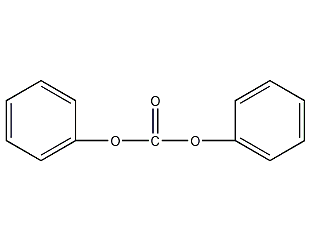
Structural formula
| Business number | 02LP |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C13H10O3 |
| Molecular weight | 214 |
| label |
Aliphatic carboxylic acids and their derivatives |
Numbering system
CAS number:102-09-0
MDL number:MFCD00003037
EINECS number:203-005-8
RTECS number:FG0500000
BRN number:1074863
PubChem number:24893613
Physical property data
1. Properties: White crystalline solid.
2. Density (g/mL, 87/4℃): 1.1215
3. Relative density (25℃, 4℃): 1.121587
4. Melting point (ºC): 83
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 306
6. Boiling point (ºC, kPa): Not available Determine
7. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.1550
8. Flash point (ºC): 168
9. Gas phase standard heat of combustion (enthalpy) ( kJ·mol-1): -6233.6
10. The gas phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -311.2
11. Liquid phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -6167.0
12. Liquid phase standard claimed heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -377.7
13. Crystal phase standard combustion heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -6143.6
14. Crystal phase standard claims heat (enthalpy) (kJ·mol-1): -401.2
15. Critical pressure (KPa) : Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
p>
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in hot ethanol, benzene, ether, carbon tetrachloride, ice Acetic acid and other organic solvents.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 1500mg/kg
2. Low toxicity, easy to cause skin allergies.
Ecological data
This substance is slightly hazardous to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 59.21
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 178.9
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 461.0
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 44.0
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 23.47
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 4
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 35.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 16
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 193
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of stereocenters of atoms: 0
12. Determine the number of stereocenters of atoms: 0
13. Determine the number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Avoid contact with oxides. It can undergo halogenation, nitration, hydrolysis, ammonialysis and other reactions.
2.This product has low toxicity. Has allergic effects on skin. Pay attention to prevent phosgene leakage during the production process, and the production site should be well ventilated. Operators should wear protective equipment.
Storage method
1. Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire, heat sources and anti-static. Keep container tightly sealed. should be kept away from oxidizer, do not store together. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills. 2. This product is packed in galvanized iron drums or polypropylene woven bags lined with kraft paper. Stored in a ventilated and dry warehouse
. Storage and transportation according to regulations on toxic chemicals
Synthesis method
There are two synthesis methods for diphenyl carbonate. (1) Synthesis of phenol and phosgene
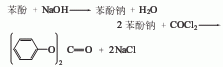
First Add 16% to 17% sodium hydroxide solution to the reaction pot, then add phenol, and add a small amount of tertiary amine catalyst in the presence of an inert solvent; then cool to about 10°C and add liquid phosgene, and control the reaction temperature to 20°C to 30°C , the diphenyl carbonate generated by the reaction continues to precipitate in the form of small solid particles. During the reaction, the reaction temperature was controlled by adjusting the addition rate of phosgene and controlling the amount of ice and salt water. The reaction is completed when the material pH=6.5~7. First drive away the remaining phosgene and hydrogen chloride gas, wait for the material to stand and layer to remove the mother liquor, and obtain the crude diphenyl carbonate; then wash and separate with salt water and cold water for many times, then use vacuum dehydration and recovery of the solvent, and finally distill under reduced pressure. and roller crystallization to obtain the desired white flaky purified diphenyl carbonate.
Introduced by my country’s patent, diphenyl carbonate can be produced by reacting lime instead of caustic soda with phenol to generate calcium phenolate salt, and then performing phosgenation reaction at high speed and quantitatively at room temperature and normal pressure. Compared with the previous phosgene synthesis method, this process has significantly lower unit consumption and cost. The process conditions are mild, the phosgenation temperature is increased from 15 to 20°C to 20 to 45°C, frozen brine can be omitted, and the phosgenation time is increased from 4 to 45°C. From 10 hours to 1 to 2 hours, the production efficiency is significantly improved and various side reactions are effectively suppressed.
(2) Ethylene carbonate method
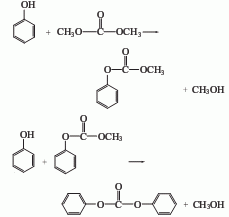
In this method, diphenyl carbonate can be obtained by exchanging dimethyl carbonate with phenol in the presence of TiO2/SiO2 catalyst. Dimethyl carbonate and excess phenol are transesterified at 200-250°C and 0.39 MPa nitrogen pressure for 3 hours. The main products are diphenyl carbonate and a small amount of methylphenyl carbonate and diphenyl ether.
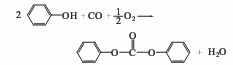
Purpose
It is mainly used as a synthetic raw material for engineering plastics such as polycarbonate and polyparaben, and can also be used as a plasticizer and solvent for nitrocellulose.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

