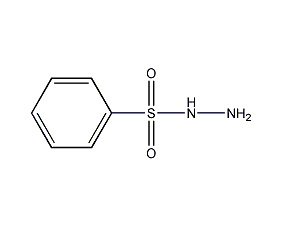
Structural formula
| Business number | 01QQ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C6H8N2O2S |
| Molecular weight | 172.20 |
| label |
Phenylsulfonyl hydrazide, Foaming agent BSH, phenylsulfohydrazide, blowing agent BSH, porofor BSH, Foaming agent |
Numbering system
CAS number:80-17-1
MDL number:MFCD00007583
EINECS number:201-255-2
RTECS number:DB6888000
BRN number:640079
PubChem number:24891736
Physical property data
1. Properties: light yellow crystal, easy to deliquesce. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): 101~103[2]
3. Relative density (water =1): 1.41~1.43[3]
4. Octanol/water partition coefficient: -0.14[4]
5. Flash point (℃): 110[5]
6. Solubility: Insoluble in water. [6]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity No data available
2. Irritation No data available
3. Others[7] LDLo: 50mg/kg (rat oral)
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity No data available
2. Biodegradability No data available
3 .Non-biodegradability No information available
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 42.84
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 127.1
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 341.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 51.8
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 16.98
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 4
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 2
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 80.6
7. Number of heavy atoms: 11
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 201
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Nitrogen, hydrogen and water are generated after heating and decomposition. Soluble in aqueous solutions of inorganic acids and alkalis and some organic solvents, but insoluble in water. Reacts with ketones to obtain the corresponding sulfonylhydrazone. No reaction to vulcanization accelerators and antioxidants. Non-toxic. Storage is unstable and the product has a bad smell.
2. Stability[8] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[9] Strong oxidants, strong bases
4. Conditions to avoid contact[10] Friction and impact
5. Polymerization hazard[11] No polymerization
6. Decomposition products[12] Nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxides, nitrogen
Storage method
Storage Precautions[13] Stored in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 35℃. The packaging must be sealed and protected from moisture. They should be stored separately from oxidants and alkalis, and avoid mixed storage. Use explosion-proof lighting and ventilation facilities. It is prohibited to use mechanical equipment and tools that are prone to sparks. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
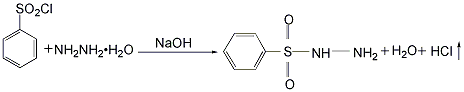
Dissolve benzene sulfonyl chloride in benzene according to the proportion, and send the prepared solution to the high-level tank for later use. Add hydrazine hydrate with a concentration of 40% and an appropriate amount of caustic soda into the stirred reaction kettle, and stir to dissolve into a uniform solution. Then, a benzene solution of benzene sulfonyl chloride was added while stirring at room temperature to perform a condensation reaction. The feeding speed should not be too fast to ensure a stable reaction, and the temperature should not exceed 50°C. After the reaction to generate benzene sulfonyl hydrazide is completed, add an appropriate amount of acid to neutralize it to make the reaction system neutral. Because benzene sulfonyl hydrazide is insoluble in water and benzene, it precipitates in solid form. The reaction product is filtered, and the filtrate is left to separate into layers. The upper layer is benzene, which can be recycled or recovered by distillation; the lower layer is an aqueous solution, and unreacted hydrazine hydrate can be recovered. The filter cake is washed with water several times to remove all the salt and other water-soluble substances contained in it, and then dried at 60°C to obtain the finished product.
Purpose
1. Foam materials used in the shoemaking industry, the dosage is 3% to 6.5%. Used for the hair growth of polyvinyl chloride, polyester, polyamide, polystyrene, phenolic resin, epoxy resin, butyl rubber, styrene-butadiene rubber, silicone rubber, polyolefin, styrene and acrylonitrile or butadiene copolymers The dosage of foaming agent is 1% to 15%. This product releases heat when decomposed and is generally mixed with sodium bicarbonate.
2. Used as a foaming agent to manufacture foam plastics and foam rubber. [14]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

