
structural formula
| business number | 01d8 |
|---|---|
| molecular formula | c2h4o2 |
| molecular weight | 60.05 |
| label |
acetic acid, glacial acetic acid, glacial acetic acid, ethanoic acid, vineger acid, methane-carboxylic acid, glacial acetic acid, sour agent, flavor enhancer, acid solvent |
numbering system
cas number:64-19-7
mdl number:mfcd00036152
einecs number:231-791-2
rtecs number:af1225000
brn number:506007
pubchem number:24848291
physical property data
1. characteristics: characteristics: colorless and transparent liquid with irritating sour odor. [1]
2. ph value: 2.4 (1.0mol/l aqueous solution) [2]
3. melting point (℃): 16.6[3]
4. boiling point (℃): 118.1 (101.7kpa) [4]
5. relative density (water=1): 1.05 (20℃)[5]
6. relative vapor density (air=1): 2.07[6]
7. saturated vapor pressure (kpa): 1.52 (20℃)[7]
8. heat of combustion (kj/mol): -873.7[8]
9. critical temperature (℃): 321.6[9]
10. critical pressure (mpa): 5.78[10]
11. octanol/water partition coefficient: -0.31~0.17[11]
12. flash point (℃): 39 (cc); 43 (oc) [12]
13. ignition temperature (℃): 426[13]
14. explosion upper limit (%): 16.0[14]
15. lower explosion limit (%): 5.4[15]
16. solubility: soluble in water, ethanol, ether, glycerin, insoluble in carbon disulfide. [16]
17.refractive index (n20ºc): 1.3719
18.refractive index (n25ºc): 1.3698
19. viscosity (mpa·s, 15ºc): 1.314
20. viscosity (mpa·s, 30ºc): 1.040
21. heat of evaporation (kj/mol, 25ºc): 23.05
22. heat of evaporation (kj/mol, b.p.): 24.39
23. heat of fusion (kj/kg): 108.83
24. heat of formation (kj/mol, 25ºc, liquid): -484.41
25. heat of combustion (kj/mol, 25ºc, liquid): 876.72
26. specific heat capacity (kj/(kg·k), 21.5ºc, constant pressure): 2.08
27. boiling point rise constant (25ºc): 1.0411
28. conductivity (s/m, 25ºc): 6×10-9
29. dissociation constant (25ºc): 1.75×10-5
30. volume expansion coefficient (k-1, 20ºc): 1.0225×10-3
31. volume expansion coefficient (k-1,60ºc): 1.0708×10-3
32. volume expansion coefficient (k-1,100ºc): 1.1257×10-3
33.lennard-jones parameter (a): 9.858
34.lennard-jones parameter (k): 163.5
35. solubility parameter (j·cm-3)0.5: 18.356
36.van der waals area (cm2·mol-1): 5.180×109
37.van der waals volume (cm3·mol-1): 33.300
38. liquid phase standard combustion heat (the acetic acid produced is the finished product. the high boilers and catalyst at the bottom of the tower can be burned to remove organic matter and recover the catalyst. acetic acid used as food sour agent shall comply with gb1903-80, the content shall be ≥98.0%, and the impurity index shall meet the requirements. purification method of reagent acetic acid: add potassium permanganate powder (1-2% of the weight of acetic acid) to industrial-grade acetic acid, stir thoroughly to dissolve. the added amount should keep potassium permanganate from fading within 1 hour. finally, divide the lower insoluble part. the acetic acid is evaporated in the distillation tower, and an appropriate amount of powdered chromic anhydride is added to the newly evaporated acetic acid. dissolve it and collect the supernatant liquid for distillation. the middle fraction is the finished product. in addition to using acetic anhydride, dehydration methods can also use azeotropic mixtures composed of ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, benzene, diisopropyl ether, etc. and water to perform azeotropic distillation and dehydration.
2. acetaldehyde oxidation method: acetaldehyde and manganese acetate are added to the oxidation tower from the bottom of the tower, and oxygen is introduced in stages. the reaction temperature is controlled at 70~75°c, the gas phase pressure at the top of the tower is maintained at 0.098mpa, and the top of the tower is vented. appropriate amount of nitrogen to prevent gas phase explosion. the solidification point of the crude acetic acid generated by the reaction should be between 8.5 and 9.0°c, and it should be continuously discharged into the refining section. the tail gas is cooled at low temperature, the condensate is returned to the oxidation tower, and the gas is vented. crude acetic acid continuously enters the concentration tower, and the temperature at the top of the tower is controlled at 95-103°c. the dilute acetic acid condensed by the condenser is recovered in the dilute acid recovery tower. the non-condensable gas enters the low-temperature condenser and is condensed into dilute acetaldehyde for recycling. the crude acetic acid with low boiling point is removed and continuously added to the acetic acid evaporator. the temperature at the top of the tower is maintained at about 120°c. the distilled acetic acid is the finished product.
