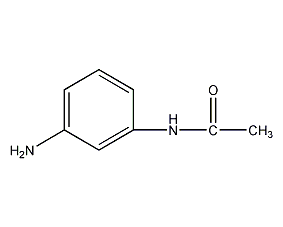
structural formula
| business number | 02lw |
|---|---|
| molecular formula | c8h10n2o |
| molecular weight | 150.18 |
| label |
n-acetyl-1,3-phenylenediamine, n-acetyl-1,3-phenylenediamine, aromatic nitrogen-containing compounds and their derivatives |
numbering system
cas number:102-28-3
mdl number:mfcd00025229
einecs number:203-021-5
rtecs number:ad8050000
brn number:none
pubchem number:24872016
physical property data
1. properties: colorless needle crystals or lamellar crystals.
2. density (g/ml, 25℃): undetermined
3. relative vapor density (g/ml, air=1): undetermined
4. melting point (ºc): 87~89
5. boiling point (ºc, normal pressure): undetermined
6. boiling point (ºc, kpa): undetermined
7. refractive index: undetermined
8. flash point (ºc): undetermined
9. specific rotation (º): undetermined
p>
10. autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºc): not determined
11. vapor pressure (mmhg, 25ºc): not determined
12. saturated vapor pressure (kpa, ºc): undetermined
13. heat of combustion (kj/mol): undetermined
14. critical temperature (ºc): undetermined
15. critical pressure (kpa): undetermined
16. log value of oil-water (octanol/water) distribution coefficient: undetermined
17. explosion upper limit (%, v /v): undetermined
18. lower explosion limit (%, v/v): undetermined
19. solubility: easily soluble in cold water, ethanol, acetone, slightly soluble in benzene.
toxicological data
1. skin/eye irritation: standard dresser test: rabbit eye contact, 500mg/24 hreaction severity, slight reaction; 2. acute toxicity: intravenous injection of mice ld50: 320mg/kg; 3. mutagenicity: mutant microorganism test : bacteria-salmonella typhimurium, 333μg/plate;
ecological data
none yet
molecular structure data
1. molar refractive index: 44.76
2. molar volume (cm3/mol): 124.7
3. isotonic specific volume (90.2k ): 336.8
4. surface tension (dyne/cm): 53.0
5. dielectric constant: 2.34
6. dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. polarizability: 17.74
compute chemical data
1. reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (xlogp): none
2. number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 2
4. number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. number of tautomers: 3
6. topological molecular polessurface area: 55.1
7. number of heavy atoms: 11
8. surface charge: 0
9. complexity: 147
10. number of isotope atoms: 0
11. number of determined atomic stereocenters: 0
12. number of uncertain atomic stereocenters: 0
13 .determined number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
14. uncertain number of stereocenters of chemical bonds: 0
15. number of covalent bond units: 1
properties and stability
toxic, see m-phenylenediamine (c283) for its toxicity. in addition to absorption through the skin, poisoning can also be caused by inhalation of dust. pay attention to dust prevention during the production process, and the site should be well ventilated. operators should wear protective equipment.
storage method
packed in fiberboard drums lined with plastic bags, with a net weight of 25kg per drum. store in a dry, ventilated place, away from sunlight. handle it with care when transporting, and protect it from moisture and heat. store and transport according to regulations on toxic substances.
synthesis method
1. meta-phenylenediamine acylation method is derived from m-phenylenediamine acylation. add water and m-phenylenediamine to the reaction pot to dissolve. then add 30% hydrochloric acid, stir for half an hour, then add acetic acid, control the reaction temperature at 40°c, keep stirring for 1 hour, add refined salt to salt out, and filter. after neutralization, meta-aminoacetanilide is obtained. the acylation operation may also use acetic anhydride as raw material. the raw material consumption quotas are m-phenylenediamine 1021kg/t, acetic anhydride 1013kg/t, and hydrochloric acid 475kg/t.
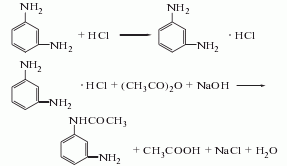
2. meta-nitroacetanilide method: mix 10g m-nitroacetanilide and 5g iron powder in a mortar evenly, sprinkle it into a 500ml beaker containing 200ml boiling water, add a few drops of acetic acid to acidify the mixture, and keep it warm for 1 hour. then, add ammonia to neutralize it until the congo red test paper becomes alkaline. boil, filter while hot, and evaporate the filtrate on a water bath until it becomes slurry. by rubbing the wall of the device or adding seed crystals to crystallize the slurry, a product close to the theoretical amount can be obtained, with a melting point of 87~89°c.
purpose
dye intermediates. mainly used to prepare reactive dyes such as reactive yellow k-rn and disperse dyes.

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

