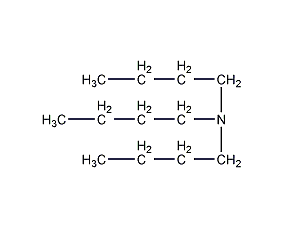
Structural formula
| Business number | 02MJ |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C12H27N |
| Molecular weight | 185.35 |
| label |
Tri-n-butylamine, Tri-n-butylamine, (CH3CH2CH2CH2)3N, petroleum additives, pesticides, emulsifier, plastic plasticizer, mineral flotation agent, Extracting agent |
Numbering system
CAS number:102-82-9
MDL number:MFCD00009431
EINECS number:203-058-7
RTECS number:YA0350000
BRN number:1698872
PubChem number:24889404
Physical property data
1. Properties: Colorless to yellow hygroscopic liquid with an ammonia-like odor. [1]
2. Melting point (℃): -70[2]
3. Boiling point (℃): 216.5[3]
4. Relative density (water = 1): 0.778[4]
5. Relative vapor Density (air=1): 6.4[5]
6. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa): 0.0387 (25℃)[6]
7. Critical temperature (℃): 365.2[7]
8. Critical pressure (MPa): 1.8[8]
9. Octanol/water partition coefficient: 1.52[9]
10. Flash point (℃): 86 (OC) [10]
11. Ignition temperature (℃): 210[11]
12. Explosion upper limit (%): 6.0 [12]
13. Lower explosion limit (%): 1.4[13]
14. Solubility: insoluble in Water, soluble in ethanol, ether and most organic solvents. [14]
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 114mg/kg; rat inhalation LCL0: 75ppm/4H; rat subcutaneous LDL0: 380mg/kg; mouse oral LD50: 114mg/kg; rabbit oral LD50 : 615mg/kg; Rabbit skin contact LD50: 250μL/kg; Guinea pig oral LD50: 350mg/kg; Mammalian oral LD50: 888mg/kg; Mammalian peritoneal cavity LD50: 107mg/kg;
2. Other multi-dose toxicity: rabbit oral TDLo: 1119mg/kg/26W-I; mammalian peritoneal TDLo: 107mg/kg/3D-I;
3. Can irritate eyes and skin, and Direct skin contact causes dermatitis.
4. Acute toxicity [15] LD50: 114mg/kg (rat oral); 250μl (195mg)/kg (rabbit transdermal )
5. Irritation No data available
6. Subacute and chronic toxicity[16] Rats were exposed to 910mg/m3, 6 hours each time, 19 times. The animals showed restlessness, uncoordinated movements, tremors and nasal irritation. There was no weight gain and no abnormality in organ histology. 220mg/m3Only mild drowsiness.
Ecological data
1. Ecotoxicity[17] LC50: 16.3mg/L (48h) (medaka)
2. Biological Degradability[18] NITI-I test, initial concentration 100mg/L, sludge concentration 30mg/L, degradation 2% after 4 weeks.
3. Non-biodegradability No data yet
4. Bioaccumulation[19] BCF: 38 (theoretical); 0.38~18 (carp, contact concentration 100mg/L, contact time 28d); 3.2~47 (carp, contact concentration 10mg/L, contact time 28d)
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 61.36
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 233.8
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 535.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 27.4
5. Dielectric constant:
6. Dipole moment (10-24cm3):
7. Polarizability: 24.32
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): 4
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 0
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 1
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 9
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 3.2
7. Number of heavy atoms: 13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 72.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: It has the chemical reaction properties of tertiary amines. Unstable to oxidizing agents. It reacts with ozone in chloroform or methanol to produce nitrogen oxides, dibutylamine, etc.
2. Stability[20] Stable
3. Incompatible substances[21] Strong oxidants, acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides
4. Polymerization hazards[22] No polymerization p>
5. Decomposition products[23] Amine
Storage method
Storage Precautions[24] Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. The storage temperature should not exceed 30℃. Keep container tightly sealed. They should be stored separately from oxidants, acids, etc., and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. The storage area should be equipped with emergency release equipment and suitable containment materials.
Synthesis method
Pour butanol, ammonia, and hydrogen into a reaction tower filled with copper-nickel acidic clay catalyst in proportion, react at about 200°C, condense the reaction gas, and obtain monobutylamine, dibutylamine, and tributylamine. The mixture is separated into three products by distillation.
Refining method: Tributylamine is produced by the reaction of butyl bromide and ammonia, or butanol and ammonia. Therefore, it is easy to contain butylamine, dibutylamine and unreacted substances. It is usually refined by fractional distillation in the presence of metallic sodium. In order to remove primary and secondary amines such as butylamine and dibutylamine, p-phenylbenzenesulfonyl chloride can also be added, and the primary and secondary amines react with it, while the tertiary amine does not react. Add dilute hydrochloric acid to convert tributylamine into water-soluble hydrochloride, which is separated from the water layer and then recrystallized. Then use alkali to decompose the hydrochloride, and the tributylamine will be freed, and the pure product will be obtained after distillation.
Purpose
1. Used in petroleum additives, solvents, extractants, anti-corrosion agents, dyes, pharmaceutical intermediates, pesticides, emulsifiers, plastic plasticizers, mineral flotation agents and surfactants.
2. Used as solvents, intermediates, pesticides, emulsifiers, etc. [25]

 微信扫一扫打赏
微信扫一扫打赏