![]()
3. liquid phase oxidation method of low carbon alkanes: usually use butane as raw material, acetic acid as solvent, cobalt acetate as catalyst, air as oxidant, and perform liquid phase catalytic oxidation at 170~180℃ and 5.5mpa. light oil at 30-100℃ can also be used as raw material. the resulting mixed acid is separated through 6 towers to obtain acetic acid. refining method: acetic acid contains impurities such as water, acetaldehyde, acetone, formic acid, propionic acid, esters, sulfates, sulfites, chlorides, and acetates. the purification method is to add anhydride equal to water in acetic acid to react with the existing water, then add chromic anhydride (2g chromic anhydride per 100ml acetic acid), heat at a temperature close to the boiling point for 1 hour, and then fractionate. you can also add 2% to 5% potassium permanganate instead of chromic anhydride, reflux for 2 to 6 hours and then fractionate. further purification can be achieved by fractional crystallization. anhydrous acetic acid (glacial acetic acid) absorbs water easily. in addition to acetic anhydride, desiccants such as magnesium perchlorate, anhydrous copper sulfate, boron triacetate, chromium triacetate, etc. can also be used for dehydration. in addition, azeotropic distillation dehydration can be carried out using azeotropic mixtures composed of ethyl acetate, butyl acetate, benzene, diisopropyl ether, etc. and water.
4. methanol carbonylation can be used industrially to produce acetic acid; then, fine acetic acid can be obtained through potassium permanganate oxidation, filtration and distillation.
![]()
crystallize acetic acid at a constant temperature at a temperature lower than 15°c, and then filter out the crystallized part by vacuum filtration or centrifugal separation, which is the finished product of pure glacial acetic acid.
5. acetylene method: acetylene and water are directly hydrated in the presence of a catalyst to obtain acetaldehyde, and then acetaldehyde is oxidized with oxygen in an acetic acid solution of manganese acetate catalyst.
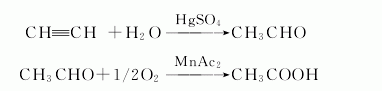
6. ethylene method: ethylene and oxygen are directly oxidized to synthesize acetaldehyde in one step in the presence of a catalyst, and then oxidized to obtain acetic acid. light oil liquid phase oxidation method: liquid phase oxidation of light oil in the presence of a cobalt catalyst to produce acetic acid, formic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid and other mixtures, which are then distilled and rectified twice.
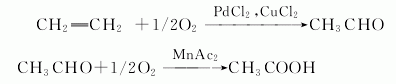
7. ethylene oxidation method
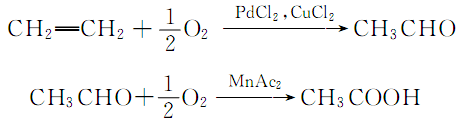
purpose
1. commonly used analytical reagents, widely used for neutralization or acidification. non-aqueous titration solvents, preparation of buffer solutions, organic synthesis. manufacture of pigments, drugs, acetate fiber, acetyl compounds, etc. also used to dissolve phosphorus, sulfur, hydrohalic acid, etc. as a sour agent, it can be used in compound seasonings to prepare vinegar, canned food, jelly and cheese. it can be used in appropriate amounts according to production needs. it can also be used as a flavor enhancer for quxiang wine, with a dosage of 0.1-0.3g/kg. used as a solvent in the manufacture of rubber, plastics, dyes, etc. it is also used as a raw material for the manufacture of vinyl acetate, cellulose acetate, acetate, acetate, photographic drugs, medicine, pesticides and other organic synthesis.
2. commonly used analytical reagents. universal solvents and non-aqueous titration solvents. used in the manufacture of acetate, cellulose acetate, medicine, pigments, esters, plastics, spices, etc.
3.ph value regulator. it can be used to prepare ethyl acetate, fibers, paints, adhesives, copolymer resins, etc., acetic anhydride, chloroacetic acid, glycolic acid, and industrial pickling.
4. can be used for industrial pickling. used to prepare fibers, coatings, adhesives, copolymer resins, etc.
5. it is an important organic chemical raw material and can be used to produce a variety of organic chemical products. it is used in the pharmaceutical industry to prepare a variety of medicines, in the dye industry to manufacture a variety of dyes, and in the synthetic materials industry to synthesize a variety of polymer materials. it is an important organic chemical intermediate. in addition, it is also used as industrial solvents, leather tanning agents, rubber latex coagulants, dye auxiliaries, artificial flavors, chemical reagents, etc. it is also used as acidifiers, flavoring agents, etc.
6. acetic acid can be used in some pickling and polishing solutions, as a buffer in weakly acidic solutions (such as zinc plating, chemical nickel plating), as an additive in semi-bright nickel plating electrolyte, and in zinc, cadmium in the passivation solution, it can improve the binding force of the passivation film, and is often used to adjust the ph of weakly acidic plating solutions. it can also be used as a solvent for certain organic additives (such as coumarin).
7. commonly used analytical reagents, general solvents and non-aqueous titration solvents, organic synthesis, synthesis of pigments and pharmaceuticals.
8. used in the manufacture of acetate, cellulose acetate, medicine, pigments, esters, plastics, spices, etc. [28]
��intermediates. in addition, it is also used as industrial solvents, leather tanning agents, rubber latex coagulants, dye auxiliaries, artificial flavors, chemical reagents, etc. it is also used as acidifiers, flavoring agents, etc.
6. acetic acid can be used in some pickling and polishing solutions, as a buffer in weakly acidic solutions (such as zinc plating, chemical nickel plating), as an additive in semi-bright nickel plating electrolyte, and in zinc, cadmium in the passivation solution, it can improve the binding force of the passivation film, and is often used to adjust the ph of weakly acidic plating solutions. it can also be used as a solvent for certain organic additives (such as coumarin).
7. commonly used analytical reagents, general solvents and non-aqueous titration solvents, organic synthesis, synthesis of pigments and pharmaceuticals.
8. used in the manufacture of acetate, cellulose acetate, medicine, pigments, esters, plastics, spices, etc. [28]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

