-100°c under normal pressure, or by catalytic hydrogenation. hydrogenation reduction using nickel as a catalyst has been researched and developed in recent years, and the yield can reach 97%-98%. 4-nitrosodiphenylamine can also be electrochemically reduced to obtain rt base, with a yield of 96%. (4). saponin reduction method: add 55l water, 23kg 50% sodium sulfide, and 6.6kg sulfur into the reaction kettle, heat to boiling with stirring to dissolve all the materials, then add 280l water, 42.4kg 100% saponin, and seal the reaction kettle was heated to 135°c and hot pressed for 5 hours. after cooling to room temperature, filter and rinse with water until the filtrate is no longer yellow, to obtain 19.9kg of 100% 4-aminodiphenylamine. the yield is 90%.
purpose
dye intermediates. mainly used to manufacture various important antioxidants such as 4010na, 4020 and 668; to manufacture blue salt rt, acidic red gr, dispersed yellow gfl, etc.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

